From f1fa24aa9e818443f3d09a9720526b51abd57d6e Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: PradeepSiddh <114388943+PradeepSiddh@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Sat, 22 Oct 2022 12:27:02 +0530
Subject: [PATCH] Create brownie.md
---
how-to/XRC20/Brownie/brownie.md | 318 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
1 file changed, 318 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 how-to/XRC20/Brownie/brownie.md
diff --git a/how-to/XRC20/Brownie/brownie.md b/how-to/XRC20/Brownie/brownie.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8e25fb6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/how-to/XRC20/Brownie/brownie.md
@@ -0,0 +1,318 @@
+---
+Id: Create-and-deploy-an-XRC20-token.
+Title: Create And Deploy An XRC20 Token.
+Description: "Create And Deploy An XRC20 Token On The XDC Network Using Brownie."
+Keywords:
+ - Documentation
+ - Brownie
+ - XDC
+ - XRC20
+ - Python
+---
+
+# Overview
+
+Python is one of the most versatile programming languages; from researchers running their test models to developers using it in heavy production environments, it has use cases in every possible technical field. In today's guide, we will learn about Brownie, a Python-based tool used to write and deploy smart contracts.
+
+# What you gonna learn
+
+In this tutorial, you will learn how to set up Brownie and use it to build, test and deploy a XRC20 Token on both the XDC Network mainnet and XDC Apothem testnet.
+
+# What you gonna do
+
+ - Install and setup Brownie
+ - Create an XRC20 token
+ - Compile the XRC20 token
+ - Deploy the XRC20 token
+ - Interact with the XRC20 token
+
+# What is Brownie?
+
+Smart contract development is majorly dominated by JavaScript-based libraries like web3.js(https://web3js.readthedocs.io/en/v1.8.0/), ethers.js(https://docs.ethers.io/v5/), Truffle(https://trufflesuite.com/docs/truffle/overview), and Hardhat(https://hardhat.org/). Python is a versatile, highly used language and can also be used for smart contracts/web3 development; web3.py(https://web3py.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) is a compelling Python library that fulfills web3 needs. Brownie framework is built on top of web3.py.
+
+Brownies are small rectangular confectionary items loved by everyone, but the Brownie(https://eth-brownie.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html#brownie) we are talking about today is a Python-based framework to develop and test smart contracts. Brownie has support for both Solidity and Vyper contracts, and it even provides contract testing via pytest(https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest).
+
+To demonstrate the process of writing and deploying a smart contract with Brownie, we will use Brownie-mixes(https://github.com/brownie-mix) which are template projects. Specifically, we will use a token mix(https://github.com/brownie-mix/token-mix), which is a template of the XRC20 implementation.
+
+# Installing dependencies
+
+Brownie is built on top of python3, so we need it installed to work with brownie; let us check if we have python3 installed on our system. To do so, type the following in your terminal/cmd:
+
+
+  +
+
+
+This should return the version of python3 installed. If not installed, download and install it from the official python website(https://www.python.org/downloads/).  +
+
+Let us make a project directory before installing brownie, and make that project directory our current working directory:
+
+
+
+
+Let us make a project directory before installing brownie, and make that project directory our current working directory:
+
+
+  +
+
+
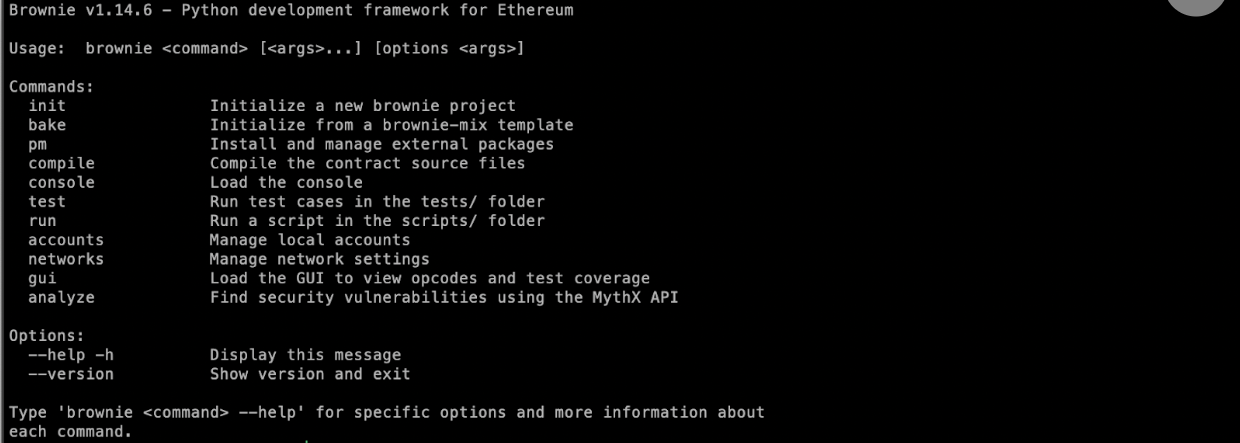
+Now that you have installed python3 on your system let us install brownie using pip, Python's package manager. Pip is similar to what npm is for JavaScript. Type the following in your terminal/cmd:
+
+
+  +
+
+
+To check if Brownie was installed correctly, type brownie in your terminal/cmd, and it should give the following output:
+
+
+  +
+
+
+To get the token mix, type the following in your terminal/cmd:
+
+
+ 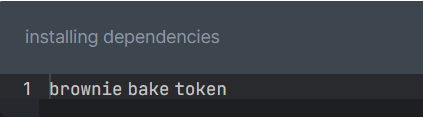 +
+
+This will create a new directory token/ in our brownieDemo directory.
