\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/class15/class15.jl b/class15/class15.jl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1a4ee90
--- /dev/null
+++ b/class15/class15.jl
@@ -0,0 +1,1537 @@
+### A Pluto.jl notebook ###
+# v0.20.20
+
+using Markdown
+using InteractiveUtils
+
+macro bind(def, element)
+ #! format: off
+ return quote
+ local iv = try Base.loaded_modules[Base.PkgId(Base.UUID("6e696c72-6542-2067-7265-42206c756150"), "AbstractPlutoDingetjes")].Bonds.initial_value catch; b -> missing; end
+ local el = $(esc(element))
+ global $(esc(def)) = Core.applicable(Base.get, el) ? Base.get(el) : iv(el)
+ el
+ end
+ #! format: on
+end
+
+# ╔═╡ 4866207c-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204424
+begin
+ class_dir = @__DIR__
+ import Pkg
+ Pkg.activate(".")
+ Pkg.instantiate()
+ using PlutoUI
+ using PlutoTeachingTools
+ using MarkdownLiteral
+end
+
+# ╔═╡ a1b2c3d4-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204425
+begin
+ using JuMP
+ using Ipopt
+ using Plots
+ using DifferentialEquations
+end
+
+# ╔═╡ e6aa5227-91bd-4cec-9448-24384708a305
+ChooseDisplayMode()
+
+# ╔═╡ 19dac419-2df3-4878-b7da-608e8ec1e53b
+md"""
+| | | |
+|-----------:|:--|:------------------|
+| Lecturer | : | Shuaicheng Tong |
+| Topic | : | Dynamic Optimal Control of Power Systems |
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 8ed6af99-1c5d-4d27-b60d-17d2e6c6ceff
+md"""
+## Chapter Outline
+
+This chapter motivates the need for optimization and control of power systems by introducing the **Economic Dispatch (ED)** and **Optimal Power Flow (OPF)** problems and analyzing the physical behaviors they capture in power system.
+
+We progressively move from solving *static optimization* problems to augmenting them with *dynamic optimal control* constraints as approaches to analyze and understand power systems.
+
+**Topics covered:**
+- **Transients and Transient Stability–Constrained OPF (TSC-OPF):**
+ What are transients, their physical behaviors, and how they are factored into stability analysis of energy systems via the TSC-OPF formulation.
+
+- **Generator Swing Equations:**
+ The physical foundation of synchronous machines — describes how mechanical torque and electrical power control frequency and machine responses to frequency changes.
+
+- **Inverter Control Models:**
+ Grid-following vs. grid-forming inverters, and how virtual inertia control emulates synchronous generator dynamics for renewables.
+
+- **Dynamic Load Models:**
+ Representations of demand that vary with voltage and frequency instead of a fixed a quantity, influencing both stability and control.
+
+> 🧭 **Overall goal:**
+> To connect steady-state optimization (ED/DC-OPF) with **dynamic optimal control**, illustrating how classical control laws and physics-based constraints shape modern power system operation.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ f742f5f3-d9d3-4374-ac9e-17073c3a2f6d
+md"""
+# Introduction to Energy Systems
+## From Economic Dispatch to Dynamic Optimal Control
+
+Optimal control of power systems builds on static optimization formulations like *economic dispatch* (ED) and *optimal power flow* (OPF).
+These problems provide the mathematical foundation for **transient stability–constrained OPF (TSC-OPF)** formulations covered later in this chapter.
+
+To illustrate the key ideas, we start with the simplest case — the economic dispatch problem on a 3-bus system.
+
+**Example:**
+- Bus 1 load: 50 MW
+- Bus 3 load: 75 MW
+- Generator 1: capacity = 100 MW, cost = \$8/MW
+- Generator 2: capacity = 40 MW, cost = \$2/MW
+
+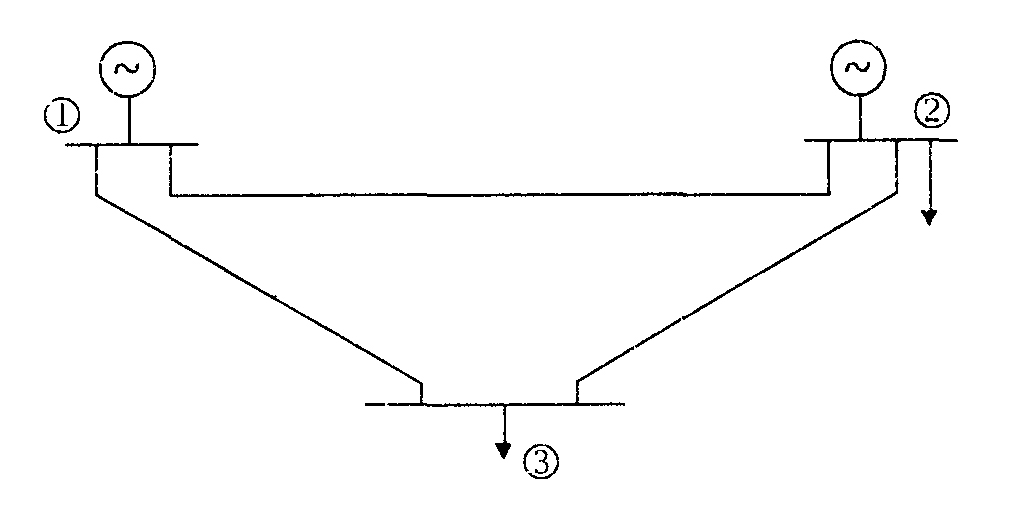
+
+**Goal:** Minimize total generation cost while meeting total demand — the simplest form of *static* optimal control in power systems.
+"""
+
+
+# ╔═╡ ad8e9d79-e226-468e-9981-52b7cda7c955
+md"""
+### Quadratic Program (QP) Formulation of Economic Dispatch
+
+Economic dispatch can be formulated as a **quadratic program**, where generation cost is convex and constraints balance supply and demand conditions.
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\min_{p_g} \quad & \sum_{g \in \mathcal{G}} C_g(p_g) \\
+\text{s.t.} \quad & \sum_{g \in \mathcal{G}} p_g = \sum_{d \in \mathcal{D}} P_d \quad \text{(power balance)} \\
+& p_g^{\min} \le p_g \le p_g^{\max}, \quad \forall g \in \mathcal{G} \quad \text{(capacity limits)}
+\end{align}
+
+
+
+where:
+
+| Symbol | Description |
+|:------------- |:-------------------------------------------------------|
+| $p_g$ | power output of generator $g$ |
+| $C_g(p_g)$ | cost function of generator $g$ (often quadratic: $a_g p_g^2 + b_g p_g + c_g$) |
+| $P_d$ | power demand at load $d$ |
+| $\mathcal{G}$ | set of generators |
+| $\mathcal{D}$ | set of loads |
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ fc329e51-e91c-4d83-b6fe-07a3bce44d5d
+md"""
+### Exercise: Formulate the ED Problem for the 3-Bus Network
+
+**Task:**
+Apply the generic formulation to the 3-bus system. Identify:
+1. The decision variables
+2. The objective function
+3. The power-balance constraint
+4. Generator bounds
+
+> 💡 *Hint:* Treat each generator’s output as a controllable decision variable. The total generation must exactly match total load.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ d767175f-290d-403e-99de-d3a8f2ccb5b5
+md"""
+#### ED formulation for the 3-bus example
+
+Here is the complete formulation for our 3-bus example:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\min_{p_1, p_2} \quad & 8p_1 + 2p_2 \\
+\text{s.t.} \quad & p_1 + p_2 = 125 \quad \text{(power balance)} \\
+& 0 \leq p_1 \leq 100 \quad \text{(Gen 1 limits)} \\
+& 0 \leq p_2 \leq 40 \quad \text{(Gen 2 limits)}
+\end{align}
+```
+
+**Solution:** $p_1$ = 85 MW, $p_2$ = 40 MW
+- Total cost: 8*85 + 2*40 = 760\$/hour
+- Gen 2 at maximum capacity (greedy)
+- Gen 1 supplies remaining demand
+
+> ⚙️ Control Interpretation: This is a static control allocation problem. In later sections, we’ll extend such formulations to time-varying states and control trajectories.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ c9d0e1f2-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204432
+md"""
+### Discussion
+
+Reflect on the ED formulation:
+
+- What type of optimization problem is this (linear, quadratic, convex)?
+- How does this formulation abstract away the **physical grid topology**? What kind of graph is it?
+- What critical physics are missing if we care about **how** power moves through lines?
+
+> 🧭 **Bridge to next topic:**
+> ED models the **steady-state optimization** problem without considering power flow through lines.
+> The next step — **DC power flow** — adds physical coupling constraints between buses.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 9d1ea9be-2d7b-4602-8a8e-8426ea31661a
+md"""
+### Why the Simplified Model Falls Short
+
+The simple ED model ignores the **network physics** that govern actual power transfer:
+- Power has **direction** — it flows through transmission lines governed by voltage phase angles so the graph needs to be directed.
+- Each line has a **thermal rating**: excessive current causes heating, sagging, or even wildfires.
+- What is a power line:
+ - Metal coil that expands and heats up when current is high.
+
+In real systems, exceeding thermal limits does not immediately stop power flow — it simply becomes unsafe, which requires branch flow constraints.
+Thus, the next layer of realism is to introduce branch constraints → **DC power flow**.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 71ba62e6-bcc1-4e9b-91cd-a8860ba0d2b5
+md"""
+## DC Power Flow
+
+To make ED more realistic, we include the grid’s topology by adding branch constraints.
+The **DC power flow model** provides a linearized approximation of AC power flow and enforce Kirchhoff’s laws.
+
+**Parameters:**
+- Line reactance $x_{ij}$
+- Line limit $F_\ell^{\max}$
+- Generator set $\mathcal{G}_i$ at bus $i$ (nodal generation)
+- Load set $\mathcal{L}_i$ at bus $i$ (nodal load)
+- Generator limits $P_j^{\min}, P_j^{\max}$
+- Costs $C_j(P_j)$ quadratic or piecewise-linear for generator $j$
+
+**Decision Variables:**
+- Generator outputs $P_j$ for $j \in \mathcal{G}_i$
+- Bus angles $\theta_i$ for $i \in \mathcal{N}$
+- Line flows $f_\ell$ for $\ell \in \mathcal{L}$
+
+> 🧩 We will see later that the bus angles $\theta_i$ enter as *state variables* in the control dynamics.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 7b4800c2-133d-4793-95b1-a654a4f19558
+md"""
+### DC Power Flow Formulation
+
+The DC power flow optimization problem combines economic dispatch with network physics:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\min_{P_j, \theta} \quad & \sum_{i \in \mathcal{N}} \sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}_i} C_j(P_j) \\
+\text{s.t.} \quad & \sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}_i} P_j - \sum_{j \in \mathcal{L}_i} P_j = \sum_{k: (i,k) \in \mathcal{L}} \frac{1}{x_{ik}} (\theta_i - \theta_k) \quad \forall i \in \mathcal{N} \\
+& f_\ell = \frac{1}{x_\ell} (\theta_{i(\ell)} - \theta_{j(\ell)}), \quad -F_\ell^{\max} \leq f_\ell \leq F_\ell^{\max} \quad \forall \ell \in \mathcal{L} \\
+& P_j^{\min} \leq P_j \leq P_j^{\max} \quad \forall j \in \mathcal{G}_i, \forall i \in \mathcal{N} \\
+& \theta_{\text{ref}} = 0
+\end{align}
+```
+
+- Reactance of line $x_{ij}$. $\frac{1}{x_{ij}} = b_{ij}$: susceptance (manufacturer specified)
+- Reference bus: only for modeling, you can pick any bus as the reference bus. We only care about angle differences (which carries current through lines
+- Individual bus angle has no physical meaning
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 7961c1d1-3e82-49ea-8201-c5f82066d70d
+md"""
+### Exercise: Solve DCOPF (solver suggested: Ipopt)
+
+Let's apply the DC power flow formulation to our 3-bus network with line constraints:
+
+
+
+**How did I get the numbers:**
+- Assume P1 generates 85 MW, with 50 MW of load, the net injection is 35 MW
+- Assume P2 generates 40 MW, with no load, net injection is 40 MW (we take upwards arrow as injection)
+- Bus 3 has no gen, only load
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 91b8a3e4-81ed-49fe-b785-4feacfd8788d
+md"""
+### DCOPF Solution
+
+Consult lecture slides for the solution and detailed analysis.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ f72775b9-818c-4a9b-9b66-cfccd88e17ed
+md"""
+### Wrap Up
+
+This section has introduced the fundamentals of static optimal power flow problems including economic dispatch and DC optimal power flow. Key takeaways:
+
+- You will see that without thermal limits, optimal dispatch can overload lines
+- Reference bus is arbitrarily picked by the solver.
+- Real systems are AC (complex voltages/currents) -- much harder. This is just a lightweight intro so we can think about expressing real-world problems as optimization formulations without overburdening ourselves with AC physics, which we will see in transient stability section.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 53ab9b31-78aa-49b6-9e24-df47aa80f25a
+md"""
+# Introduction to Transient Stability
+
+While static optimization provides a foundation, real power systems are dynamic. When disturbances occur—faults, switching events, or sudden load changes—the system experiences transients before settling to a new equilibrium. Understanding and controlling these transients is essential for system stability.
+
+## Transient Dynamics
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 1e337cdf-8add-42ab-a62f-23069e34ec39
+md"""
+## What are transients?
+
+When current or voltage changes suddenly — switching, faults, lightning, equipment failures, etc. — the system experiences a **transient**
+
+- Transients are short-lived, high-frequency events where stored magnetic and electric energy exchange rapidly.
+- **Faraday's law** of electromagnetic induction governs these effects:
+
+ A change in magnetic flux through a circuit induces a voltage across it.
+
+ ```math
+ v(t) = \frac{d\Phi(t)}{dt}
+ ```
+
+ where $\Phi(t)$ is the magnetic flux through the circuit.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 23dc8fd4-59a1-414f-a165-b509458abd18
+md"""
+## Transients Continued
+
+The relationship between flux and current leads us to the fundamental equations governing inductors:
+
+- For an inductor, the magnetic flux $\Phi$ is proportional to the current:
+
+ ```math
+ \Phi(t) = L\,i(t)
+ ```
+
+ where $L$ is the inductance (magnetic energy stored per unit current).
+
+- Substituting gives the familiar time-domain voltage rule:
+
+ ```math
+ \boxed{v_L(t) = L\,\frac{di(t)}{dt}}
+ ```
+
+Note that steady-state phasor analysis no longer holds due to the time-varying nature of the magnetic flux. I will draw the connection later.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 5814ece5-51b3-4dba-953d-c1f4b6ab04a8
+md"""
+## Sinusoidal steady state
+
+To connect time-domain transients with frequency-domain analysis, we assume all quantities have angular frequency $\omega$ to extract the phasors in steady-state. The current in time-domain is:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+i(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ I\,e^{j\omega t} \right\},
+\end{align}
+```
+
+Differentiate the current:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\frac{di(t)}{dt} &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ j\omega I\, e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+\end{align}
+```
+
+Substitute into $v_L(t) = L\,\frac{di}{dt}$:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+v_L(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ (j\omega L I)\, e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+\end{align}
+```
+
+## Phasor (frequency-domain) relation
+
+We are now ready to extract the phasor representation of voltage. By definition, the **phasor** is the complex amplitude multiplying $e^{j\omega t}$.
+
+From the previous expression,
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+v_L(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ (j\omega L I)\, e^{j\omega t} \right\},
+\end{align}
+```
+
+the **voltage phasor** is
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\boxed{V = j\omega L\, I}.
+\end{align}
+```
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ c1d2e3f4-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204445
+md"""
+## Capacitor law: from time domain to phasor
+
+Similar to inductors, capacitors also exhibit transient behavior. Let's derive the capacitor relationships:
+
+A capacitor stores energy in an **electric field**. The stored charge $q(t)$ is proportional to voltage $v(t)$:
+
+```math
+q(t) = C\,v(t)
+``` where $C$ is the capacitance.