+
+## File Structure
+
+First of all, lets cd into the token directory:
+
+
+  +
+
+Now, open the token directory in your text editor. Under the contracts/ folder, you will find Token.sol, which is our main contract; you can write your own contracts or modify this. Under the scripts/ folder, you will find token.py python script; this script will be used to deploy the contract, and modifications are needed based on contracts.
+
+
+ 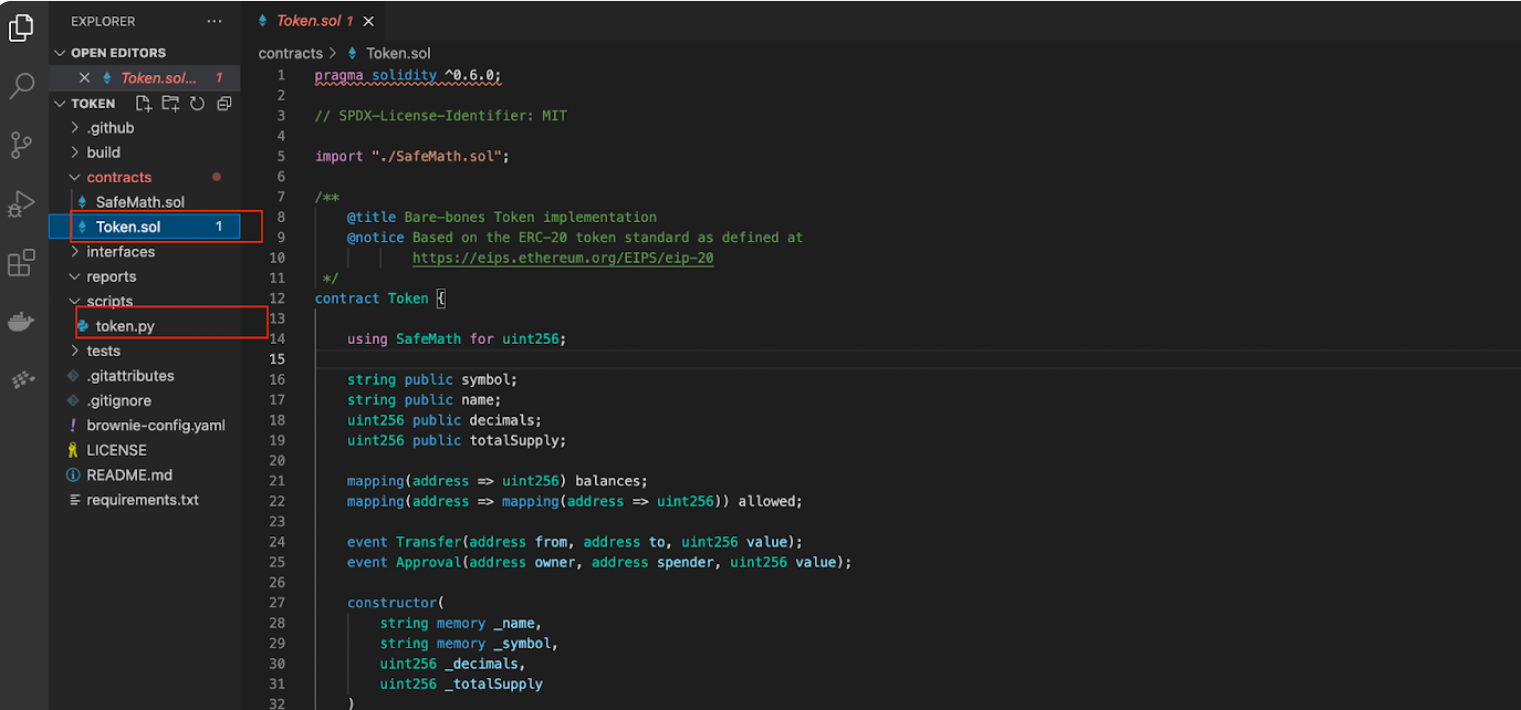 +
+
+
+The contract is an XRC20 contract; now you will learn more about the XRC20 standards and contracts.
+
+### Guide on XRC20 Token
+
+# what is XRC20 Token?
+
+XRC-20 stands for XinFin Request for Comment, and 20 is the proposal identifier number. XRC-20 was designed to improve the XinFin XDC network. XRC-20 is one of the most significant XRCs. It has emerged as the technical standard for writing smart contracts on the XinFin blockchain network, used for token implementation.
+
+XRC-20 is a standard or guideline for creating new tokens. The standard defines six mandatory functions that a smart contract should implement and three optional ones.
+
+To start you can give your token a name, a symbol, and mention how dividable your token is, by specifying the decimals. XRC specifies a set of mandatory functions, which are a bit more complex and listed below:
+
+ - `totalSupply`: A method that defines the total supply of your tokens, When this limit is reached the smart contract will refuse to create new tokens.
+ - `balanceOf`: A method that returns the number of tokens a wallet address has.
+ - `transfer`: A method that takes a certain amount of tokens from the total supply and gives it to a user.
+ - `transferFrom`: Another type of transfer method which is used to transfer tokens between users.
+ - `approve`: This method verifies whether a smart contract is allowed to allocate a certain amount of tokens to a user, considering the total supply.
+ - `allowance`: This method is exactly the same as the approved method except that it checks if one user has enough balance to send a certain amount of tokens to another.
+
+If you know something about Object Oriented programming you can compare XRC-20 to an Interface. If you want your token to be an XRC-20 token, you have to implement the XRC-20 interface and that forces you to implement these 6 methods.
+
+## Creating our own token
+
+Now that we know what ERC-20 tokens are and how they work, let’s see how we can build and deploy our own token.
+
+To get started, you will need the Metamask browser extension to create an XDCPay Wallet.  +
+Head over to the Ethereum Remix IDE(https://remix.ethereum.org/) and make a new Solidity file, for example - XRC20.sol
+
+Head over to the Ethereum Remix IDE(https://remix.ethereum.org/) and make a new Solidity file, for example - XRC20.sol 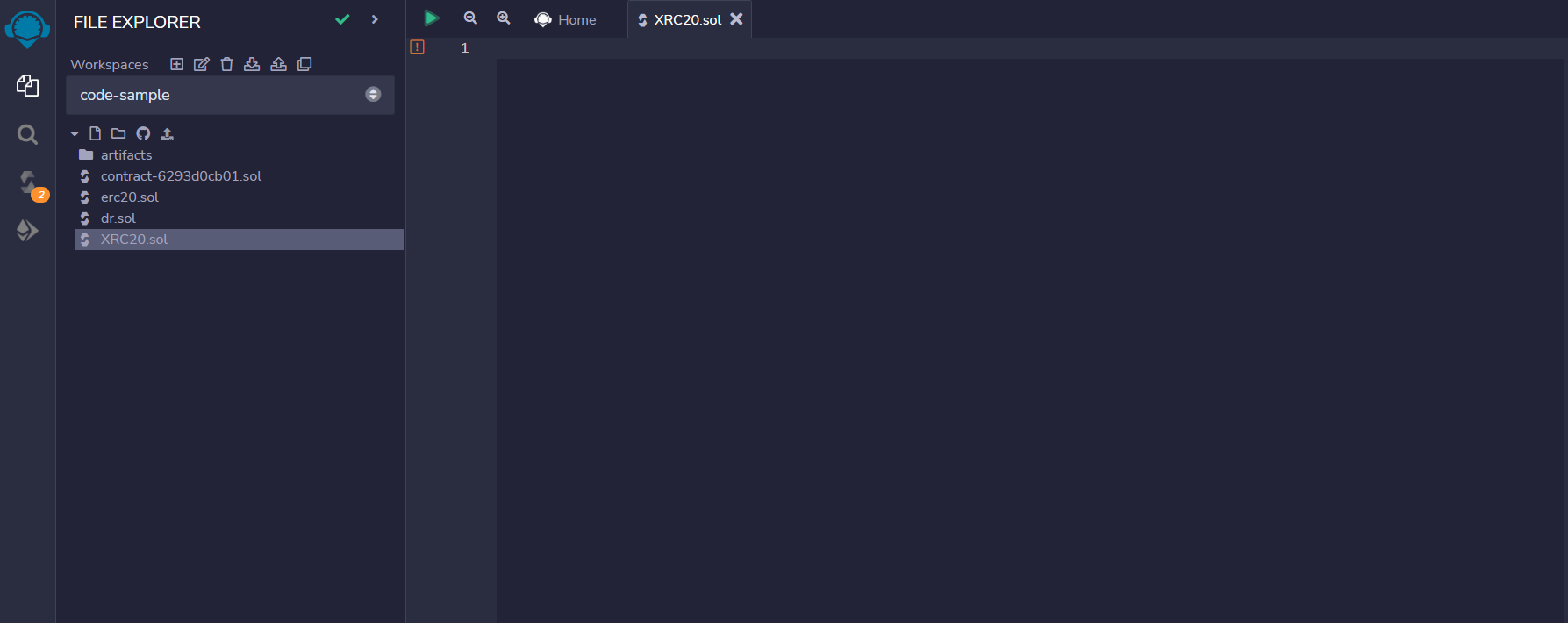 +
+Now, writing our smart sontract into our new `Solidity` script:
+
+ ```
+ // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
+ pragma solidity ^0.4.26;
+
+ //Safe Math Interface
+
+ contract SafeMath {
+
+ function safeAdd(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a + b;
+ require(c >= a);
+ }
+
+ function safeSub(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b <= a);
+ c = a - b;
+ }
+
+ function safeMul(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a * b;