+
+* The current is the rate of change of charge:
+```math
+i_C(t) = \frac{dq(t)}{dt} = C\,\frac{dv(t)}{dt}
+```
+
+With $v(t)=\operatorname{Re}\{V e^{j\omega t}\}$,
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\frac{dv(t)}{dt} &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ j\omega V e^{j\omega t} \right\}, \\
+i_C(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ (j\omega C V) e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+\end{align}
+```
+
+Hence, the **phasor relationship** is:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\boxed{I = j\omega C\,V}, \qquad
+\boxed{Y_C = j\omega C}, \qquad
+\boxed{Z_C = \frac{1}{j\omega C}}.
+\end{align}
+```
+where $Y_C$ is the capacitive admittance and $Z_C$ is the capacitive impedance, and susceptance $B_C$ is imaginary part of $Y_C$.
+The real part of $Y_C$ is conductance $G_C$, which is used in steady-state AC optimal power flow problems.
+You could of course derive admittance and impedance for inductors following similar steps. The above steps connect the time-domain and phasor domain. Note that the above is for ideal inductors and capacitors.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ ca8dc9ed-0974-4205-9af4-a21c8a7cb707
+md"""
+## More realistic transmission line model
+
+So far, we've considered circuit elements without considering their coordinates on the line.
+In real transmission lines, however, voltage $v(x,t)$ and current $i(x,t)$ vary **both** in time and along the line coordinate $x$.
+
+Their spatial derivatives represent how these quantities change **per unit length:**
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} &\;\Rightarrow\; \text{voltage drop per unit length (V/m)}, \\
+\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial x} &\;\Rightarrow\; \text{current change per unit length (A/m)}.
+\end{align}
+```
+
+**Real lines are lossy:**
+- Conductor series resistance causes Ohmic losses (heat dissipation) in voltage $\Rightarrow$ adds $-R'\,i(x,t)$.
+- Current leakage due to shunt conductance $\Rightarrow$ adds $-G'\,v(x,t)$.
+
+Hence, the full **telegrapher's equations** are:
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} &= -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t} - R'\,i(x,t),\\
+\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial x} &= -C'\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial t} - G'\,v(x,t).
+\end{align}
+```
+where $L'$ and $C'$ are the inductance and capacitance per unit length, and $R'$ and $G'$ are the resistance and conductance per unit length.
+You can think about $R'$ and $G'$ as damping terms to account for losses and leakage.
+$L,C$ relate to energy storage, and $R,G$ relate to energy dissipation.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 9716f6a5-54d6-4abc-b0df-82f5a30e0196
+md"""
+## How the above was derived
+
+Consider a small line segment between $x$ and $x+dx$.
+- Coordinate $x$ increases in the direction of current flow ($+x$).
+- Current flowing in $+x$ direction: $i(x,t)$.
+- Voltage between conductors (top to bottom) at position $x$: $v(x,t)$.
+
+**1. Voltage change between segment ends:**
+
+```math
+v(x,t) - v(x+dx,t) = -\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x}\,dx.
+```
+
+**2. Series drops over $dx$:**
+
+```math
+\begin{align}
+\text{Resistive drop} &:\; R'\,i(x,t)\,dx,\\
+\text{Inductive drop} &:\; L'\,\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t}\,dx.
+\end{align}
+```
+
+**3. Apply Kirchhoff Voltage Law:**
+
+(The sum of voltage drops along the closed path must equal zero.)
+
+```math
+(R'\,i + L'\tfrac{\partial i}{\partial t})\,dx + \big[v(x+dx,t) - v(x,t)\big] = 0.
+```
+
+**4. Substitute and simplify:**
+
+```math
+\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x}\,dx = -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t}\,dx - R'\,i(x,t)\,dx.
+```
+
+**5. Divide by $dx$:**
+
+```math
+\boxed{\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} = -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t} - R'i(x,t)}.
+```
+
+The negative sign indicates that voltage **drops** in the $+x$ direction due to both inductive ($L'\,\partial i/\partial t$) and resistive ($R'i$) effects.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a5b6c7d8-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204451
+md"""
+# How does physics relate to optimization?
+
+We now connect the time-domain physics to **Transient Stability–Constrained Optimal Power Flow (TSC-OPF)**, where the optimization must respect both steady-state **and** dynamic constraints after a disturbance.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 34595bd9-874e-4ca9-bf3c-3ebef9a37cec
+md"""
+## TSCOPF formulation
+
+```math
+\begin{align*}
+\min_{p,\,x(t),\,y(t)} \quad & C(p) && \text{(1)}\\
+\text{s.t.}\quad
+& g_s(p) = 0 && \text{(2)}\\
+& h_s^{-} \le h_s(p) \le h_s^{+} && \text{(3)}\\
+& p^{-} \le p \le p^{+} && \text{(4)}\\[3pt]
+& \dot{x} = f(x,y,p), \quad x(t_0)=I_x^0(p) && \text{(5)}\\
+& 0 = g(x,y,p), \quad y(t_0)=I_y^0(p) && \text{(6)}\\
+& h(x(t),y(t)) \le 0, \quad \forall t && \text{(7)}
+\end{align*}
+```
+
+**Objective:** minimize operating cost or transmission losses. Eq. (2) includes steady-state nodal power balance constraints. Eq. (3) includes apparent/real power/reactive power/current flow constraints on lines. Eq. (4) includes generator capacity or voltage magnitude constraints.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a9f00e8c-205e-45a9-83d4-1dea5b7627c1
+md"""
+## Dynamic Transient Constraints: (5)--(7)
+
+The dynamic constraints (5)-(7) embed the time-parametrized physics of transient behavior into the optimization problem:
+
+**Eq. (5):**
+- State variables $x$ (rotor angles, speeds, control states). Initial states computed from steady-state solution corresponding to control variables $p$.
+- System dynamics $f(x,y,p)$ — e.g., generator swing equations, Telegrapher equations, or capacitor/inductor transient models.
+- Dependent variables $y$ (nodal voltages magnitude and angle, line currents, etc.).
+- Control variables $p$ (generator setpoints, tap settings, shunt positions, etc.)
+- Enforce the physics of transient after a disturbance.
+
+**Eq. (6):** embed dynamics into steady-state constraints.
+- The steady-state constraints $g(x,y,p)$ have same physical laws as (2) e.g. KCL but now must hold at every instant $t$'s states $x(t), y(t)$.
+
+The final set of constraints ensures that the system remains within safe operating limits throughout the transient:
+
+**(7) Transient limits:**
+
+```math
+h(x(t), y(t)) \le 0, \quad \forall t
+```
+
+- Enforce time-domain operating limits during the transient response.
+- Examples:
+ - Bus voltage magnitudes stay within limits.
+ - Rotor angle differences remain stable.
+ - Line thermal limits respected.
+- Ensures **transient stability** under all time steps during disturbance.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 22d5c113-82f0-4598-8c47-ead1face730e
+md"""
+## Solution Methods for TSC-OPF
+
+Solving TSCOPF is computationally challenging due to the nonlinear nature of AC power and the embedded differential equations. Several approaches have been developed:
+
+**Indirect (variational) Methods:**
+- Based on Pontryagin's Maximum Principle.
+- Replace the differential equations of dynamics with inequalities that approximate the behavior in steady-state by linearizing into additional static conditions.
+- Examples: energy or Lyapunov functions or impose stability margin constraints on linearized Jacobian.
+
+Instead of having to integrate over time, we get back a static nonlinear optimization problem that can be solved using standard solvers.
+
+**In practice:**
+- Mainly used for planning/screening/preventive security dispatch due to loss in accuracy.
+- Not sufficient to guarantee transient stability under large disturbances.
+- Validation still relies on time-domain (direct) simulation.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 47e011b8-4fb8-4534-a504-ffe3009beb6e
+md"""
+## Direct Method: Simultaneous Discretization/Constraint Transcription
+
+An approach that directly discretizes the differential equations. **Main idea:** Converts the time-dependent diff. eq. into a finite set of algebraic constraints before solving the optimization problem so transient stability simulator can be reused.
+
+**Discretization approach:**
+- The simulation horizon is divided into multiple time steps $t_0, t_1, \dots, t_N$.
+- The diff. eq. is approximated at each step using numerical integration like implicit trapezoidal rule:
+
+ ```math
+ x(t) - \frac{\Delta t}{2} f(x(t), y(t), p)
+ - x(t-\Delta t)
+ - \frac{\Delta t}{2} f(x(t-\Delta t), y(t-\Delta t), p) = 0.
+ ```
+
+**Pros and Cons:**
+- Produces one large-scale NLP that enforces the dynamics exactly for the entire trajectory (within discretization accuracy).
+- Computationally demanding due to the high dimensionality of variables and constraints from discretization. Accurate gradients is expensive from trajectory sensitivity analysis. Hessians often approximated using BFGS updates.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a3786b2d-9951-440f-854c-dfd40ad727f1
+md"""
+## Direct Method: Multiple Shooting
+
+Multiple shooting offers a more numerically stable alternative to simultaneous discretization. It divides the simulation horizon into smaller time segments $[t_0,t_1], [t_1,t_2], \dots, [t_{N-1},t_N]$.
+
+- Each segment starts from its own initial condition $x_i(t_i)$ and is integrated forward using the diff. eq. $\dot{x}=f(x,y,p),\, 0=g(x,y,p)$ to obtain the predicted final state $\hat{x}_i(t_{i+1})$.
+- Constraint to ensure continuity between segments:
+
+ ```math
+ x_{i+1}(t_{i+1}) = \hat{x}_i(t_{i+1}),
+ ```
+
+Abstractly, the constraint form is:
+
+```math
+s_i = S_i(s_{i-1},p), \quad \forall i \in 1,\dots,N_S,
+```
+
+where $S_i(\cdot)$ is an implicit function that can be numerically integrated over segment $i$. This can be used for variables $x,y$.
+
+**Pros:** Each segment can be integrated independently, so the Jacobian of the resulting NLP is better conditioned because the coupling is limited to segment boundaries instead of the entire trajectory. This segmentation improves numerical stability and allows for more efficient large-scale computation.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ c3d4e5f6-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204458
+md"""
+## Trajectory Sensitivity Analysis of TSC-OPF
+
+Both direct methods require gradient information. Sensitivity analysis can provide this efficiently.
+**Purpose:** Quantify how system variables $x(t),y(t)$ changes with respect to small variations in control variables $p$ or initial conditions.
+Recall that with different control settings $p$, the entire transient trajectory changes and we would need to simulate the dynamics again to see the consequences.
+This is expensive. Sensitivity analysis tells you how the trajectory and stability margins change with small variations in $p: \frac{\partial x}{\partial p}$ without running the full simulation for every small perturbation.
+
+**Relation to numerical methods:**
+- These sensitivities provide gradient information for solvers, which is used for both multiple shooting and constraint transcription.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 946ad231-4ddf-43a3-b2b9-95d502f4b5e9
+md"""
+## Forward Sensitivity Method
+
+The forward sensitivity method computes gradients by integrating sensitivity equations forward in time:
+
+- Perform a forward integration of the sensitivity equations alongside the original diff. eq. system.
+- Efficient when the number of parameters is small.
+- The computational complexity is $\mathcal{O}(n_p)$, since $n_p$ forward integrations are required to compute the sensitivities.
+
+**Formulation:**
+
+For the original diff. eq. system:
+
+```math
+F(\dot{x}(t),\, x(t),\, p) = 0.
+```
+
+The corresponding variational diff. eq. for the sensitivities is:
+
+```math
+\frac{\partial F}{\partial \dot{x}}\,\dot{s}
++ \frac{\partial F}{\partial x}\,s
++ \frac{\partial F}{\partial p} = 0,
+```
+
+with initial condition
+
+```math
+s(t_0) = \frac{\partial x(t_0)}{\partial p}.
+```
+
+- Each parameter $p_i$ perturbs the system differently.
+- Forward method tracks this by integrating a new "copy" of the linearized system, which shares the same Jacobian (including state dynamics and algebraic equations of KCL etc.) as the original differential equations.
+
+**Pros and cons:**
+- **Pros:** Simple to implement, accurate efficient when number of parameters is small.
+- **Cons:** Computational cost grows linearly with number of parameters.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ f6399741-9b5f-4bd3-bae7-6cc1ed1bd718
+md"""
+## Adjoint Method
+
+When the number of parameters is large, the forward method becomes expensive. The adjoint method is an alternative that only needs one backward integration in time to compute the sensitivities.
+
+**Formulation:**
+
+- Consider
+
+ ```math
+ G(p) = \int_{t_0}^{T} g(x, p)\,dt.
+ ```
+
+- We want the gradient given by:
+
+ ```math
+ \frac{\partial G}{\partial p}
+ =
+ \int_{t_0}^{T}
+ \left(
+ \frac{\partial g}{\partial p}
+ - \lambda^{\mathsf{T}} \frac{\partial F}{\partial p}
+ \right) dt,
+ ```
+
+- The adjoint multiplier $\lambda(t)$ satisfies
+
+ ```math
+ \dot{\lambda}
+ =
+ -\,\frac{\partial g}{\partial x}
+ + \lambda^{\mathsf{T}}\frac{\partial F}{\partial x}.
+ ```
+
+ where $\lambda(T)=0$.
+
+**Pros:**
+- Efficient when the number of parameters is large.
+- The gradient is obtained in one backward integration.
+
+**Cons:**
+- Higher memory cost due to storage of trajectory data and state variables in backward integration.
+
+One can also obtain the gradients by finite differences, which is based on truncated Taylor series expansion.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 214eacc5-0b60-44b8-8a53-9cce369debdd
+md"""
+# Power System History and Modern Power System
+
+To understand why transient stability matters today, we must go back to see how power systems have evolved. The grid's dynamic behavior has fundamentally changed with the integration of renewable energy.
+
+## The Fuel Era (20th Century)
+
+Electricity produced mostly by coal, gas, nuclear. Generators are large synchronous machines with big spinning masses. Stable and predictable. Inertia from these machines naturally provides flexibility in frequency stability. Grid ran reliably for decades.
+
+## The Renewable Era (2000s--Today)
+
+Wind expanded in 2000s, solar PV took off after 2010. Renewables now more than 20--40% of real-time demand in some regions; dynamics changed.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a7b8c9d0-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204464
+md"""
+## Synchronous Generators: How electricity is generated
+
+
+
+- Rotor (heavy spinning mass) driven by turbines (steam, gas, hydro)
+- Faraday's law: changing magnetic field induces voltage in stator
+- Called "synchronous" because the rotor spins in sync with the grid's frequency (50 Hz in Europe, 60 Hz in North America)
+- If the grid frequency is 60 Hz, the rotor turns at a speed locked to 60 Hz
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 6b64a495-6039-408c-91a9-4dfddf21d857
+md"""
+## Spinning Mass in a Generator
+
+- Inside a synchronous generator is a rotor — basically a giant heavy wheel of steel and copper (tens or hundreds of tons)
+- Turbines (steam from coal/nuclear, gas combustion, or flowing water in hydro) push on the rotor to make it spin
+- That rotor's mechanical rotation creates a rotating magnetic field, according to Faraday's law of induction, a changing magnetic field induces an alternating voltage in the stator windings
+- This is why the system is predictable: we know how to control these rotors. Put in more fuel to generate more power
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ b5159081-3b0a-459a-9c5b-c2b4911d79e2
+md"""
+## Generator Frequency Formula
+
+**Frequency Formula:**
+
+```math
+f = \frac{N \times \text{RPM}}{120}
+```
+
+where $N$ = number of poles, RPM = rotor speed
+
+**Examples:**
+- 2 poles, 3600 RPM → 60 Hz
+- 4 poles, 1800 RPM → 60 Hz
+
+**Why 50/60 Hz?** Historical choices: early engineers (Westinghouse, Edison, etc.) picked values that balanced motor performance and generator design. Once infrastructure was built, it became a standard.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ ad22ab28-884e-4c3b-8265-51a44685343d
+md"""
+## Kinetic Energy
+
+**The rotor has stored kinetic energy:**
+
+```math
+E_{\text{kinetic}} = \frac{1}{2} J \omega^2
+```
+
+where $J$ = moment of inertia (depends on mass + geometry), $\omega$ = rotor speed
+
+**If demand suddenly exceeds supply (a generator trips):**
+- That small slow down of a rotor releases some of its stored kinetic energy into the grid instantly
+- But because there are so many large spinning machines, the grid behaves like a conveyor belt with so many wheels tied together. If one slows a bit, the others share the imbalance, so frequency changes slowly because the system has a huge inertia
+- This gives time for operators to fix things
+- Even if there are imbalances, things wouldn't get out of hand fast since there are so many other generators. They can share the load so each only needs to spin a little faster to keep up the frequency
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 01ebbe37-0681-47bb-b851-5f16b9f4aeb5
+md"""
+## Inverters - Renewables
+
+The modern power grid faces new challenges with the integration of renewable energy sources. **Today, renewables supply 20–40\%+ of real-time demand.**
+
+Cleaner, cheaper, more sustainable — but dynamics changed.