+ require(a == 0 || c / a == b);
+ }
+
+ function safeDiv(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b > 0);
+ c = a / b;
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ //XRC Token Standard #20 Interface
+
+ contract XRC20Interface {
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint);
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance);
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining);
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+
+ event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint tokens);
+ event Approval(address indexed tokenOwner, address indexed spender, uint tokens);
+ }
+
+
+ //Contract function to receive approval and execute function in one call
+
+ contract ApproveAndCallFallBack {
+ function receiveApproval(address from, uint256 tokens, address token, bytes data) public;
+ }
+
+ //Actual token contract
+
+ contract XRCToken is XRC20Interface, SafeMath {
+ string public symbol;
+ string public name;
+ uint8 public decimals;
+ uint public _totalSupply;
+
+ mapping(address => uint) balances;
+ mapping(address => mapping(address => uint)) allowed;
+
+ constructor() public {
+ symbol = "XRC";
+ name = "XRC Token";
+ decimals = 2;
+ _totalSupply = 100000;
+ balances[0] = _totalSupply;
+ emit Transfer(address(0), 25, _totalSupply);
+ }
+
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint) {
+ return _totalSupply - balances[address(0)];
+ }
+
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance) {
+ return balances[tokenOwner];
+ }
+
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[msg.sender] = safeSub(balances[msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(msg.sender, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[from] = safeSub(balances[from], tokens);
+ allowed[from][msg.sender] = safeSub(allowed[from][msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(from, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining) {
+ return allowed[tokenOwner][spender];
+ }
+
+ function approveAndCall(address spender, uint tokens, bytes data) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ ApproveAndCallFallBack(spender).receiveApproval(msg.sender, tokens, this, data);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function () public payable {
+ revert();
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+# Booting our Ethereum node
+
+We will deploy our contract on the XDC Apothem testnet(https://apothem.network/#stats) instead of running our own node. It is more convenient to get a free trial endpoint from QuickNode(https://www.quicknode.com/?utm_source=internal&utm_campain=guides). Make sure to select Ethereum as the chain and XDC Apothem as the network during checkout.