+
+Most renewables (solar PV, modern wind turbines, batteries) produce DC electricity (direct current).
+
+**What's the problem of DC power?**
+- It only has amplitude (magnitude of voltage/current)
+- No phase, no frequency
+- But recall AC current has the waveform (that's why we have leading/lagging current which controls reactive power and power factor correction)
+- We need amplitude, frequency, and phase to describe AC current
+- That's why we need inverters, power electronics device that synthesizes sinusoidal AC from DC
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 86d07665-753e-4dbe-aa84-5b23ec0a616f
+md"""
+## Inverter Operation
+
+**How it operates?**
+
+1. Takes DC input from solar panels, wind turbine
+2. Use power electronics that switches thousands of time per second to synthesize an AC waveform
+3. Note that even the output is a smooth sinusoidal AC waveform, inside the inverter the switches turn the DC voltage on and off thousands of times per second (typical switching frequency = 2–20 kHz, sometimes higher) to approximate that smooth waveform
+4. So even though the output is continuous, it's created by on/off pulses internally
+5. The inverter synchronizes the AC output to the grid's frequency and phase. If grid is 60 Hz → inverter outputs 60 Hz. If grid is 59.9 Hz (after a disturbance) → inverter follows 59.9 Hz.
+6. The voltage, current, and power factor are controlled through the programmed algorithms
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 8e4dc912-14ff-4290-8f96-926493e5ef81
+md"""
+## Inverter Control Modes
+
+**In summary, the inverters are programmable devices by operators with control algorithms to act like generators. They wait for a signal from a grid so they can be:**
+
+- **Grid-following:** track the grid's voltage and frequency → inject current accordingly
+- **Grid-forming:** behave like a voltage source, set their own frequency/voltage reference, and to adjust for power imbalance (some research area I heard of)
+
+They are not really generators - no spinning mass, no inertia, but they use control algorithms to mimic generator behavior.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ c5d6e7f8-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204471
+md"""
+## Internal View of Inverters
+
+
+
+- Capacitors and switching components on electronic mainboards (like in computer's motherboard, blue cylinders in upper left corner of the picture)
+- Programmable behavior defined by control firmware
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ c0cc1b94-e651-40c2-8084-e9ebfad2a457
+md"""
+## Problems with Inverters
+
+**This is all software-based. You do not have a natural physical property like a spinning rotor and inertia.**
+
+- No big spinning mass directly tied to frequency, so frequency changes much faster after a disturbance
+- The device measures grid signal and forces its output to follow
+- Unless explicitly programmed, they don't know when the conveyor belt slows down or speeds up (recall the previous analogy)
+- Even if they do, they don't have the capacity like big generators
+- **This is the key part:** they are just switching circuits with no agency to ramp up the power output (nature of renewables is their output is often independent of human control). Output is limited by weather and energy availability (sun/wind).
+- Renewables also locate in remote areas with long transmission lines, and the nature of their unpredictability (weather), makes their generation highly uncertain
+
+**We will build up to inverter control after we cover the generator swing equations.**
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 4702e992-a163-40f3-ab55-f9e8e848d0c7
+md"""
+# Generator Swing Equations
+
+The generator swing equations are the cornerstone of power system dynamics. They describe how generators respond to power imbalances, connecting mechanical and electrical power through rotational forces.
+
+## Newton's Second Law
+
+We begin with the fundamental physics. **Linear Version:**
+
+```math
+F = ma
+```
+
+where $F$ = force (N), $m$ = mass (kg), $a$ = acceleration (m/s²)
+
+This says: imbalance of forces → acceleration of mass.
+
+**Rotational Version:**
+
+For a rotating body (like a generator rotor), the equation is:
+
+```math
+T = J\alpha
+```
+
+where $T$ = torque (N·m), $J$ = moment of inertia (kg·m²), the rotational mass. $\alpha$ = angular acceleration (rad/s²)
+
+This says: imbalance of torques → rotor accelerates or decelerates.
+
+Think torque as the angular equivalent of force.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 1566dce2-fd36-4110-8220-97eefe043cbb
+md"""
+## Applied to Generator Dynamics
+
+Now we apply Newton's second law to a generator rotor. **There are two main torques acting on a synchronous generator's rotor:**
+
+- Mechanical torque from the turbine (steam, gas, water) pushing the rotor: $T_m$
+- Electromagnetic torque from the stator's magnetic field resisting the rotor (this is the grid "pulling" power out): $T_e$
+
+**Torque imbalance:**
+
+```math
+J\alpha = T_m - T_e
+```
+
+where $\omega$: angular speed of rotor (rad/s), $\alpha = \dot{\omega}$: angular acceleration (rad/s²)
+
+**If $T_m > T_e$:** rotor accelerates
+
+**If $T_m < T_e$:** rotor slows down
+
+**If equal:** steady rotation
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 9bd48789-5d3d-495c-acd3-6586ae616136
+md"""
+## From Torque to Power
+
+To connect torque dynamics with electrical power, we relate rotational motion to power. Recall $P = Fv$ (mechanical power is generated by a force $F$ on a body moving at a velocity $v$). In rotational systems, power is related by torque and angular speed (you can think about it as rotational equivalent as force)
+
+**Power = torque × speed:**
+
+```math
+P = T \cdot \omega
+```
+
+So:
+- Mechanical power input: $P_m = T_m \cdot \omega$
+- Electrical power output: $P_e = T_e \cdot \omega$
+
+Multiply the torque balance by $\omega$:
+
+```math
+J\omega\dot{\omega} = P_m - P_e
+```
+
+This relates how fast the mass is spinning ($\omega$) to the imbalance of power input (generation) and power withdrawal (load + losses).
+
+In practice, generators operate close to system frequency, so the generators spin at an angular velocity that is close to that 60 Hz constant. Since the variations are mostly tiny, we can define inertia constant $M = J\omega$
+
+And we get the generator swing equation:
+
+```math
+M\dot{\omega} = P_m - P_e
+```
+
+**Interpretation:**
+- Inertia constant $M$, measures how much the rotor resists speed change (bigger mass → slower frequency drift)
+- Mechanical input power (from fuel, water, steam): $P_m$
+- Electrical output power delivered to the grid: $P_e$
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a9b0c1d2-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204477
+md"""
+## Per-Unit Generator Swing Equation
+
+**Per-unit versions:**
+
+Power are often defined at per unit, so we have:
+
+```math
+\frac{J\omega_s}{S_{\text{base}}} \dot{\omega} = (P_m - P_e)_{\text{pu}}
+```
+
+There are sources that define $H = \frac{1}{2}\frac{J\omega_s^2}{S_{\text{base}}} \Rightarrow \frac{2H}{\omega_s} = \frac{J\omega_s}{S_{\text{base}}}$
+
+$H \triangleq \frac{E_k}{S_{\text{base}}} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}J\omega_s^2}{S_{\text{base}}}$ comes from kinetic energy
+
+So we have per unit swing:
+
+```math
+\frac{2H}{\omega_s} \dot{\omega} = (P_m - P_e)_{\text{pu}}
+```
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ abcd31d0-c6eb-4bc7-a752-83a8d7f6fda1
+md"""
+## Damping and Another Form of Generator Swing Equations
+
+Some also add damping:
+
+```math
+M\dot{\omega} + D(\omega - \omega_s) = P_m - P_e
+```
+
+as penalties to frequency deviation. $D$ captures any restoring force, or frictions and losses
+
+We can also write the per-unit acceleration form:
+
+```math
+2H \dot{\omega}_{\text{pu}} = (P_m - P_e)_{\text{pu}}
+```
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ b16732b7-ec08-43c7-9c08-489c8c8bbecb
+md"""
+## Why This Matters
+
+- Stability depends on balancing generation and demand
+- Inertia slows down changes in frequency, buying time for control actions
+
+**Power imbalance effects:**
+- If $P_m > P_e$: extra power → rotor speeds up → frequency rises
+- If $P_m < P_e$: shortage → rotor slows → frequency falls
+
+**Inertia $M$ slows down how fast this happens.**
+- With many generators, $M$ is big. For a given imbalance, frequency drifts slowly → grid is flexible
+- With fewer machines (more renewables), $M$ is smaller → frequency changes faster → grid is fragile
+
+This is shown by writing the equation as $\dot{\omega} = \frac{P_m - P_e}{M}$. For a big $M$, the angular acceleration (frequency) is smaller when there is an imbalance.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 8ee16365-6d48-4073-9482-44dd58b7e338
+md"""
+## How Does It Relate to Inverters?
+
+The swing equation framework extends beyond traditional generators. We previously discussed grid-following inverters.
+
+**Its control law works as:**
+
+1. Measure voltage and frequency of the grid
+2. Gets desired power output from an operator or solved from a market
+3. Adjust its AC current output to deliver the desired power output at voltage and frequency GIVEN by the grid
+
+The problem is it has no control over other parameters like voltage and frequency. The power output is only stable if the rest of the grid maintains a good reference.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ f05940b2-5a30-46dc-8811-5f3d6b0c74a0
+md"""
+## Grid-forming Inverters
+
+Grid-forming inverters represent a more advanced control paradigm that enables renewables to provide grid support:
+
+- It behaves as controlled voltage source that defines its own reference voltage and frequency
+- Let the frequency shift slightly to reflect power imbalance between the renewable generation and the rest of the grid, so other machines (generators) know to ramp up or down
+- Able to define its own frequency is the key for the renewable to behave like a synchronous generator, and we now have the ability to model it in a swing equation by giving it a virtual mass defined by the local frequency
+
+We can now emulate synchronous machine behavior via controlling the "virtual inertia".
+
+**Reference:** J. Driesen and K. Visscher, "Virtual synchronous generators," 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting - Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2008, pp. 1-3.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 75deac76-f89c-4b84-a132-67591177f5dd
+md"""
+## Virtual Inertia Law in Grid-Forming Inverter
+
+**Physics is replaced by software:**
+
+```math
+M_{\text{virtual}} \dot{\omega} = P_{\text{ref}} - P
+```
+
+**Parameters:**
+- Tunable parameter by the controller $M_{\text{virtual}}$, chosen to represent how fast the inverter responds to frequency changes
+- Recall $M = J\omega$. Since we have no physical inertia $J$, the virtual mass is just a modeling choice
+- Reference active power dispatch (from operator): $P_{\text{ref}}$
+- Measured actual active power delivered: $P$
+- Inverter's internal frequency reference value: $\omega$
+
+**Effect of $M_{\text{virtual}}$:**
+- A larger $M_{\text{virtual}}$ means the inverter allows its frequency to drift slower, a "heavier" machine
+- A smaller $M_{\text{virtual}}$ means the inverter reacts more quickly, a "lighter" machine
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 0a2c4c0a-c68e-4f21-afbb-1b80791ec166
+md"""
+## Virtual Inertia
+
+**How it works:**
+- The inverter adjusts its internal frequency reference according to power imbalance
+- That frequency reference drives its voltage output, which the grid "sees"
+- To the rest of the system, this looks just like a synchronous machine rotor slowing/speeding under imbalance
+
+- There's no heavy rotor. It emulates the inertia behavior of synchronous machines through software control.
+- But this is not sustained. It can only hold it until the renewable saturates, which is less than a second since they don't have as much buffer as traditional generators.
+- Other problems: semiconductor ratings, thermal limits, hard to tune $M_{\text{virtual}}$, cost, legacy devices, etc.
+
+**Why this is such a big deal:** renewables can now respond to a grid-wide drop in frequency because it can behave almost like a synchronous generator through control law
+
+## Demo of swing equation / virtual inertia response:
+- When there's a positive power imbalance, the frequency will increase.
+- Larger inertia slows down the rate at which frequency rises. This shows up as a curve that rises more gently (less sharply concave) because a heavier system resists acceleration more.
+- Increasing damping reduces the steady-state frequency deviation for a given imbalance and allows the system to settle faster. Higher damping provides a stronger corrective force that pulls frequency back toward nominal.
+- In the plot, we will see it makes the plot level off sooner.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ e14c2b45-3a7d-4e27-9c13-79ae514b1881
+@bind M Slider(0.5:0.5:10.0, default=5.0, show_value=true)
+
+# ╔═╡ 6ff3fd90-23cd-4cd0-95cf-d4e1d5ac3bdf
+@bind D Slider(0.0:0.1:5.0, default=1.0, show_value=true)
+
+# ╔═╡ b32a299d-4d0a-4e8b-b576-15bb32acad24
+@bind ΔP Slider(-0.5:0.05:0.5, default=0.2, show_value=true)
+
+# ╔═╡ 4db9cfa4-66c7-4b71-b0b3-5c16eaa2bb9e
+md"""
+### Interactive: Swing Equation / Virtual Inertia Response
+
+Use the sliders above to adjust:
+
+- **M** — inertia (or virtual inertia)
+- **D** — damping
+- **ΔP** — power imbalance (positive = deficit in electrical power, negative = surplus)
+
+The plot shows the **frequency deviation** response over time.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a0b43f28-8e17-4633-8eab-b9554e05c8f6
+begin
+ # Nonlinear swing-like ODE: M * dω/dt + D*ω = ΔP
+ function swing!(dω, ω, p, t)
+ M, D, ΔP = p
+ dω[1] = (ΔP - D*ω[1]) / M
+ end
+
+ ω0 = [0.0] # initial frequency deviation
+ p = (M, D, ΔP)
+ tspan = (0.0, 10.0)
+
+ prob = ODEProblem(swing!, ω0, tspan, p)
+ sol = solve(prob, Tsit5())
+
+ plot(sol.t, [u[1] for u in sol.u],
+ xlabel = "Time (s)",
+ ylabel = "Frequency deviation",
+ title = "Generator Swing / Virtual Inertia Frequency Response",
+ legend = false)
+end
+
+
+# ╔═╡ c7d8e9f0-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204484
+md"""
+## Grid-following inverters - Droop Control
+
+Droop control enables automatic power sharing among generators and inverters: generators naturally slow down if overloaded, resulting in a drop in frequency (droop). Droop control allows each generator to increase its power output in response, but in proportion to its droop coefficient, so that all generators share the load change fairly.
+
+Grid-forming inverters are programmed with droop control:
+
+```math
+P = P_{\text{set}} - \frac{1}{K_p} (\omega - \omega_0)
+```
+
+where $\omega_0$: nominal frequency, $P_{\text{set}}$: reference power output, $K_p$: droop constant (rad/s per MW or Hz per MW) telling inverter how much to adjust power output when frequency changes. Hence when frequency drops, power will rise.
+
+Overload leads to frequency drop, and power will rise according to the relationship. If frequency rises, power will decrease to maintain the frequency.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 20d5d03f-0225-4d3c-b0d2-d7440340b821
+md"""
+## Reactive Power and Voltage Control (Q-V Droop)
+
+Just as frequency droop controls active power balance, voltage droop controls reactive power balance. Analogous for voltage support:
+
+```math
+V = V_0 - K_q (Q - Q_{\text{set}})
+```
+
+or
+
+```math
+Q = Q_{\text{set}} - \frac{1}{K_q} (V - V_0)
+```
+
+If reactive demand $\uparrow$ (voltage dips), generator/inverter increases reactive power injection.
+
+**Two important components of stability:** frequency and voltage. If there are deviations, adjust active and reactive power accordingly
+
+- Interpretation of $1/K_p$ = MW per Hz: "How much active power do I add if frequency drops by 0.1 Hz?"
+- Interpretation of $1/K_q$ = Mvar per V → "How much reactive power do I add if voltage drops by 0.01 pu?"
+
+## Summary: Generator and Inverter Dynamics
+
+Synchronous generators naturally provide inertia and adjust their output through physical dynamics, giving the grid its inherent frequency stability.
+Inverters lack this physical behavior, so control algorithms such as virtual inertia and droop control are introduced to let them share changes in load and maintain frequency and voltage—just as generators have always done.
+Droop control is essential because it enables multiple devices to automatically coordinate their power output. With generator and inverter dynamics in place, we now turn to **dynamic load models**, which describe how electricity demand behaves during disturbances.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 37f242b9-454f-4361-a2e1-98acae57b6fe
+md"""
+# Dynamic Load Models
+
+So far, we've focused on generation dynamics. However, loads also exhibit dynamic behavior that significantly impacts system stability. Understanding how loads respond to voltage and frequency changes is crucial for accurate transient analysis.
+
+## Dynamic Load Models
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 4211a2c2-4a3a-4a63-8d2e-dc6c94e0cfc6
+md"""
+## Steady-State Load Models in ACOPF/DCOPF
+
+We begin by reviewing how loads are typically modeled in static optimization. In optimal power flow (OPF), all quantities are **time-invariant**. $\dot{x} = 0$, time parameter $t$ does not appear in the equations.
+
+At each load bus:
+
+```math
+P_D = \text{fixed real power demand}, \qquad
+Q_D = \text{fixed reactive demand}.
+```
+
+These loads can be either:
+- Constant power: $P_D, Q_D$ are specified numerical values; or
+- Voltage-dependent (ZIP) as motors draw different amount current to maintain torque:
+
+ ```math
+ P(V) = P_0 (a_P V^2 + b_P V + c_P), \quad
+ Q(V) = Q_0 (a_Q V^2 + b_Q V + c_Q).
+ ```
+
+Power-flow balance:
+
+```math
+P_G - P_D = \text{network losses}, \qquad
+Q_G - Q_D = 0.
+```
+
+However, the static load model has important limitations. Interpretation of the above model:
+- Loads are fixed regardless of system conditions, or at most respond to nodal voltage.
+- No memory or dynamics -- they change only between static operating points.
+- The OPF represents a single equilibrium snapshot of the system.
+
+**Next:** Dynamic models generalize this by letting $P_D$ and $Q_D$ **evolve over time** with voltage and frequency. The grid's sink can be dynamic too even though we tend to think about it as a fixed parameter.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 8ca0ad91-2fb5-4e64-9f6f-5498fa39d44b
+md"""
+## Dynamic Load Models - Induction Motor Model
+
+Dynamic load models capture the time-dependent response of loads to system disturbances. In dynamic load models, the active and reactive power is represented as a function of the past and present voltage magnitude and frequency of the load bus. This type of model is commonly derived from the equivalent circuit of an induction motor.
+
+Most real-world loads (fans, pumps, compressors) are induction motors.
+
+Their active/reactive power do not change instantaneously with voltage change but rather dynamically by changing the motor's rotor speed $\omega_r$ to maintain torque. Hence, the power consumption depends on both voltage and frequency.
+
+```math
+P_d = f_P(V, \omega_r), \qquad Q_d = f_Q(V, \omega_r),
+```
+
+so the load has internal dynamics, unlike static $P_D, Q_D$ in ACOPF.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a1b2c3d4-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204490
+md"""
+## Rotor Dynamics
+
+The key parameter describing induction motor operation is slip, which relates rotor speed to synchronous speed:
+
+**Slip:**
+
+```math
+s = \frac{\omega_s - \omega_r}{\omega_s},
+```
+
+where
+- Synchronous electrical speed is $\omega_s$ (given by $2\pi f_s$), set by system frequency,
+- Mechanical rotor speed (frequency at the load): $\omega_r$
+
+**Operating regions:**
+- When rotor is synchronous with system frequency: $s = 0$ $\rightarrow$ no induced torque.
+- Normal operation: $0 < s < 1$. Rotor is slightly slower than the rotating field $\rightarrow$ induces current $\rightarrow$ produces torque.
+- Stall: $s \to 1$. Rotor stopped, max current, high losses.
+
+**Mechanical dynamics (sign flip if you differentiate w.r.t. slip):**
+
+```math
+J\frac{d\omega_r}{dt} = T_e(V,\omega_r) - T_m
+\quad\Longleftrightarrow\quad
+J\,\omega_s\,\frac{ds}{dt} = T_m - T_e(V,s).
+```
+
+**Variable definitions:**
+- Rotor inertia (kg·$m^2$): $J$
+- Rotor mechanical speed/frequency (rad/s): $\omega_r$
+- Electromagnetic torque: $T_e$ (depends on bus voltage $V$, frequency $\omega_s$ (slip formulation), or $\omega_r$ (standard formulation)),
+- Mechanical load torque: $T_m$
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 160fd7d9-a3c2-4f22-951e-deed6f32e09b
+md"""
+## Example: Induction Motor Response During a Voltage Sag
+
+**Sequence of events:**
+
+1. **Voltage drop:** $V$ suddenly decreases.
+2. **Torque imbalance:** Electromagnetic torque $T_e(V,\omega_r)$ falls below mechanical torque $T_m$.
+3. **Rotor slowdown:** $\omega_r$ decreases $\Rightarrow$ slip $s$ increases.
+4. **Increased current and VAR demand:** The motor draws more current to restore torque, which further depresses voltage.
+5. **Possible stalling:** If $V$ remains low, the motor stalls — reactive power skyrockets $\Rightarrow$ voltage collapse.
+
+IM Modeling is key to capture this nonlinear instability mechanism.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 56b58c9f-f8ce-4117-8105-70083c23fde9
+md"""
+## How TSC-OPF Prevents Motor Stalling and Voltage Collapse
+
+The transient stability-constrained optimization framework directly addresses these instability mechanisms. **In TSC-OPF, dynamics and limits are enforced directly:**
+
+```math
+\dot{x} = f(x, y, p), \qquad 0 = g(x, y, p), \qquad h(x(t), y(t)) \le 0, \;\forall t.
+```
+
+**The IM model contributes to the dynamic states $x$ in TSC-OPF:**
+- Induction motor slip $s$, generator rotor angles, inverter controls, etc.
+- Their evolution $f(x,y,p)$ describes how voltages and speeds change after a disturbance.
+- Dynamic constraints ensure stall condition is not reached.
+
+**Constraint function $h(x(t),y(t))$:**
+- Enforces time-domain limits such as
+
+ ```math
+ V_i(t) \ge V_{\min}, \quad \forall t \in [0, T_{\text{rec}}],
+ ```
+
+ where $T_{\text{rec}}$ is the recovery time. This ensures bus voltages remain within safe recovery bounds during the entire horizon after a disturbance.
+- Prevents continued voltage sag that would drive $T_e(V,s)$ down and cause stalling.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 03d81d40-f285-47d6-bbf4-db3e8efc7bd1
+md"""
+## Wrap up (Induction Motor Models)
+
+Controls $p$ are chosen so that $f$ remains stable under disturbances, and the chain of events above is prevented since motor and network dynamics are embedded in $f$, $g$, and $h$.
+
+This model is typically used when there's a fast transient or stalling, and the time scale is in milliseconds to second. Useful for short-term voltage stability and transient studies.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a4b027e0-15e6-4097-acc9-358fb075fd7f
+md"""
+## Exponential Recovery Load (ERL): Motivation and Concept
+
+Beyond individual motor dynamics, aggregate load behavior exhibits exponential recovery patterns. **Goal:** Represent aggregate load behavior during voltage recovery after a disturbance.
+
+**Empirical Observation:**
+- When voltage dips, total active and reactive loads drop immediately.
+- Loads such as motor controls and HVAC systems **slowly restore** their power draw as voltage recovers.
+- The recovery follows an **exponential time pattern**, not an instantaneous jump.
+
+**Idea:**
+
+Introduce internal states that describe this gradual return:
+
+```math
+P_d(t) = f_P(V(t),x_p(t)), \qquad Q_d(t) = f_Q(V(t),x_q(t)).
+```
+
+where $x_p(t)$ and $x_q(t)$ are the internal states of the active and reactive load.
+
+These states evolve according to first-order differential equations, capturing the "memory" of how far the load has recovered.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ e93c6dc1-2f8d-4e2f-bbed-db926643f32a
+md"""
+## Adaptive Exponential Recovery Load (ERL) Model
+
+The adaptive ERL model captures voltage-dependent recovery through differential equations. **Mathematical Form:**
+
+```math
+\begin{aligned}
+T_p \frac{dx_p}{dt} &= -x_p\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{ps}}
+ + P_0\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}},\\[3pt]
+P_d &= x_p\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}},\\[6pt]
+T_q \frac{dx_q}{dt} &= -x_q\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{qs}}
+ + Q_0\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{qt}},\\[3pt]
+Q_d &= x_q\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{qt}}.
+\end{aligned}
+```
+
+**Parameters:**
+- Internal recovery states (how much of the load has recovered): $x_p, x_q$
+- Time constants (larger values $\Rightarrow$ slower recovery): $T_p, T_q$
+- Nominal power withdrawals at reference voltage $V_0$: $P_0, Q_0$
+- Transient exponents (immediate voltage sensitivity): $N_{pt}, N_{qt}$. How sharply load power reacts immediately when voltage changes (the short-term dip).
+- Steady-state exponents (long-term voltage dependence): $N_{ps}, N_{qs}$. How much the load power changes in the long term after voltage settles to a new level.
+
+**Interpretation:**
+- After a voltage dip, power first follows the transient curve, then recovers exponentially toward the steady-state curve.
+- When $V$ is weak, the recovery term $(V/V_0)^{N_{ps}}$ slows the rate of change — recovery stalls under low voltage.
+- Recovery speed and power response both scale with voltage and almost halts under deep voltage sag.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 3f7130a0-51d6-4493-b07e-e5bf178ce834
+md"""
+## Standard vs. Adaptive ERL Models
+
+**Standard ERL model:**
+
+```math
+\begin{aligned}
+T_p \frac{dx_p}{dt} &= -x_p + P_0\!\left[\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{ps}} - \left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}}\!\right],\\
+P_d &= x_p + P_0\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}}.
+\end{aligned}
+```
+
+**Key difference:**
+- In the **standard** model, $dx_p/dt$ depends on $V$ only through the voltage-dependent driving term. The state $x_p$ recovers constantly—independent of voltage.
+- In the **adaptive** model, recovery slows when $V$ is low: the term $(V/V_0)^{N_{ps}}$ reduces the rate of change. The two differ in how strongly the voltage affects recovery speed back to pre-disturbance load.
+
+**Physical interpretation:**
+- Standard ERL: suitable for moderate voltage dips.
+- Adaptive ERL: more realistic for deep voltage sags.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 18207180-a40b-4bb7-87bb-9a0752286cea
+md"""
+## ERL Parameters
+
+- Parameters $(T_p, T_q, N_{ps}, N_{pt}, N_{qs}, N_{qt})$ are fitted empirically from from measurements of load recovery after voltage disturbances.
+- They are not linked to physical machine constants, but to observed aggregate behavior of customer loads.
+
+**Compared to IM Model:**
+- Models **voltage-driven recovery** of active/reactive power demand, not frequency-driven mechanical motion.
+- Represents the slower phase of system response (seconds to minutes) vs. fast electromechanical transients.
+
+**Steady-state check:**
+
+Setting $\dot{x}_p=\dot{x}_q=0$ gives $P_d=P_0(V/V_0)^{N_{ps}}$, $Q_d=Q_0(V/V_0)^{N_{qs}}$, so ERL naturally reduces to a static voltage-dependent load, showing that when dynamics died out, the model reduces to a steady-state load.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 4d6fd1e2-9457-4f4c-84b1-62958a8b49de
+md"""
+## ERL in TSC-OPF and Contrast with Induction Motor Model
+
+**TSC-OPF representation:**
+
+```math
+\dot{x} = f(x,y,p), \qquad 0 = g(x,y,p), \qquad h(x(t),y(t)) \le 0.
+```
+
+- ERL contributes states $x_p,x_q$ to $x$, with recovery dynamics embedded in $f(x,y,p)$.
+- $P_d(V,x_p), Q_d(V,x_q)$ enter the algebraic equations $g(x,y,p)$ for power balance at each bus.
+- Voltage-recovery limits in $h(x(t),y(t))$ ensure $V_i(t)\!\ge\!V_{\min}$ throughout the recovery window $[0,T_{\text{rec}}]$.
+
+**Contrast with IM model:**
+- **Induction Motor (IM):** physics-based; state $s=(\omega_s-\omega_r)/\omega_s$; captures fast electromechanical and frequency-coupled transients (0.1–2 s).
+- **ERL:** empirical; states $x_p,x_q$; captures slow, voltage-driven recovery (1–60 s).
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 011a1e50-0316-42ec-9295-eeee64b76299
+md"""
+## Wrap up
+### Why We Go Beyond Steady-State OPF
+
+In this chapter, we motivated from the physical principles and operation constraints to demonstrate that power systems are fundamentally dynamic. **The bigger picture:**
+- Even though steady-state analysis is helpful for many purposes and have lower computational burden, power systems are **dynamic systems.**
+- After every change — a fault, switching event, or sudden load or generation shift — voltages, currents, and frequencies evolve continuously before settling.
+- Understanding and controlling these dynamics is essential for keeping the grid stable, secure, and resilient.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ 81952b3e-93c9-4179-8b12-5933d49749a6
+md"""
+### Four Building Blocks of System Dynamics
+
+Throughout this chapter, we have explored four fundamental components that govern power system dynamics:
+
+- **Transients:** capture the immediate electromagnetic wave response that propagates through the network.
+- **Generator swing equations:** describe how machines adjust speed and angle to balance mechanical and electrical power.
+- **Inverters:** the new generation interface that emulates inertia and voltage support with renewables.
+- **Dynamic loads:** model how real demand recovers and interacts with voltage and frequency.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ a3b4c5d6-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204503
+md"""
+### Why We Need Dynamic Optimization (TSC-OPF)
+
+These building blocks come together in transient stability-constrained optimization. **Why we need optimization with system dynamics embedded (TSC-OPF):**
+- Steady-state OPF finds an economical operating point **only at equilibrium.**
+- Transient Stability-Constrained OPF ensures that, even during those dynamic transitions, voltages remain safe, machines stay synchronized, and inverters and loads respond smoothly.