+
+
+
+Now, writing our smart sontract into our new `Solidity` script:
+
+ ```
+ // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
+ pragma solidity ^0.4.26;
+
+ //Safe Math Interface
+
+ contract SafeMath {
+
+ function safeAdd(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a + b;
+ require(c >= a);
+ }
+
+ function safeSub(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b <= a);
+ c = a - b;
+ }
+
+ function safeMul(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a * b;
+ require(a == 0 || c / a == b);
+ }
+
+ function safeDiv(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b > 0);
+ c = a / b;
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ //XRC Token Standard #20 Interface
+
+ contract XRC20Interface {
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint);
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance);
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining);
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+
+ event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint tokens);
+ event Approval(address indexed tokenOwner, address indexed spender, uint tokens);
+ }
+
+
+ //Contract function to receive approval and execute function in one call
+
+ contract ApproveAndCallFallBack {
+ function receiveApproval(address from, uint256 tokens, address token, bytes data) public;
+ }
+
+ //Actual token contract
+
+ contract XRCToken is XRC20Interface, SafeMath {
+ string public symbol;
+ string public name;
+ uint8 public decimals;
+ uint public _totalSupply;
+
+ mapping(address => uint) balances;
+ mapping(address => mapping(address => uint)) allowed;
+
+ constructor() public {
+ symbol = "XRC";
+ name = "XRC Token";
+ decimals = 2;
+ _totalSupply = 100000;
+ balances[0] = _totalSupply;
+ emit Transfer(address(0), 25, _totalSupply);
+ }
+
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint) {
+ return _totalSupply - balances[address(0)];
+ }
+
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance) {
+ return balances[tokenOwner];
+ }
+
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[msg.sender] = safeSub(balances[msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(msg.sender, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[from] = safeSub(balances[from], tokens);
+ allowed[from][msg.sender] = safeSub(allowed[from][msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(from, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining) {
+ return allowed[tokenOwner][spender];
+ }
+
+ function approveAndCall(address spender, uint tokens, bytes data) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ ApproveAndCallFallBack(spender).receiveApproval(msg.sender, tokens, this, data);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function () public payable {
+ revert();
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+# Booting our Ethereum node
+
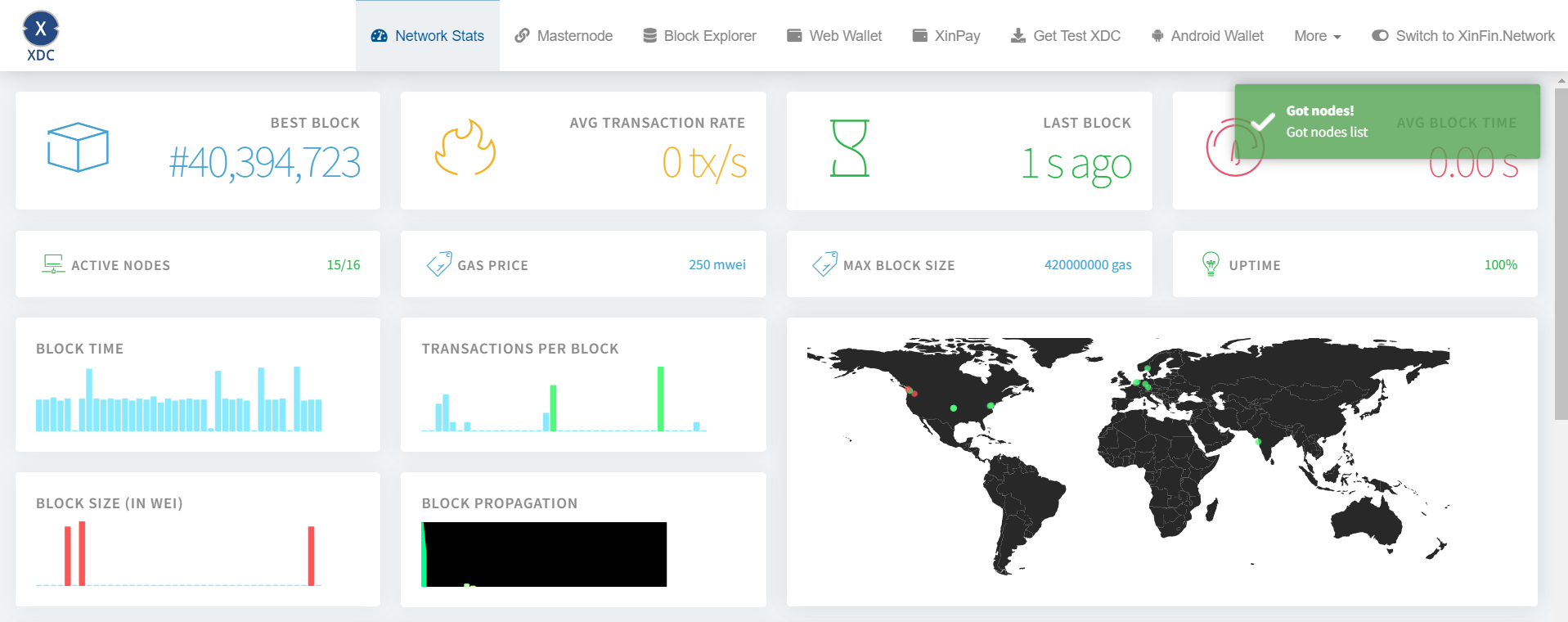
+We will deploy our contract on the XDC Apothem testnet(https://apothem.network/#stats) instead of running our own node. It is more convenient to get a free trial endpoint from QuickNode(https://www.quicknode.com/?utm_source=internal&utm_campain=guides). Make sure to select Ethereum as the chain and XDC Apothem as the network during checkout.