+"""
+
+# ╔═╡ Cell order:
+# ╟─4866207c-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204424
+# ╟─a1b2c3d4-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204425
+# ╟─e6aa5227-91bd-4cec-9448-24384708a305
+# ╟─19dac419-2df3-4878-b7da-608e8ec1e53b
+# ╟─8ed6af99-1c5d-4d27-b60d-17d2e6c6ceff
+# ╟─f742f5f3-d9d3-4374-ac9e-17073c3a2f6d
+# ╟─ad8e9d79-e226-468e-9981-52b7cda7c955
+# ╟─fc329e51-e91c-4d83-b6fe-07a3bce44d5d
+# ╟─d767175f-290d-403e-99de-d3a8f2ccb5b5
+# ╟─c9d0e1f2-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204432
+# ╟─9d1ea9be-2d7b-4602-8a8e-8426ea31661a
+# ╟─71ba62e6-bcc1-4e9b-91cd-a8860ba0d2b5
+# ╟─7b4800c2-133d-4793-95b1-a654a4f19558
+# ╟─7961c1d1-3e82-49ea-8201-c5f82066d70d
+# ╟─91b8a3e4-81ed-49fe-b785-4feacfd8788d
+# ╟─f72775b9-818c-4a9b-9b66-cfccd88e17ed
+# ╟─53ab9b31-78aa-49b6-9e24-df47aa80f25a
+# ╟─1e337cdf-8add-42ab-a62f-23069e34ec39
+# ╟─23dc8fd4-59a1-414f-a165-b509458abd18
+# ╟─5814ece5-51b3-4dba-953d-c1f4b6ab04a8
+# ╟─c1d2e3f4-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204445
+# ╟─ca8dc9ed-0974-4205-9af4-a21c8a7cb707
+# ╟─9716f6a5-54d6-4abc-b0df-82f5a30e0196
+# ╟─a5b6c7d8-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204451
+# ╟─34595bd9-874e-4ca9-bf3c-3ebef9a37cec
+# ╟─a9f00e8c-205e-45a9-83d4-1dea5b7627c1
+# ╟─22d5c113-82f0-4598-8c47-ead1face730e
+# ╟─47e011b8-4fb8-4534-a504-ffe3009beb6e
+# ╟─a3786b2d-9951-440f-854c-dfd40ad727f1
+# ╟─c3d4e5f6-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204458
+# ╟─946ad231-4ddf-43a3-b2b9-95d502f4b5e9
+# ╟─f6399741-9b5f-4bd3-bae7-6cc1ed1bd718
+# ╟─214eacc5-0b60-44b8-8a53-9cce369debdd
+# ╟─a7b8c9d0-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204464
+# ╟─6b64a495-6039-408c-91a9-4dfddf21d857
+# ╟─b5159081-3b0a-459a-9c5b-c2b4911d79e2
+# ╟─ad22ab28-884e-4c3b-8265-51a44685343d
+# ╟─01ebbe37-0681-47bb-b851-5f16b9f4aeb5
+# ╟─86d07665-753e-4dbe-aa84-5b23ec0a616f
+# ╟─8e4dc912-14ff-4290-8f96-926493e5ef81
+# ╟─c5d6e7f8-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204471
+# ╟─c0cc1b94-e651-40c2-8084-e9ebfad2a457
+# ╟─4702e992-a163-40f3-ab55-f9e8e848d0c7
+# ╟─1566dce2-fd36-4110-8220-97eefe043cbb
+# ╟─9bd48789-5d3d-495c-acd3-6586ae616136
+# ╟─a9b0c1d2-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204477
+# ╟─abcd31d0-c6eb-4bc7-a752-83a8d7f6fda1
+# ╟─b16732b7-ec08-43c7-9c08-489c8c8bbecb
+# ╟─8ee16365-6d48-4073-9482-44dd58b7e338
+# ╟─f05940b2-5a30-46dc-8811-5f3d6b0c74a0
+# ╟─75deac76-f89c-4b84-a132-67591177f5dd
+# ╟─0a2c4c0a-c68e-4f21-afbb-1b80791ec166
+# ╟─e14c2b45-3a7d-4e27-9c13-79ae514b1881
+# ╟─6ff3fd90-23cd-4cd0-95cf-d4e1d5ac3bdf
+# ╟─b32a299d-4d0a-4e8b-b576-15bb32acad24
+# ╟─4db9cfa4-66c7-4b71-b0b3-5c16eaa2bb9e
+# ╟─a0b43f28-8e17-4633-8eab-b9554e05c8f6
+# ╟─c7d8e9f0-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204484
+# ╟─20d5d03f-0225-4d3c-b0d2-d7440340b821
+# ╟─37f242b9-454f-4361-a2e1-98acae57b6fe
+# ╟─4211a2c2-4a3a-4a63-8d2e-dc6c94e0cfc6
+# ╟─8ca0ad91-2fb5-4e64-9f6f-5498fa39d44b
+# ╟─a1b2c3d4-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204490
+# ╟─160fd7d9-a3c2-4f22-951e-deed6f32e09b
+# ╟─56b58c9f-f8ce-4117-8105-70083c23fde9
+# ╟─03d81d40-f285-47d6-bbf4-db3e8efc7bd1
+# ╟─a4b027e0-15e6-4097-acc9-358fb075fd7f
+# ╟─e93c6dc1-2f8d-4e2f-bbed-db926643f32a
+# ╟─3f7130a0-51d6-4493-b07e-e5bf178ce834
+# ╟─18207180-a40b-4bb7-87bb-9a0752286cea
+# ╟─4d6fd1e2-9457-4f4c-84b1-62958a8b49de
+# ╟─011a1e50-0316-42ec-9295-eeee64b76299
+# ╟─81952b3e-93c9-4179-8b12-5933d49749a6
+# ╟─a3b4c5d6-0894-4340-a18b-72f8e1204503
diff --git a/class15/class15.md b/class15/class15.md
index b42e350..d6b4761 100644
--- a/class15/class15.md
+++ b/class15/class15.md
@@ -6,5 +6,51 @@
---
-Add notes, links, and resources below.
+# Overview
+
+This chapter introduces the foundational dynamic behaviors of electric power systems and shows how they are incorporated into modern optimal control formulations such as Transient Stability–Constrained Optimal Power Flow (TSC-OPF). We begin with the physics of electromagnetic transients to motivate the formulation of TSC-OPF, move through generator and inverter dynamics, and conclude with dynamic load models that capture how demand responds during disturbances. Together, these components form the backbone required to understand, simulate, and optimize real-world power system behavior.
+
+# Materials
+
+The chapter is implemented as a [Pluto notebook](https://learningtooptimize.github.io/LearningToControlClass/dev/class15/class15.html), which contains derivations, visuals, and algorhtmic examples. The [lecture slide](https://learningtooptimize.github.io/LearningToControlClass/dev/class15/class15_lecture.pdf) contains the material of the video recording.
+
+# Topics Covered
+
+## Transients and Electromagnetic Dynamics
+- Physical origin of transients in power system
+- Connection between Faraday's law, inductors/capacitors, and transient behavior
+- Relation of time-domain differential equations to steady-state phasor models
+- Introduction to transmission-line dynamics and telegrapher’s equations
+
+## Generator Swing Equation
+- Rotor acceleration and deceleration under power imbalance
+- Role of inertia in stabilizing frequency
+- Per-unit formulation and damping effects
+
+## Inverter Dynamics and Grid Control
+- Differences between synchronous generators and renewable inverters
+- Grid-following vs. grid-forming behavior
+- Virtual inertia and frequency droop control for renewable integration
+
+## Dynamic Load Models
+- Limitations of static OPF load representations
+- Induction motor dynamics: slip, torque imbalance, and stalling behavior
+- Voltage recovery models such as Exponential Recovery Load (ERL)
+- Differences between physics-based motor models and empirical aggregate models
+
+## Transient Stability–Constrained Optimal Power Flow (TSC-OPF)
+- Time-domain constraints ensuring system stability during disturbances
+- Solution methods such as direct transcription and multiple-shooting formulations
+- Forward and adjoint sensitivity analysis for efficient gradient calculation
+
+# Learning Objectives
+
+By the end of this chapter, readers will be able to:
+
+- Describe the physical origins of transients and how they propagate in networks
+- Explain generator swing dynamics and how they regulate grid frequency
+- Understand how inverter controls emulate generator behavior for stability
+- Distinguish between static and dynamic load models and when each is appropriate
+- Interpret how system dynamics are embedded in TSC-OPF formulations
+- Understand the role of sensitivity analysis in dynamic optimal control
diff --git a/class15/class15.tex b/class15/class15.tex
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e5d81fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/class15/class15.tex
@@ -0,0 +1,1413 @@
+\documentclass[aspectratio=169]{beamer}
+\usetheme{CambridgeUS}
+\usecolortheme{dolphin}
+\setbeamertemplate{navigation symbols}{}
+\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
+\usepackage{hyperref}
+\usepackage{amsmath, amssymb}
+\usepackage{graphicx}
+\usepackage{booktabs}
+\title{Dynamic Optimal Control of Power Systems}
+\author{Shuaicheng Tong}
+\date{}
+
+\begin{document}
+
+\begin{frame}
+ \titlepage
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Outline}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Transients
+ \item Generator swing equations
+ \item Inverters
+ \item Dynamic Load Models
+ \end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% % --- Fuel-Powered Plants
+% \begin{frame}{What is Power System?}
+% \textbf{Fuel-Powered Plants}
+% \begin{columns}[T,onlytextwidth]
+% \column{0.5\textwidth}
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item Coal Power Plants
+% \item Natural Gas Plants
+% \item Nuclear Power Plants
+% \end{itemize}
+% \column{0.5\textwidth}
+% \begin{figure}
+% \centering
+% \includegraphics[width=0.8\textwidth]{images/gasPlant.jpeg}
+% \caption{Gas Power Plant}
+% \end{figure}
+% \end{columns}
+% \end{frame}
+
+% % --- Renewable Generation
+% \begin{frame}{What is Power System?}
+% \begin{columns}[T,onlytextwidth]
+% \column{0.5\textwidth}
+% \textbf{Renewable Generation}
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item Wind Farms
+% \item Solar Plants
+% \item Hydroelectric Plants
+% \end{itemize}
+% \column{0.5\textwidth}
+% \begin{figure}
+% \centering
+% \includegraphics[width=0.8\textwidth]{images/hydroPlant.jpg}
+% \caption{Hydroelectric Plant}
+% \end{figure}
+% \end{columns}
+% \end{frame}
+
+% % --- Warm-up
+% \begin{frame}{Warm-up Questions}
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item Classic problems in power system:
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item Optimization
+% \item Generator Dispatch
+% \end{itemize}
+% \item How they relate to control
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item Think general control that you see in your daily life for now: flipping a switch, pressing a button, etc.
+% \end{itemize}
+% \item What real-world problems are they trying to address
+% \item What problems they are \emph{not} addressing
+% \item What are the constraints? Which are soft and which are hard?
+% \end{itemize}
+% \end{frame}
+
+% --- 3 Bus Network – Economic Dispatch
+\begin{frame}{3 Bus Network -- Economic Dispatch}
+\begin{columns}[T,onlytextwidth]
+\column{0.5\textwidth}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Bus 1 load: 50 MW
+ \item Bus 3 load: 75 MW
+ \item Generator 1: Capacity 100 MW, Cost \$8/MW
+ \item Generator 2: Capacity 40 MW, Cost \$2/MW
+\end{itemize}
+\column{0.5\textwidth}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.9\textwidth]{images/3Bus.png}
+\caption{3-Bus Power System Network}
+\end{figure}
+\end{columns}
+\end{frame}
+
+% % --- Economic Dispatch Question
+% \begin{frame}{Economic Dispatch Question}
+% \begin{block}{Question}
+% What is the Economic Dispatch problem (in its most basic form)?
+% \end{block}
+% \begin{block}{Answer}
+% An optimization problem that aims to find the lowest-cost generation dispatch that satisfies the load demand given the load, generation, and cost.
+% \end{block}
+% \end{frame}
+
+% --- QP formulation of ED
+\begin{frame}{Quadratic Program (QP) formulation of ED}
+\begin{align}
+\min_{p_g} \quad & \sum_{g \in \mathcal{G}} C_g(p_g) \\
+\text{s.t.} \quad & \sum_{g \in \mathcal{G}} p_g = \sum_{d \in \mathcal{D}} P_d \quad \text{(power balance)} \\
+& p_g^{\min} \leq p_g \leq p_g^{\max} \quad \forall g \in \mathcal{G} \quad \text{(capacity bounds)}
+\end{align}
+
+where:
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $p_g$: power output of generator $g$
+ \item $C_g(p_g)$: cost function of generator $g$ (often quadratic: $a_g p_g^2 + b_g p_g + c_g$)
+ \item $P_d$: power demand at load $d$
+ \item $\mathcal{G}$: set of generators, $\mathcal{D}$: set of loads
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Exercise - formulate the ED problem for the 3-bus network
+\begin{frame}{Exercise: Formulate the ED problem for the 3-bus network}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.7\textwidth]{images/3Bus.png}
+\caption{3-Bus Power System Network}
+\end{figure}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- ED Formulation Answer
+\begin{frame}{ED Formulation Answer}
+\begin{align}
+\min_{p_1, p_2} \quad & 8p_1 + 2p_2 \\
+\text{s.t.} \quad & p_1 + p_2 = 125 \quad \text{(power balance)} \\
+& 0 \leq p_1 \leq 100 \quad \text{(Gen 1 limits)} \\
+& 0 \leq p_2 \leq 40 \quad \text{(Gen 2 limits)}
+\end{align}
+
+\textbf{Solution:} $p_1 = 85$ MW, $p_2 = 40$ MW
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Total cost: $8 \times 85 + 2 \times 40 = 760$ \$/hour
+ \item Gen 2 at maximum capacity (greedy)
+ \item Gen 1 supplies remaining demand
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Discussion Questions
+\begin{frame}{Discussion Questions}
+What do you observe from your formulation?
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item What kind of problem is this (linear, quadratic, etc.)?
+ \item The power network is a graph -- what type? What is missing here?
+ \item The flow is not controllable - we did not place branch constraints.
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- What's the Problem?
+\begin{frame}{What's the Problem?}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item The graph should be directed: power has flow directions
+ \item Line ratings and safety are ignored in ED
+ % \item I like to think about suspension bridges over rivers. Is it safe for hundreds of people to cross at the same time? Would it be safe for the concrete bridge on 5th street?
+ \item Overloading lines is dangerous (thermal expansion, sag, wildfire risk)
+ \item What is a power line:
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Metal coil that expands and heats up when current is higher.
+ \item That’s why we have rating (magnitude of power flow cannot exceed this amount). Physically you can exceed it (nothing is preventing the power to flow) a bit, but there are consequences above ...
+ \end{itemize}
+ \item We need branch (line) constraints to ensure safe operation
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- DC Power Flow
+\begin{frame}{DC Power Flow}
+\textbf{Data:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Generator set $\mathcal{G}_i$ at bus $i$ (nodal generation)
+ \item Load set $\mathcal{L}_i$ at bus $i$ (nodal load)
+ \item Costs $C_j(P_j)$ quadratic or piecewise-linear for generator $j$
+ \item Line limits $F_\ell^{\max}$, generator bounds $P_j^{\min}, P_j^{\max}$
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Decision variables:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Generator outputs $P_j$ for $j \in \mathcal{G}_i$
+ \item Bus angles $\theta_i$ for $i \in \mathcal{N}$
+ \item Line flows $f_\ell$ for $\ell \in \mathcal{L}$
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- DC Power Flow Formulation
+\begin{frame}{DC Power Flow Formulation}
+\begin{align}
+\min_{P_j, \theta} \quad & \sum_{i \in \mathcal{N}} \sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}_i} C_j(P_j) \\
+\text{s.t.} \quad & \sum_{j \in \mathcal{G}_i} P_j - \sum_{j \in \mathcal{L}_i} P_j = \sum_{k: (i,k) \in \mathcal{L}} \frac{1}{x_{ik}} (\theta_i - \theta_k) \quad \forall i \in \mathcal{N} \\
+& f_\ell = \frac{1}{x_\ell} (\theta_{i(\ell)} - \theta_{j(\ell)}), \quad -F_\ell^{\max} \leq f_\ell \leq F_\ell^{\max} \quad \forall \ell \in \mathcal{L} \\
+& P_j^{\min} \leq P_j \leq P_j^{\max} \quad \forall j \in \mathcal{G}_i, \forall i \in \mathcal{N} \\
+& \theta_{\text{ref}} = 0
+\end{align}
+
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $x_{ij}$: reactance of line. $1/x_{ij} = b_{ij}$: susceptance (manufacturer specified)
+ \item Reference bus: only for modeling, you can pick any bus as the reference bus. We only care about angle differences (which carries current through lines
+ \item Individual bus angle has no physical meaning
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Exercise: solve DCOPF after ED
+\begin{frame}{Exercise: Solve DCOPF (solver suggested: Ipopt)}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.7\textwidth]{images/3BusWConstraints.png}
+\caption{3-Bus Network with Constraints}
+\end{figure}
+
+\textbf{How did I get the numbers:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Assume P1 generates 85 MW, with 50 MW of load, the net injection is 35 MW
+ \item Assume P2 generates 40 MW, with no load, net injection is 40 MW (we take upwards arrow as injection)
+ \item Bus 3 has no gen, only load
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- DCOPF Solution
+\begin{frame}{DCOPF Solution}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.3\textwidth]{images/DCOPFAnswer1.png}
+\caption{DCOPF Solution Results}
+\end{figure}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- DCOPF Solution Details
+\begin{frame}{DCOPF Solution Details}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.5\textwidth]{images/DCOPFAnswer2.jpeg}
+\caption{DCOPF Detailed Analysis}
+\end{figure}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Wrap up
+\begin{frame}{Wrap Up}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item You will see that without thermal limits, optimal dispatch can overload lines
+ % \item In operation, operators typically solve a DCOPF (e.g., with Ipopt solver)
+ \item Reference bus is arbitrarily picked by the solver.
+ \item Real systems are AC (complex voltages/currents) -- much harder. This is just a lightweight intro so we can think about expressing real-world problems as optimization formulations without overburdening ourselves with AC physics, which we will see in transient stability section.
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Introduction to Transient Stability}
+\begin{center}
+\Huge
+Transient Dynamics
+\end{center}
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{What are transients?}
+When current or voltage changes suddenly — switching, faults, lightning, equipment failures, etc. — the system experiences a \textbf{transient}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Transients are short-lived, high-frequency events where stored magnetic and electric energy exchange rapidly.
+ \item \textbf{Faraday’s law} of electromagnetic induction governs these effects:\\[4pt]
+ A change in magnetic flux through a circuit induces a voltage across it.
+ \begin{align*}
+ v(t) &= \frac{d\Phi(t)}{dt}
+ \end{align*}
+ where $\Phi(t)$ is the magnetic flux through the circuit.
+\end{itemize}
+
+
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Transients Continued}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item For an inductor, the magnetic flux $\Phi$ is proportional to the current:
+ \begin{align*}
+ \Phi(t) &= L\,i(t)
+ \end{align*}
+ where $L$ is the inductance (magnetic energy stored per unit current).
+ \item Substituting gives the familiar time-domain voltage rule:
+ \begin{align*}
+ \boxed{v_L(t) = L\,\frac{di(t)}{dt}}
+ \end{align*}
+\end{itemize}
+Note that steady-state phasor analysis no longer holds due to the time-varying nature of the magnetic flux. I will draw the connection later.
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Sinusoidal steady state}
+ Assume all quantities have angular frequency $\omega$:
+ \begin{align*}
+ i(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ I\,e^{j\omega t} \right\}, \\
+ % v_L(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ V\,e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+ \end{align*}
+ Differentiate the current:
+ \begin{align*}
+ \frac{di(t)}{dt} &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ j\omega I\, e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+ \end{align*}
+
+ Substitute into $v_L(t) = L\,\frac{di}{dt}$:
+ \begin{align*}
+ v_L(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ (j\omega L I)\, e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+ \end{align*}
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Phasor (frequency-domain) relation}
+ By definition, the \textbf{phasor} is the complex amplitude multiplying $e^{j\omega t}$.
+
+ From the previous expression,
+ \begin{align*}
+ v_L(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ (j\omega L I)\, e^{j\omega t} \right\},
+ \end{align*}
+ so the \textbf{voltage phasor} is
+ \begin{align*}
+ \boxed{V = j\omega L\, I}.
+ \end{align*}
+
+ % Thus the inductor's impedance is
+ % \begin{align*}
+ % \boxed{Z_L = \frac{V}{I} = j\omega L}.
+ % \end{align*}
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Capacitor law: from time domain to phasor domain}
+ \textbf{Physical basis:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item A capacitor stores energy in an \textbf{electric field}.The stored charge $q(t)$ is proportional to voltage:
+ \begin{align*}
+ q(t) &= C\,v(t)
+ \end{align*}
+ where $C$ is the capacitance.
+ \item The current is the rate of change of charge:
+ \begin{align*}
+ \boxed{i_C(t) = \frac{dq(t)}{dt} = C\,\frac{dv(t)}{dt}}.
+ \end{align*}
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Under sinusoidal steady state:}
+ \begin{align*}
+ v(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ V e^{j\omega t} \right\}
+ \end{align*}
+ where $V$ is the voltage phasor.
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Capacitor law: from time domain to phasor domain}
+ \begin{align*}
+ \frac{dv(t)}{dt} &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ j\omega V e^{j\omega t} \right\}, \\
+ i_C(t) &= \operatorname{Re}\!\left\{ (j\omega C V) e^{j\omega t} \right\}.
+ \end{align*}
+
+ Hence, the \textbf{phasor relationship} is:
+ \begin{align*}
+ \boxed{I = j\omega C\,V}, \qquad
+ \boxed{Y_C = j\omega C}, \qquad
+ \boxed{Z_C = \frac{1}{j\omega C}}.
+ \end{align*}
+You could of course derive admittance and impedance for inductors following similar steps. This is how you go from time domain to phasor domain. Note that the above is for ideal inductors and capacitors.
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{More realistic transmission line model}
+ The voltage $v(x,t)$ and current $i(x,t)$ vary \textbf{both} in time and along the line coordinate $x$.
+ Their spatial derivatives represent how these quantities change \textbf{per unit length:}
+ \begin{align*}
+ \frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} &\;\Rightarrow\; \text{voltage drop per unit length (V/m)}, \\
+ \frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial x} &\;\Rightarrow\; \text{current change per unit length (A/m)}.
+ \end{align*}
+ \textbf{Real lines are lossy:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Conductor series resistance causes Ohmic losses (heat dissipation) $\Rightarrow$ add $-R'\,i(x,t)$.
+ \item Current leakage due to shunt conductance $\Rightarrow$ add $-G'\,v(x,t)$.
+ \end{itemize}
+ \vspace{0.2cm}
+ Hence, the full \textbf{telegrapher's equations} become:
+ % \begin{align*}
+ % \frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} &= -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t} - R'\,i(x,t),\\
+ % \end{align*}
+ \end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{More on realistic transmission line model}
+ \begin{align*}
+ \frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} &= -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t} - R'\,i(x,t),\\
+ \frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial x} &= -C'\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial t} - G'\,v(x,t).
+ \end{align*}
+ You can think about $R'$ and $G'$ as damping terms. $L$ and $C$ relate to energy storage, and $R$ and $G$ relate to energy dissipation.
+
+ % The minus sign is because we take the forward direction as positive for $x$, while voltage and current drop in the same direction (they diminish due to energy storage or loss).
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{How the above was derived}
+
+ \textbf{Setup:} Consider a small transmission line segment between $x$ and $x+dx$.
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $x$ increases in the direction of current flow ($+x$).
+ \item $i(x,t)$: current flowing in $+x$ direction.
+ \item $v(x,t)$: voltage between conductors (top to bottom) at position $x$.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{1. Voltage change between segment ends:}
+ \[
+ v(x,t) - v(x+dx,t) = -\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x}\,dx.
+ \]
+
+ \textbf{2. Series drops over $dx$:}
+ \begin{align*}
+ \text{Resistive drop} &:\; R'\,i(x,t)\,dx,\\
+ \text{Inductive drop} &:\; L'\,\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t}\,dx.
+ \end{align*}
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{How the above was derived}
+ \textbf{3. Apply Kichhoff Voltage Law:}\\[2pt]
+ (The sum of voltage drops along the closed path must equal zero.)
+ \[
+ (R'\,i + L'\tfrac{\partial i}{\partial t})\,dx + \big[v(x+dx,t) - v(x,t)\big] = 0.
+ \]
+
+ \textbf{4. Substitute and simplify:}
+ \[
+ \frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x}\,dx = -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t}\,dx - R'\,i(x,t)\,dx.
+ \]
+
+ \textbf{5. Divide by $dx$:}
+ \[
+ \boxed{\frac{\partial v(x,t)}{\partial x} = -L'\frac{\partial i(x,t)}{\partial t} - R'i(x,t)}.
+ \]
+
+ \small The negative sign indicates that voltage \emph{drops} in the $+x$ direction
+ due to both inductive ($L'\,\partial i/\partial t$) and resistive ($R'i$) effects.
+\end{frame}
+
+
+\begin{frame}{How does physics relate to optimization?}
+ \LARGE
+ Transient Stability Constrained Optimal Power Flow (TSCOPF)
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{TSCOPF formulation}
+ \begin{align*}
+ \min_{p,\,x(t),\,y(t)} \quad & C(p) && \text{(1)}\\
+ \text{s.t.}\quad
+ & g_s(p) = 0 && \text{(2)}\\
+ & h_s^{-} \le h_s(p) \le h_s^{+} && \text{(3)}\\
+ & p^{-} \le p \le p^{+} && \text{(4)}\\[3pt]
+ & \dot{x} = f(x,y,p), \quad x(t_0)=I_x^0(p) && \text{(5)}\\
+ & 0 = g(x,y,p), \quad y(t_0)=I_y^0(p) && \text{(6)}\\
+ & h(x(t),y(t)) \le 0, \quad \forall t && \text{(7)}
+ \end{align*}
+
+ \textbf{Objective:} minimize operating cost or transmission losses. (2) includes steady-state nodal power balance constraints. (3) includes apparent/real power/reactive power/current flow constraints on lines. (4) includes generator capacity or voltage magnitude constraints.
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Dynamic Transient Constraints: (5)--(7)}
+ % \[
+ % \dot{x} = f(x, y, p), \qquad x(t_0) = I_x^0(p)
+ % \]
+ Eq. (5):
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $x$: state variables (rotor angles, speeds, control states). Initial states computed from steady-state solution corresponding to control variables $p$.
+ \item $f(x,y,p)$: system dynamics — e.g., generator swing equations, Telegrapher equations, or capacitor/inductor transient models.
+ \item $y$: dependent variables (nodal voltages magnitude and angle, line currents, etc.).
+ \item $p$: control variables (generator setpoints, tap settings, shunt positions, etc.)
+ \item Enforce the physics of transient after a disturbance.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ % \[
+ % 0 = g(x, y, p), \qquad y(t_0) = I_y^0(p)
+ % \]
+ Eq. (6): embed dynamics into steady-state constraints.
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $g(x,y,p)$: Same physical laws as (2) e.g. KCL but now applied at every instant $t$'s states $x(t), y(t)$ to extend to the dynamics.
+ % \item $h(x(t),y(t)) \le 0$: Operational constraints need to be respected for the entire trajectory $x(t), y(t)$.
+ \end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Dynamic and Transient Constraints: (7)}
+
+ \textbf{(7) Transient limits:}
+ \[
+ h(x(t), y(t)) \le 0, \quad \forall t
+ \]
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Enforce time-domain operating limits during the transient response.
+ \item Examples:
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Bus voltage magnitudes stay within limits.
+ \item Rotor angle differences remain stable.
+ \item Line thermal limits respected.
+ \end{itemize}
+ \item Ensures \textbf{transient stability} under all time steps during instability.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Solution Methods for TSC-OPF}
+
+ \textbf{Indirect (variational) Methods:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Based on Pontryagin's Maximum Principle.
+ \item Replace the differential equations of dynamics with inequalities that approximate the behavior in steady-state by linearizing into static conditions.
+ \item Examples: energy or Lyapunov functions or impose stability margin constraints on linearized Jacobian.
+ \end{itemize}
+ Instead of having to integrate over time, you get back a static nonlinear optimization problem that can be solved using standard solvers.
+ \textbf{In practice:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Mainly used for planning/screening/preventive security dispatch due to loss in accuracy.
+ \item Not sufficient to guarantee transient stability under large disturbances.
+ \item Validation still relies on time-domain (direct) simulation.
+ \end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Direct Method: Simultaneous Discretization/Constraint Transcription}
+
+ \textbf{Main idea:} Converts the time-dependent diff. eq. into a finite set of algebraic constraints before optimization so transient stabilitysimulator can be reused.
+
+ \textbf{Discretization approach:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item The simulation horizon is divided into multiple time steps $t_0, t_1, \dots, t_N$.
+ \item The diff. eq. is approximated at each step using numerical integration like implicit trapezoidal rule:
+ \[
+ x(t) - \frac{\Delta t}{2} f(x(t), y(t), p)
+ - x(t-\Delta t)
+ - \frac{\Delta t}{2} f(x(t-\Delta t), y(t-\Delta t), p) = 0.
+ \]
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Pros and Cons:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Produces one large-scale NLP that enforces the dynamics exactly for the entire trajectory (within discretization accuracy).
+ \item Computationally demanding due to the high dimensionality of variables and constraints from discretization. Accurate gradients is expensive from trajectory sensitivivity analysis. Hessians often approximated using BFGS updates.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Direct Method: Multiple Shooting}
+ The multiple shooting method divides the simulation horizon into smaller time segments
+ $\,[t_0,t_1], [t_1,t_2], \dots, [t_{N-1},t_N]$.
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Each segment starts from its own initial condition
+ $x_i(t_i)$ and is integrated forward using the diff. eq.
+ $\dot{x}=f(x,y,p),\, 0=g(x,y,p)$
+ to obtain the predicted final state $\hat{x}_i(t_{i+1})$.
+ \item Constraint to ensure continuity between segments:
+ \[
+ x_{i+1}(t_{i+1}) = \hat{x}_i(t_{i+1}),
+ \]
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Constraint form:}
+ \[
+ s_i = S_i(s_{i-1},p), \quad \forall i \in 1,\dots,N_S,
+ \]
+ where $S_i(\cdot)$ is an implicit function that can be numerically integrated over segment $i$. \\
+ Pros: Each segment can be integrated independently, so the Jacobian of the resulting NLP is better conditioned because the coupling is limited to adjacent segments instead of the entire trajectory. This segmentation improves numerical stability and allows for more efficient large-scale computation.
+
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Trajectory Sensitivity Analysis of TSC-OPF}
+
+ \textbf{Purpose:} Quantify how system variables $x(t),y(t)$ changes with respect to small variations in control variables $p$ or intial conditions. Recall that with different control settings $p$, the entire transient trajectory changes and we would need to simulate the dynamics again to see what happens. This is expensive. Sensitivity analysis tells you how the trajectory and stability margins change with small changes in $p: \frac{\partial x}{\partial p}$ without running a new full simulation for every small perturbation.
+
+ \textbf{Relation to numerical methods:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item These sensitivities provide gradient information for solvers, which is used for both multiple shooting and constraint transcription.
+ % \item Complement the direct methods (discretization, shooting) by enabling efficient gradient-based updates of $p$.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Forward Sensitivity Method}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Computed by performing a forward integration of the sensitivity equations alongside the original diff. eq. system.
+ \item Efficient when the number of parameters is small.
+ \item The computational complexity is $\mathcal{O}(n_p)$, since $n_p$ forward integrations are required to compute the sensitivities.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Formulation:}
+ For the original diff. eq. system:
+ \[
+ F(\dot{x}(t),\, x(t),\, p) = 0.
+ \]
+ The corresponding variational diff. eq. for the sensitivities is:
+ \[
+ \frac{\partial F}{\partial \dot{x}}\,\dot{s}
+ + \frac{\partial F}{\partial x}\,s
+ + \frac{\partial F}{\partial p} = 0,
+ \]
+ with initial condition
+ \[
+ s(t_0) = \frac{\partial x(t_0)}{\partial p}.
+ \]
+
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Forward Sensitivity Method}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Each parameter $p_i$ perturbs the system differently.
+ \item Forward method tracks this by integrating a new "copy" of the linearized system, which shares the same Jacobian as the original DAE.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Pros and cons:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item \textbf{Pros:} Simple and accurate, efficient when number of parameters is small.
+ \item \textbf{Cons:} Computational cost grows linearly with number of parameters.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Adjoint Method}
+ Efficient when the number of parameters is large. This only needs one backward integration in time to compute the sensitivities.
+ Formulation:
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Consider \[
+ G(p) = \int_{t_0}^{T} g(x, p)\,dt.
+ \]
+ \item We want the gradient given by:
+ \[
+ \frac{\partial G}{\partial p}
+ =
+ \int_{t_0}^{T}
+ \left(
+ \frac{\partial g}{\partial p}
+ - \lambda^{\mathsf{T}} \frac{\partial F}{\partial p}
+ \right) dt,
+ \]
+ \item The adjoint multiplier $\lambda(t)$ satisfies
+ \[
+ \dot{\lambda}
+ =
+ -\,\frac{\partial g}{\partial x}
+ + \lambda^{\mathsf{T}}\frac{\partial F}{\partial x}.