+
+
+  +
+
+
+# Network and Account Set Up
+
+We need to set up our QuickNode endpoint with Brownie. To do so, type the following in your terminal/cmd:
+
+```
+brownie networks add XDC Apothemquicknode host=YOUR_QUICKNODE_URL chainid=3
+```
+
+Replace `YOUR_QUICKNODE_URL` with the URL we got in the last step.
+
+In the above command, `XDC` is the name of the environment, and `Apothemquicknode` is the custom name of the network; you can give any name to your custom network.
+
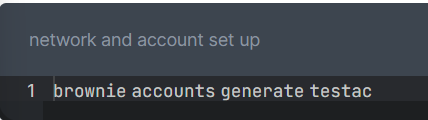
+The next thing we need to do here is to create a new wallet using Brownie. To do so, type the following in your terminal/cmd. You will be asked to set up a password for your account.
+
+
+  +
+
+
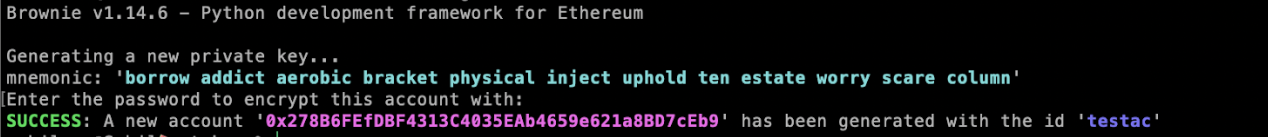
+This will generate an account along with a mnemonic phrase and save it offline. The name testac is the name for our account. You can choose any name that you would like.
+
+
+  +
+
+**NOTE**: Mnemonic phrases can be used to recover an account or import the account to other non-custodial wallets. The account you see in the image above was just created for this guide.
+
+Copy the account address so that we can get some test XDC, which will be required to deploy our contract.
+
+## Getting test XDC
+
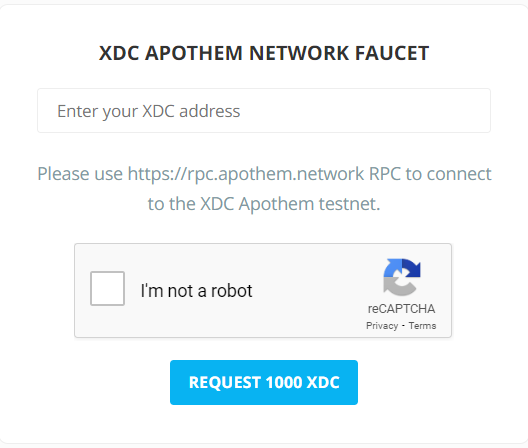
+As our contract will be deployed on the Apothem testnet, we will require some test xdc tokens to pay for the gas fee. Head over to the Apothem faucet(https://faucet.apothem.network/), paste your address in the field, and click on "Request 1000XDC".
+
+
+  +
+
+
+
+## Deploying our contract
+
+Before deploying the contract, we need to compile it using:
+
+
+ 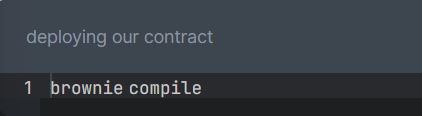 +
+
+
+Now, 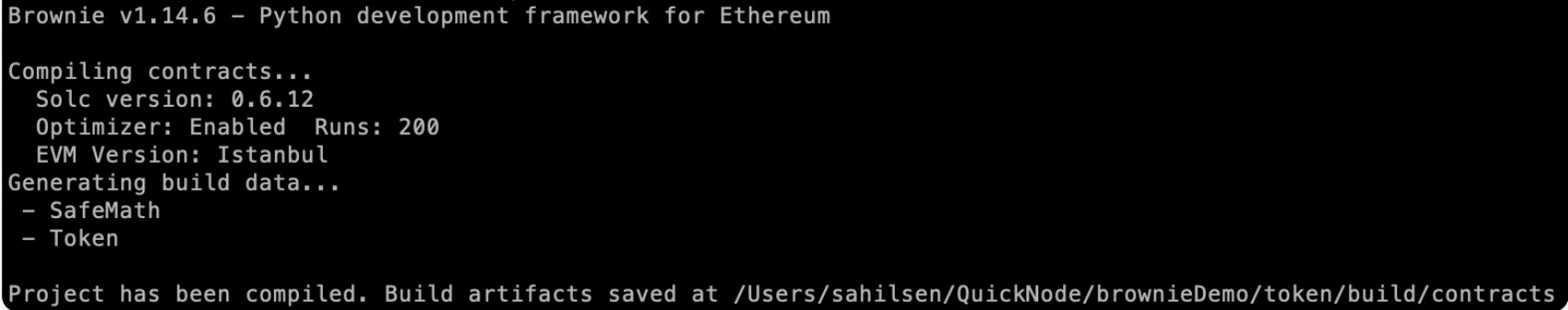 +
+Now open the scripts/token.py in your text editor, and make the following changes:
+
+
+
+Now open the scripts/token.py in your text editor, and make the following changes:
+
+
+ 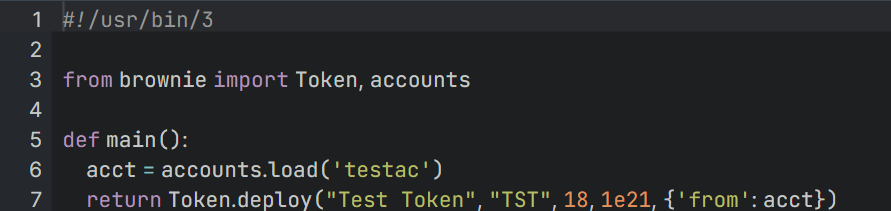 +
+
+`Line 6`: We added this line to import the testac account we created earlier and stored it in the acct variable.
+
+`Line 7`: On this line, we edited the 'From': part to have our acct variable.
+
+FINALLY, we will deploy our contract using the deployment script (scripts/token.py here):
+
+
+  +
+
+
+In the above command, apothemquicknode is the name of the custom network which we created earlier. The prompt will ask you for the password which we set earlier while making the account. After running the above command, you must get the transaction hash, and Brownie will wait for the transaction to get confirmed. Once the transaction is confirmed, it will return the address at which our contract is deployed on the XDC Apothem testnet.
+
+
+ 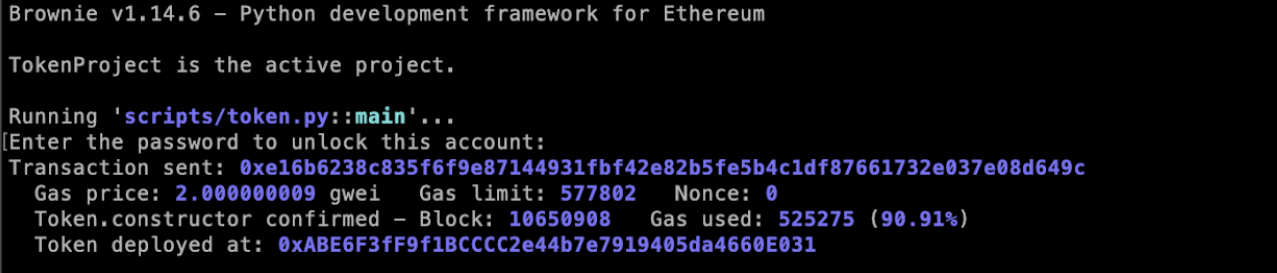 +
+
+
+You can check out the deployed contract by copy-pasting the contract address at Apothem network(https://explorer.apothem.network/).
+
+
+## Conclusion
+
+So, today we learned brownies are good, but Brownie the framework is the best. We learned how to import a Brownie-mix, add a custom network, create an account, and compile and deploy a contract, and we used Brownie for the entire process!
+
+
+
+
 +
+ +
+ +
+
+Let us make a project directory before installing brownie, and make that project directory our current working directory:
+
+
+
+
+Let us make a project directory before installing brownie, and make that project directory our current working directory:
+
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+Head over to the Ethereum Remix IDE(https://remix.ethereum.org/) and make a new Solidity file, for example - XRC20.sol
+
+Head over to the Ethereum Remix IDE(https://remix.ethereum.org/) and make a new Solidity file, for example - XRC20.sol  +
+Now, writing our smart sontract into our new `Solidity` script:
+
+ ```
+ // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
+ pragma solidity ^0.4.26;
+
+ //Safe Math Interface
+
+ contract SafeMath {
+
+ function safeAdd(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a + b;
+ require(c >= a);
+ }
+
+ function safeSub(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b <= a);
+ c = a - b;
+ }
+
+ function safeMul(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a * b;
+ require(a == 0 || c / a == b);
+ }
+
+ function safeDiv(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b > 0);
+ c = a / b;
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ //XRC Token Standard #20 Interface
+
+ contract XRC20Interface {
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint);
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance);
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining);
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+
+ event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint tokens);
+ event Approval(address indexed tokenOwner, address indexed spender, uint tokens);
+ }
+
+
+ //Contract function to receive approval and execute function in one call
+
+ contract ApproveAndCallFallBack {
+ function receiveApproval(address from, uint256 tokens, address token, bytes data) public;
+ }
+
+ //Actual token contract
+
+ contract XRCToken is XRC20Interface, SafeMath {
+ string public symbol;
+ string public name;
+ uint8 public decimals;
+ uint public _totalSupply;
+
+ mapping(address => uint) balances;
+ mapping(address => mapping(address => uint)) allowed;
+
+ constructor() public {
+ symbol = "XRC";
+ name = "XRC Token";
+ decimals = 2;
+ _totalSupply = 100000;
+ balances[0] = _totalSupply;
+ emit Transfer(address(0), 25, _totalSupply);
+ }
+
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint) {
+ return _totalSupply - balances[address(0)];
+ }
+
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance) {
+ return balances[tokenOwner];
+ }
+
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[msg.sender] = safeSub(balances[msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(msg.sender, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[from] = safeSub(balances[from], tokens);
+ allowed[from][msg.sender] = safeSub(allowed[from][msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(from, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining) {
+ return allowed[tokenOwner][spender];
+ }
+