+ \]
+ where $\lambda(T)=0$.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Adjoint Method and wrapping up}
+ \textbf{Pros:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Efficient when the number of parameters is large.
+ \item The gradient is obtained in one pass.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Cons:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Higher memory cost due to storage of trajectory data and state variables in backward integration.
+ \end{itemize}
+ One can also obtain the gradients by finite differences, which is based on truncated Taylor series expansion.
+
+ \end{frame}
+
+
+
+
+% --- Power System History and Modern Power System
+\begin{frame}{Power System History and Modern Power System}
+\begin{block}{The Fuel Era (20th Century)}
+Electricity produced mostly by coal, gas, nuclear. Generators are large synchronous machines with big spinning masses. Stable and predictable. Inertia from these machines naturally provides flexibility infrequency stability. Grid ran reliably for decades.
+\end{block}
+\begin{block}{The Renewable Era (2000s--Today)}
+Wind expanded in 2000s, solar PV took off after 2010. Renewables now 20--40\%+ of real-time demand in some regions; dynamics changed.
+\end{block}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Synchronous Generators: How electricity is generated
+\begin{frame}{Synchronous Generators: How electricity is generated}
+\begin{columns}[T,onlytextwidth]
+\column{0.5\textwidth}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Rotor (heavy spinning mass) driven by turbines (steam, gas, hydro)
+ \item Faraday's law: changing magnetic field induces voltage in stator
+ \item Called "synchronous" because the rotor spins in sync with the grid's frequency (50 Hz in Europe, 60 Hz in North America)
+ \item If the grid frequency is 60 Hz, the rotor turns at a speed locked to 60 Hz
+\end{itemize}
+\column{0.5\textwidth}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.9\textwidth]{images/syncgen.png}
+\caption{Generator Cross-Section}
+\end{figure}
+\end{columns}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Spinning Mass in a Generator
+\begin{frame}{Spinning Mass in a Generator}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Inside a synchronous generator is a rotor — basically a giant heavy wheel of steel and copper (tens or hundreds of tons)
+ \item Turbines (steam from coal/nuclear, gas combustion, or flowing water in hydro) push on the rotor to make it spin
+ \item That rotor's mechanical rotation creates a rotating magnetic field, according to Faraday's law of induction, a changing magnetic field induces an alternating voltage in the stator windings
+ \item This is why the system is predictable: we know how to control these rotors. Put in more fuel to generate more power
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Generator Frequency Formula
+\begin{frame}{Generator Frequency Formula}
+\textbf{Frequency Formula:}
+\begin{align}
+f = \frac{N \times \text{RPM}}{120}
+\end{align}
+where $N$ = number of poles, RPM = rotor speed
+
+\textbf{Examples:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item 2 poles, 3600 RPM → 60 Hz
+ \item 4 poles, 1800 RPM → 60 Hz
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Why 50/60 Hz?} Historical choices: early engineers (Westinghouse, Edison, etc.) picked values that balanced motor performance and generator design. Once infrastructure was built, it became a standard.
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Kinetic Energy
+\begin{frame}{Kinetic Energy}
+\textbf{The rotor has stored kinetic energy:}
+\begin{align}
+E_{\text{kinetic}} = \frac{1}{2} J \omega^2
+\end{align}
+where $J$ = moment of inertia (depends on mass + geometry), $\omega$ = rotor speed
+
+\textbf{If demand suddenly exceeds supply (a generator trips):}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item That small slow down of a rotor releases some of its stored kinetic energy into the grid instantly
+ \item But because there are so many large spinning machines, the grid behaves like a conveyor belt with so many wheels tied together. If one slows a bit, the others share the imbalance, so frequency changes slowly because the system has a huge inertia
+ \item This gives time for operators to fix things
+ \item Even if there are imbalances, things wouldn't get out of hand fast since there are so many other generators. They can share the load so each only needs to spin a little faster to keep up the frequency
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Renewables and Inverters
+\begin{frame}{Inverters - Renewables}
+\textbf{Today, renewables can supply 20–40\%+ of real-time demand.}
+Cleaner, cheaper, more sustainable — but dynamics changed.
+
+Most renewables (solar PV, modern wind turbines, batteries) produce DC electricity (direct current).
+
+\textbf{What's the problem of DC power?}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item It only has amplitude (magnitude of voltage/current)
+ \item No phase, no frequency
+ \item But recall AC current has the waveform (that's why we have leading/lagging current which controls reactive power and power factor correction)
+ \item We need amplitude, frequency, and phase to describe AC current
+ \item That's why we need inverters, power electronics device that synthesizes sinusoidal AC from DC
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Inverter Operation (continued)
+\begin{frame}{Inverter Operation}
+\textbf{How it operates?}
+\begin{enumerate}
+ \item Takes DC input from solar panels, wind turbine
+ \item Use power electronics that switches thousands of time per second to synthesize an AC waveform
+ \item Note that even the output is a smooth sinusoidal AC waveform, inside the inverter the switches turn the DC voltage on and off thousands of times per second (typical switching frequency = 2–20 kHz, sometimes higher) to approximate that smooth waveform
+ \item So even though the output is continuous, it's created by on/off pulses internally
+ \item The inverter synchronizes the AC output to the grid's frequency and phase. If grid is 60 Hz → inverter outputs 60 Hz. If grid is 59.9 Hz (after a disturbance) → inverter follows 59.9 Hz.
+ \item The voltage, current, and power factor are controlled through the programmed algorithms
+\end{enumerate}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Inverter Control Modes
+\begin{frame}{Inverter Control Modes}
+\textbf{In summary, the inverters are programmable devices by operators with control algorithms to act like generators. They wait for a signal from a grid so they can be:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item \textbf{Grid-following}: track the grid's voltage and frequency → inject current accordingly
+ \item \textbf{Grid-forming}: behave like a voltage source, set their own frequency/voltage reference, and to adjust for power imbalance (some research area I heard of)
+\end{itemize}
+
+They are not really generators - no spinning mass, no inertia, but they use control algorithms to mimic generator behavior.
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Internal view of inverters (placeholder)
+\begin{frame}{Internal View of Inverters}
+\begin{figure}
+\centering
+\includegraphics[width=0.3\textwidth]{images/inverter.jpg}
+\caption{Internal View of Inverter}
+\end{figure}
+
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Capacitors and switching components on electronic mainboards (like in computer's motherboard, blue cylinders in upper left corner of the picture)
+ \item Programmable behavior defined by control firmware
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Problems with inverters
+\begin{frame}{Problems with Inverters}
+\textbf{This is all software-based. You do not have a natural physical property like a spinning rotor and inertia.}
+
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item No big spinning mass directly tied to frequency, so frequency changes much faster after a disturbance
+ \item The device measures grid signal and forces its output to follow
+ \item Unless explicitly programmed, they don't know when the conveyor belt slows down or speeds up (recall the previous analogy)
+ \item Even if they do, they don't have the capacity like big generators
+ \item \textbf{This is the key part:} they are just switching circuits with no agency to ramp up the power output (nature of renewables is their output is often independent of human control). Output is limited by weather and energy availability (sun/wind).
+ \item Renewables also locate in remote areas with long transmission lines, and the nature of their unpredictability (weather), makes their generation highly uncertain
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{We will build up to inverter control after we cover the generator swing equations.}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Generator Swing Equations
+\begin{frame}{Newton's Second Law}
+\textbf{Linear Version:}
+\begin{align}
+F = ma
+\end{align}
+where $F$ = force (N), $m$ = mass (kg), $a$ = acceleration (m/s²)
+
+This says: imbalance of forces → acceleration of mass.
+
+\textbf{Rotational Version:}
+For a rotating body (like a generator rotor), the equation is:
+\begin{align}
+T = J\alpha
+\end{align}
+where $T$ = torque (N·m), $J$ = moment of inertia (kg·m²), the rotational mass. $\alpha$ = angular acceleration (rad/s²)
+
+This says: imbalance of torques → rotor accelerates or decelerates.
+Think torque as the angular equivalent of force.
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Applied to Generator Dynamics
+\begin{frame}{Applied to Generator Dynamics}
+\textbf{Two main torques act on a synchronous generator's rotor:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $T_m$: mechanical torque from the turbine (steam, gas, water) pushing the rotor
+ \item $T_e$: electromagnetic torque from the stator's magnetic field resisting the rotor (this is the grid "pulling" power out)
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Torque imbalance:}
+\begin{align}
+J\alpha = T_m - T_e
+\end{align}
+where $\omega$: angular speed of rotor (rad/s), $\alpha = \dot{\omega}$: angular acceleration (rad/s²)
+
+\textbf{If $T_m > T_e$:} rotor accelerates
+
+\textbf{If $T_m < T_e$:} rotor slows down
+
+\textbf{If equal:} steady rotation
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- From Torque to Power
+\begin{frame}{From Torque to Power}
+Recall $P = Fv$ (mechanical power is generated by a force $F$ on a body moving at a velocity $v$). In rotational systems, power is related by torque and angular speed (you can think about it as rotational equivalent as force)
+
+\textbf{Power = torque × speed:}
+\begin{align}
+P = T \cdot \omega
+\end{align}
+
+So:
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Mechanical power input: $P_m = T_m \cdot \omega$
+ \item Electrical power output: $P_e = T_e \cdot \omega$
+\end{itemize}
+
+Multiply the torque balance by $\omega$:
+\begin{align}
+J\omega\dot{\omega} = P_m - P_e
+\end{align}
+
+This relates how fast the mass is spinning ($\omega$) to the imbalance of power input (generation) and power withdrawal (load + losses).
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- From Torque to Power (Continued)
+\begin{frame}{From Torque to Power (Continued)}
+But recall that generators operate close to system frequency, so the generators spin at, i.e. the angular velocity is close to that 60 Hz constant. Since the variations are mostly tiny, we can define inertia constant $M = J\omega$
+
+And we get the generator swing equation:
+\begin{align}
+M\dot{\omega} = P_m - P_e
+\end{align}
+
+\textbf{Interpretation:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $M$: inertia constant, measures how much the rotor resists speed change (bigger mass → slower frequency drift)
+ \item $P_m$: mechanical input power (from fuel, water, steam)
+ \item $P_e$: electrical output power delivered to the grid
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Per-Unit Generator Swing Equation
+\begin{frame}{Per-Unit Generator Swing Equation}
+\textbf{Per-unit versions:}
+Power are often defined at per unit, so we have:
+\begin{align}
+\frac{J\omega_s}{S_{\text{base}}} \dot{\omega} = (P_m - P_e)_{\text{pu}}
+\end{align}
+
+There are sources that define $H = \frac{1}{2}\frac{J\omega_s^2}{S_{\text{base}}} \Rightarrow \frac{2H}{\omega_s} = \frac{J\omega_s}{S_{\text{base}}}$
+
+$H \triangleq \frac{E_k}{S_{\text{base}}} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}J\omega_s^2}{S_{\text{base}}}$ comes from kinetic energy
+
+\vspace{0.5cm}
+So we have per unit swing:
+\begin{align}
+\frac{2H}{\omega_s} \dot{\omega} = (P_m - P_e)_{\text{pu}}
+\end{align}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Damping and Advanced Forms
+\begin{frame}{Damping and Advanced Forms}
+Some also add damping:
+\begin{align}
+M\dot{\omega} + D(\omega - \omega_s) = P_m - P_e
+\end{align}
+as penalties to frequency deviation. $D$ captures any restoring force, or frictions and losses
+
+We can also write the per-unit acceleration form:
+\begin{align}
+2H \dot{\omega}_{\text{pu}} = (P_m - P_e)_{\text{pu}}
+\end{align}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Why this matters
+\begin{frame}{Why This Matters}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item Stability depends on balancing generation and demand
+ \item Inertia slows down changes in frequency, buying time for control actions
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Power imbalance effects:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item If $P_m > P_e$: extra power → rotor speeds up → frequency rises
+ \item If $P_m < P_e$: shortage → rotor slows → frequency falls
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Inertia $M$ slows down how fast this happens.}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item With many generators, $M$ is big. For a given imbalance, frequency drifts slowly → grid is flexible
+ \item With fewer machines (more renewables), $M$ is smaller → frequency changes faster → grid is fragile
+\end{itemize}
+
+This is shown by writing the equation as $\dot{\omega} = \frac{P_m - P_e}{M}$. For a big $M$, the angular acceleration (frequency) is smaller when there is an imbalance.
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- How does it relate to Inverters
+\begin{frame}{How Does It Relate to Inverters?}
+We previously discussed grid-following inverters.
+
+\textbf{Its control law works as:}
+\begin{enumerate}
+ \item Measure voltage and frequency of the grid
+ \item Gets desired power output from an operator or solved from a market
+ \item Adjust its AC current output to deliver the desired power output at voltage and frequency GIVEN by the grid
+\end{enumerate}
+
+\textbf{What's the problem with it?} No control over other parameters like voltage and frequency. The power output is only stable if the rest of the grid is stable.
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Grid-forming Inverters
+\begin{frame}{Grid-forming Inverters}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item The inverter doesn't blindly follow the grid frequency, it defines its own reference voltage and frequency like a voltage source
+ \item Let the frequency shift slightly to reflect power imbalance between the renewable generation and the rest of the grid, so other machines (generators) know to ramp up or down
+ \item Able to define its own frequency is the key for the renewable to behave like a synchronous generator, and we now have the ability to model it in a swing equation by giving it a virtual mass defined by the local frequency
+\end{itemize}
+
+We can now emulate synchronous machine behavior via controlling the ``virtual inertia''.
+
+\textbf{Reference:} J. Driesen and K. Visscher, "Virtual synchronous generators," 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting - Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2008, pp. 1-3.
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Grid-Forming Response to Disturbances
+% \begin{frame}{Grid-Forming Response to Disturbances}
+% \textbf{If the system is disturbed (load spike, generator trip):}
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item The inverter does not instantly follow the dip like a grid-follower
+% \item It adjusts frequency slightly in proportion to imbalance, so it behaves as it has inertia
+% \item This stabilizes the grid frequency, slowing the drop
+% \end{itemize}
+
+% \textbf{If the inverter alone can't cover the imbalance:}
+% \begin{itemize}
+% \item Its frequency will drift a bit away from 60 Hz
+% \item That frequency deviation is a \emph{signal} to other generators or grid-forming inverters to pick up more power
+% \item This is exactly how synchronous generators share load via droop control
+% \end{itemize}
+% \end{frame}
+
+% --- Virtual Inertia Law
+\begin{frame}{Virtual Inertia Law in Grid-Forming Inverter}
+\textbf{Physics is replaced by software:}
+\begin{align}
+M_{\text{virtual}} \dot{\omega} = P_{\text{ref}} - P
+\end{align}
+
+\textbf{Parameters:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $M_{\text{virtual}}$: a tunable parameter by the controller, chosen to represent how fast the inverter responds to frequency changes
+ \item Recall $M = J\omega$. Since we have no physical inertia $J$, the virtual mass is just a modeling choice
+ \item $P_{\text{ref}}$: reference active power dispatch (from operator)
+ \item $P$: measured actual active power delivered
+ \item $\omega$: inverter's internal frequency reference value
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Effect of $M_{\text{virtual}}$:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item A larger $M_{\text{virtual}}$ means the inverter allows its frequency to drift slower, a "heavier" machine
+ \item A smaller $M_{\text{virtual}}$ means the inverter reacts more quickly, a "lighter" machine
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Virtual Inertia (continued)
+\begin{frame}{Virtual Inertia (continued)}
+\textbf{How it works:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item The inverter adjusts its internal frequency reference according to power imbalance
+ \item That frequency reference drives its voltage output, which the grid "sees"
+ \item To the rest of the system, this looks just like a synchronous machine rotor slowing/speeding under imbalance
+\end{itemize}
+
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item There's no heavy rotor. It emulates the inertia behavior of synchronous machines through software control.