+ function approveAndCall(address spender, uint tokens, bytes data) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ ApproveAndCallFallBack(spender).receiveApproval(msg.sender, tokens, this, data);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function () public payable {
+ revert();
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+# Booting our Ethereum node
+
+We will deploy our contract on the XDC Apothem testnet(https://apothem.network/#stats) instead of running our own node. It is more convenient to get a free trial endpoint from QuickNode(https://www.quicknode.com/?utm_source=internal&utm_campain=guides). Make sure to select Ethereum as the chain and XDC Apothem as the network during checkout.
+
+
+
+Now, writing our smart sontract into our new `Solidity` script:
+
+ ```
+ // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
+ pragma solidity ^0.4.26;
+
+ //Safe Math Interface
+
+ contract SafeMath {
+
+ function safeAdd(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a + b;
+ require(c >= a);
+ }
+
+ function safeSub(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b <= a);
+ c = a - b;
+ }
+
+ function safeMul(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ c = a * b;
+ require(a == 0 || c / a == b);
+ }
+
+ function safeDiv(uint a, uint b) public pure returns (uint c) {
+ require(b > 0);
+ c = a / b;
+ }
+ }
+
+
+ //XRC Token Standard #20 Interface
+
+ contract XRC20Interface {
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint);
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance);
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining);
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
+
+ event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint tokens);
+ event Approval(address indexed tokenOwner, address indexed spender, uint tokens);
+ }
+
+
+ //Contract function to receive approval and execute function in one call
+
+ contract ApproveAndCallFallBack {
+ function receiveApproval(address from, uint256 tokens, address token, bytes data) public;
+ }
+
+ //Actual token contract
+
+ contract XRCToken is XRC20Interface, SafeMath {
+ string public symbol;
+ string public name;
+ uint8 public decimals;
+ uint public _totalSupply;
+
+ mapping(address => uint) balances;
+ mapping(address => mapping(address => uint)) allowed;
+
+ constructor() public {
+ symbol = "XRC";
+ name = "XRC Token";
+ decimals = 2;
+ _totalSupply = 100000;
+ balances[0] = _totalSupply;
+ emit Transfer(address(0), 25, _totalSupply);
+ }
+
+ function totalSupply() public constant returns (uint) {
+ return _totalSupply - balances[address(0)];
+ }
+
+ function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public constant returns (uint balance) {
+ return balances[tokenOwner];
+ }
+
+ function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[msg.sender] = safeSub(balances[msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(msg.sender, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success) {
+ balances[from] = safeSub(balances[from], tokens);
+ allowed[from][msg.sender] = safeSub(allowed[from][msg.sender], tokens);
+ balances[to] = safeAdd(balances[to], tokens);
+ emit Transfer(from, to, tokens);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public constant returns (uint remaining) {
+ return allowed[tokenOwner][spender];
+ }
+
+ function approveAndCall(address spender, uint tokens, bytes data) public returns (bool success) {
+ allowed[msg.sender][spender] = tokens;
+ emit Approval(msg.sender, spender, tokens);
+ ApproveAndCallFallBack(spender).receiveApproval(msg.sender, tokens, this, data);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ function () public payable {
+ revert();
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+# Booting our Ethereum node
+
+We will deploy our contract on the XDC Apothem testnet(https://apothem.network/#stats) instead of running our own node. It is more convenient to get a free trial endpoint from QuickNode(https://www.quicknode.com/?utm_source=internal&utm_campain=guides). Make sure to select Ethereum as the chain and XDC Apothem as the network during checkout.
+
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+Now open the scripts/token.py in your text editor, and make the following changes:
+
+
+
+Now open the scripts/token.py in your text editor, and make the following changes:
+
+ +
+ +
+ +
+