+ \item But this is not sustained. It can only hold it until the renewable saturates, which is less than a second since they don't have as much buffer as traditional generators.
+ \item Other problems: semiconductor ratings, thermal limits, hard to tune $M_{\text{virtual}}$, cost, legacy devices, etc.
+\end{itemize}
+
+\textbf{Why this is such a big deal:} renewables can now respond to a grid-wide drop in frequency because it can behave almost like a synchronous generator through control law
+\end{frame}
+
+% --- Droop Control
+\begin{frame}{Grid-following inverters - Droop Control}
+Generators naturally slow down if overloaded, resulting in a drop in frequency (droop). Droop control allows each generator to increase its power output in response, but in proportion to its droop coefficient, so that all generators share the load change fairly.
+
+Grid-forming inverters are programmed with droop control:
+
+\begin{align}
+P = P_{\text{set}} - \frac{1}{K_p} (\omega - \omega_0)
+\end{align}
+where $\omega_0$: nominal frequency, $P_{\text{set}}$: reference power output, $K_p$: droop constant (rad/s per MW or Hz per MW) telling inverter how much to adjust power output when frequency changes. Hence when frequency drops, power will rise.
+
+Overload leads to frequency drop, and power will rise according to the relationship. If frequency rises, power will decrease to maintain the frequency.
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Reactive Power and Voltage Control (Q-V Droop)}
+% \textbf{Reactive Power – Voltage (Q–V Droop)}
+
+Analogous for voltage support:
+\begin{align}
+V = V_0 - K_q (Q - Q_{\text{set}})
+\end{align}
+or
+\begin{align}
+Q = Q_{\text{set}} - \frac{1}{K_q} (V - V_0)
+\end{align}
+
+If reactive demand $\uparrow$ (voltage dips), generator/inverter increases reactive power injection.
+
+\textbf{Two important components of stability:} frequency and voltage. If there are deviations, adjust active and reactive power accordingly
+
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $1/K_p$ = MW per Hz: "How much active power do I add if frequency drops by 0.1 Hz?"
+ \item $1/K_q$ = Mvar per V → "How much reactive power do I add if voltage drops by 0.01 pu?"
+ % \item $K_p$ and $1/K_p$ both are the frequency-power slope, just in different units. Larger slope means more correction
+\end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Dynamic Load Models}
+ \Large
+ Dynamic Load Models
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Steady-State Load Models in ACOPF/DCOPF}
+ In optimal power flow (OPF), all quantities are \emph{time-invariant}. $\dot{x} = 0, t$ does not appear.
+
+ At each load bus:
+ \[
+ P_D = \text{fixed real power demand}, \qquad
+ Q_D = \text{fixed reactive demand}.
+ \]
+
+ These loads can be either:
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Constant power: $P_D, Q_D$ are specified numerical values; or
+ \item Voltage-dependent (ZIP) as motors draw different amount current to maintain torque:
+ \[
+ P(V) = P_0 (a_P V^2 + b_P V + c_P), \quad
+ Q(V) = Q_0 (a_Q V^2 + b_Q V + c_Q).
+ \]
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ Power-flow balance:
+ \[
+ P_G - P_D = \text{network losses}, \qquad
+ Q_G - Q_D = 0.
+ \]
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Steady-State Load Models Continued}
+ Interpretation of the above model:
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Loads are fixed regardless of system conditions, or at most respond to nodal voltage.
+ \item No memory or dynamics -- they change only between static operating points.
+ \item The OPF represents a single equilibrium snapshot of the system.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Next:} Dynamic models generalize this by letting $P_D$ and $Q_D$
+ \emph{evolve over time} with voltage and frequency. The grid's sink can be dynamic too even though we tend to think about it as a fixed parameter.
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Dynamic Load Models - Induction Motor Model}
+ In dynamic models, the active and reactive power is represented as a function of the past and present voltage magnitude and frequency of the load bus. This type of model is commonly derived from the equivalent circuit of an induction motor.
+
+ Most real-world loads (fans, pumps, compressors) are induction motors.
+ Their active/reactive power do not change instantaneously with voltage change but rather dynamically by changing the motor's rotor speed $\omega_r$ to maintain torque. Hence, the power consumption depends on both voltage and frequency.
+ \[
+ P_d = f_P(V, \omega_r), \qquad Q_d = f_Q(V, \omega_r),
+ \]
+ so the load has internal dynamics, unlike static $P_D, Q_D$ in ACOPF.
+
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Rotor Dynamics}
+
+ \textbf{Slip:}
+ \[
+ s = \frac{\omega_s - \omega_r}{\omega_s},
+ \]
+ where
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $\omega_s$: synchronous electrical speed ($2\pi f_s$), set by system frequency,
+ \item $\omega_r$: mechanical rotor speed (frequency at the load).
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Operating regions:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $s = 0$: rotor synchronous with system frequency $\rightarrow$ no induced torque.
+ \item $0 < s < 1$: normal operation. Rotor is slightly slower than the rotating field $\rightarrow$ induces current $\rightarrow$ produces torque.
+ \item $s \to 1$: stall. Rotor stopped, max current, high losses.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Mechanical dynamics (sign flip if you differentiate w.r.t. slip):}
+\[
+J\frac{d\omega_r}{dt} = T_e(V,\omega_r) - T_m
+\quad\Longleftrightarrow\quad
+J\,\omega_s\,\frac{ds}{dt} = T_m - T_e(V,s).
+\]
+\end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Continued}
+ \textbf{Variable definitions:}
+\begin{itemize}
+ \item $J$: rotor inertia (kg·m$^2$),
+ \item $\omega_r$: rotor mechanical speed/frequency (rad/s),
+ \item $T_e$: electromagnetic torque (depends on bus voltage $V$, frequency $\omega_s$ (slip formulation), or $\omega_r$ (standard formulation)),
+ \item $T_m$: mechanical load torque.
+\end{itemize}
+ \end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Example: Induction Motor Response During a Voltage Sag}
+
+ \textbf{Sequence of events:}
+
+ \begin{enumerate}
+ \item \textbf{Voltage drop:} $V$ suddenly decreases.
+ \item \textbf{Torque imbalance:} Electromagnetic torque $T_e(V,\omega_r)$
+ falls below mechanical torque $T_m$.
+ \item \textbf{Rotor slowdown:} $\omega_r$ decreases $\Rightarrow$ slip $s$ increases.
+ \item \textbf{Increased current and VAR demand:}
+ The motor draws more current to restore torque, which further depresses voltage.
+ \item \textbf{Possible stalling:} If $V$ remains low, the motor stalls —
+ reactive power skyrockets $\Rightarrow$ voltage collapse.
+ \end{enumerate}
+
+ IM Modeling is key to capture this nonlinear instability mechanism.
+
+ % \textbf{Interpretation:}
+ % \begin{itemize}
+ % \item Positive feedback loop: $V\downarrow \Rightarrow T_e\downarrow \Rightarrow s\uparrow
+ % \Rightarrow Q\uparrow \Rightarrow V\downarrow$.
+ % \item Accurate IM modeling is essential to capture this nonlinear instability mechanism.
+ % \end{itemize}
+ \end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{How TSC-OPF Prevents Motor Stalling and Voltage Collapse}
+ \textbf{In TSC-OPF, dynamics and limits are enforced directly:}
+ \[
+ \dot{x} = f(x, y, p), \qquad 0 = g(x, y, p), \qquad h(x(t), y(t)) \le 0, \;\forall t.
+ \]
+ \textbf{Dynamic states $x$:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Induction motor slip $s$, generator rotor angles, inverter controls, etc.
+ \item Their evolution $f(x,y,p)$ describes how voltages and speeds change after a disturbance.
+ \item Dynamic constraints ensure stall condition is not reached.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Constraint function $h(x(t),y(t))$:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Enforces time-domain limits such as
+ \[
+ V_i(t) \ge V_{\min}, \quad \forall t \in [0, T_{\text{rec}}],
+ \]
+ where $T_{\text{rec}}$ is the recovery time. This ensures bus voltages remain within safe recovery bounds during the entire horizon after a disturbance.
+ \item Prevents continued voltage sag that would drive $T_e(V,s)$ down and cause stalling.
+ \end{itemize}
+ \end{frame}
+
+\begin{frame}{Wrap up}
+ Controls $p$ are chosen so that f remains stable under disturbances, and the chain of events above is prevented since motor and network dynamics are embedded in $f,g,h$.
+
+ This model is typically used when there's a fast transient or stalling, and the time scale is in milliseconds to second. Useful for short-term voltage stability and transient studies.
+\end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Exponential Recovery Load (ERL): Motivation and Concept}
+
+ \textbf{Goal:} Represent aggregate load behavior during voltage recovery after a disturbance.
+
+ \textbf{Empirical Observation:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item When voltage dips, total active and reactive loads drop immediately.
+ \item Loads such as motor controls and HVAC systems \textbf{slowly restore} their power draw as voltage recovers.
+ \item The recovery follows an \textbf{exponential time pattern}, not an instantaneous jump.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Idea:}
+ Introduce internal states that describe this gradual return:
+ \[
+ P_d(t) = f_P(V(t),x_p(t)), \qquad Q_d(t) = f_Q(V(t),x_q(t)).
+ \]
+ where $x_p(t)$ and $x_q(t)$ are the internal states of the active and reactive load.
+
+ These states evolve according to first-order differential equations, capturing the "memory" of how far the load has recovered.
+ \end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Adaptive Exponential Recovery Load (ERL) Model}
+
+ \textbf{Mathematical Form:}
+ \[
+ \begin{aligned}
+ T_p \frac{dx_p}{dt} &= -x_p\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{ps}}
+ + P_0\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}},\\[3pt]
+ P_d &= x_p\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}},\\[6pt]
+ T_q \frac{dx_q}{dt} &= -x_q\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{qs}}
+ + Q_0\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{qt}},\\[3pt]
+ Q_d &= x_q\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{qt}}.
+ \end{aligned}
+ \]
+
+ \textbf{Parameters:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $x_p, x_q$: internal recovery states (how much of the load has recovered).
+ \item $T_p, T_q$: time constants — larger values $\Rightarrow$ slower recovery.
+ \end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+\begin{frame}{Continued}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item $P_0, Q_0$: nominal power withdrawals at reference voltage $V_0$.
+ \item $N_{pt}, N_{qt}$: transient exponents (immediate voltage sensitivity). How sharply load power reacts immediately when voltage changes (the short-term dip).
+ \item $N_{ps}, N_{qs}$: steady-state exponents (long-term voltage dependence). How much the load power changes in the long term after voltage settles to a new level.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Interpretation:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item After a voltage dip, power first follows the transient curve, then recovers exponentially toward the steady-state curve.
+ \item When $V$ is weak, the recovery term
+ $(V/V_0)^{N_{ps}}$ slows the rate of change — recovery stalls under low voltage.
+ \item Recovery speed and power response both scale with voltage and almost halts under deep voltage sag.
+ \end{itemize}
+ \end{frame}
+
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Standard vs. Adaptive ERL Models}
+
+ \textbf{Standard ERL model:}
+ \[
+ \begin{aligned}
+ T_p \frac{dx_p}{dt} &= -x_p + P_0\!\left[\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{ps}} - \left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}}\!\right],\\
+ P_d &= x_p + P_0\!\left(\frac{V}{V_0}\right)^{N_{pt}}.
+ \end{aligned}
+ \]
+
+ \textbf{Key difference:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item In the \textbf{standard} model, $dx_p/dt$ depends on $V$ only through the voltage-dependent driving term. The state $x_p$ recovers constantly—independent of voltage.
+ \item In the \textbf{adaptive} model, recovery slows when $V$ is low:the term $(V/V_0)^{N_{ps}}$ reduces the rate of change. The two differ in how strongly the voltage affects recovery speed.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Physical interpretation:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Standard ERL: suitable for moderate voltage dips.
+ \item Adaptive ERL: more realistic for deep voltage sags.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{ERL Parameters}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Parameters $(T_p, T_q, N_{ps}, N_{pt}, N_{qs}, N_{qt})$
+ are fitted empirically from from measurements of load recovery after voltage disturbances.
+ \item They are not linked to physical machine constants,
+ but to observed aggregate behavior of customer loads.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Compared to IM Model:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Models \textbf{voltage-driven recovery} of active/reactive power demand,
+ not frequency-driven mechanical motion.
+ \item Represents the slower phase of system response
+ (seconds to minutes) vs. fast electromechanical transients.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ % \textbf{Dynamic enforcement:}
+ % \begin{itemize}
+ % \item The differential equations ensure $P_d(t), Q_d(t)$ follow
+ % realistic \textbf{transient trajectories}, not step changes.
+ % \item In simulation or optimization, the states $x_p,x_q$
+ % evolve continuously according to these recovery laws.
+ % \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Steady-state check:}
+ Setting $\dot{x}_p=\dot{x}_q=0$ gives
+ $P_d=P_0(V/V_0)^{N_{ps}}$, $Q_d=Q_0(V/V_0)^{N_{qs}}$,
+ so ERL naturally reduces to a static voltage-dependent load, showing that when dynamics died out, the model reduces to a steady-state load.
+ \end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{ERL in TSC-OPF and Contrast with Induction Motor Model}
+
+ \textbf{TSC-OPF representation:}
+ \[
+ \dot{x} = f(x,y,p), \qquad 0 = g(x,y,p), \qquad h(x(t),y(t)) \le 0.
+ \]
+
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item ERL contributes its states $x_p,x_q$ to $x$,
+ with recovery dynamics embedded in $f(x,y,p)$.
+ \item $P_d(V,x_p), Q_d(V,x_q)$ enter the algebraic equations $g(x,y,p)$
+ for power balance at each bus.
+ \item Voltage-recovery limits in $h(x(t),y(t))$ ensure $V_i(t)\!\ge\!V_{\min}$
+ throughout the recovery window $[0,T_{\text{rec}}]$.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ \textbf{Contrast with IM model:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item \textbf{Induction Motor (IM):}
+ physics-based; state $s=(\omega_s-\omega_r)/\omega_s$;
+ captures fast electromechanical and frequency-coupled transients (0.1–2 s).
+ \item \textbf{ERL:}
+ empirical; states $x_p,x_q$; captures slow, voltage-driven recovery (1–60 s).
+ \end{itemize}
+ \end{frame}
+
+% ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Why We Go Beyond Steady-State OPF}
+
+ \textbf{The bigger picture:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Power systems are not static networks — they are \textbf{dynamic systems.}
+ \item After every change — a fault, switching event, or sudden load or generation shift — voltages, currents, and frequencies evolve continuously before settling.
+ \item Understanding and controlling these dynamics is essential for keeping the grid stable, secure, and resilient.
+ \end{itemize}
+ \end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Four Building Blocks of System Dynamics}
+
+ \textbf{Four building blocks of system dynamics:}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item \textbf{Transients:} capture the immediate electromagnetic wave response
+ that propagates through the network.
+ \item \textbf{Generator swing equations:} describe how machines adjust speed and angle
+ to balance mechanical and electrical power.
+ \item \textbf{Inverters:} the new generation interface that emulates inertia and voltage support with renewables.
+ \item \textbf{Dynamic loads:} model how real demand recovers and interacts with voltage and frequency.
+ \end{itemize}
+\end{frame}
+
+ % ======================================================
+\begin{frame}{Why We Need Dynamic Optimization (TSC-OPF)}
+ \textbf{Why we need dynamic optimization (TSC-OPF):}
+ \begin{itemize}
+ \item Steady-state OPF finds an economical operating point \emph{only at equilibrium.}
+ \item Transient Stability-Constrained OPF ensures that,
+ even during those dynamic transitions,
+ voltages remain safe, machines stay synchronized,
+ and inverters and loads respond smoothly.
+ \end{itemize}
+
+ % \textbf{In short:}
+ % \[
+ % \text{Steady-state OPF ensures economy; TSC-OPF ensures security and survivability.}
+ % \]
+ \end{frame}
+
+
+\end{document}
diff --git a/class15/class15_lecture.pdf b/class15/class15_lecture.pdf
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d1ac9a2
Binary files /dev/null and b/class15/class15_lecture.pdf differ