-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Description
Twitter Sentiment Analysis Using Combined LSTM-CNN Models
FEBRUARY 19, 2018
A year ago I had written a paper for a Neural Networks class that I hadn't gotten around to publish. I decided to take a small break from most of my hacking posts to talk a bit about Machine Learning. This paper was a continuation of some previous work I had done (outlined in this past post) regarding Sentiment Analysis of Twitter data. (I recommend taking a look at that post if you are new to Neural Networks)
1년 전 나는 Neural Network 수업을 위한 논문을 작성했지만 공개하지 않았다. 나는 Machine Learning에 대해 조금 이야기하기 위해서 내 개시물 업로드를 휴재하기로 결정했다. 이 논문은 Sentiment Analysis of Twitter data와 관련하여 이전에 수행했던 몇 가지 작업(과거 게시물)의 연속이다. (Neural Networks가 처음이라면 과거 게시물을 살펴보기를 권장한다.)
This is a shorter version of the research paper I wrote, so feel free to check that out if you want to go into more details. Also, if you only care about the implementation check out my Github project.
이 글은 내가 쓴 연구 논문의 짧은 버전으로, 자세한 내용을 확인하고 싶다면 논문을 확인해라. 만약 구현에만 관심이 있다면 Github project를 확인하면 된다.
1. Motivation
Twitter is now a platform that hosts about 350 million active users, which post around 500 million tweets per day! It has become a direct link between companies/organizations and their customers, and such it is being used to build branding, understand customer demands, and better communicate with them. From a data scientist point of view, Twitter is a gold mine that can be used, among a million other interesting things, for gauging customer sentiment towards a brand.
Twitter는 현재 하루에 5억개의 tweet을 게시하는 3억 5천만의 활성 사용자를 호스팅하는 플랫폼이다. Twitter는 기업/조직과 그들 고객 사이의 직접적인 연결고리가 되었고, branding을 만들고, 고객의 요구를 이해하며 그들과 더 나은 소통을 하는 데 사용되고 있다. Data scientist의 관점에서, Twitter는 백만개의 흥미로운 것들 중에서 하나의 브랜드에 대한 고객의 정서를 측정하는데 사용될 수 있는 좋은 플랫폼이다.
My personal stake in this project stemmed from my curiosity to better understand Neural Networks, particularly CNN and LSTMs. In a previous class, I had created simple Feed-Forward Neural Networks to solve this very problem, however I knew that my results could be substantially better when harnessing the power of more specialized networks.
이 프로젝트는 나의 호기심인 Neural Network, 특히 CNN과 LSTMs을 더 잘 이해하기 위한 개인적인 관심에서 비롯되었다. 이전 수업에서 나는 이 문제를 풀기 위한 간단한 Feed-Forward Neural Networks를 만들었지만, 더 전문화된 network의 힘을 활용할 때 결과가 훨씬 더 좋을 수 있음을 알게 되었다.
Furthermore, I wanted to do something I hadn't really seen other people do and I was curious about the results of combining these two networks.
또한 나는 다른 사람이 실제로 본 적이 없는 것을 하고 싶었고, 두 network를 결합한 결과가 궁금했다.
2. Intuition: Why CNNs and LSTMs?
Before starting, let's give a brief introduction to these networks along with a short analysis of why I thought they would benefit my sentiment analysis task.
시작하기 전에 network의 소개와, sentiment analysis 작업에 왜 이 network들이 도움이 될 것이라고 생각했는지 살펴보자.
2-1) CNNs
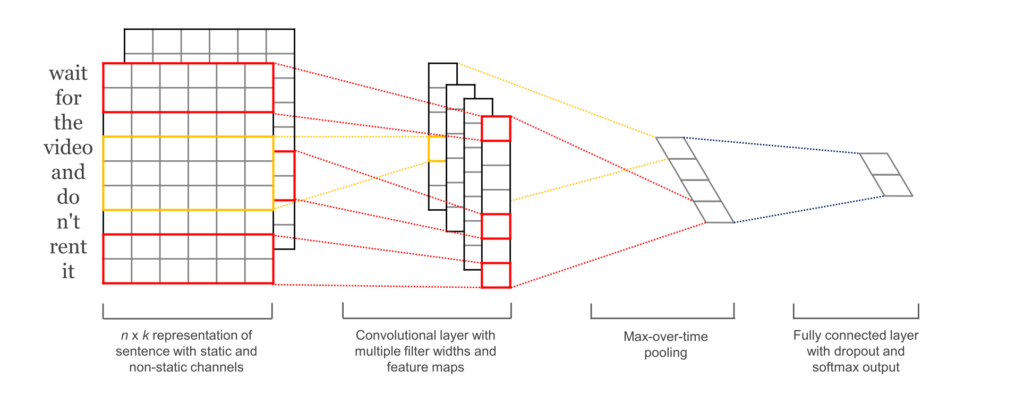
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are networks initially created for image-related tasks that can learn to capture specific features regardless of locality.
Convolutional Neural Networks는 지역성에 관계 없이 특정 feature를 포착하는 법을 배울 수 있는 이미지 관련 작업을 위해 처음 만들어진 network다.
For a more concrete example of that, imagine we use CNNs to distinguish pictures of Cars vs. pictures of Dogs. Since CNNs learn to capture features regardless of where these might be, the CNN will learn that cars have wheels, and every time it sees a wheel, regardless of where it is on the picture, that feature will activate.
좀 더 자세한 예를 들면, 자동차와 개의 사진을 구별하기 위해 CNN을 사용하는 것을 생각해보자. CNN은 사물이 어디에 있든 상관없이 feature를 포착하는 방법을 배우기 때문에 자동차가 바퀴를 가지고 있다는 것을 알게 될 것이고, 자동차가 사진의 어느 위치에 있는지와는 관계없이 바퀴를 볼 때마다 해당 feature를 활성화시킬 것이다.
In our particular case, it could capture a negative phrase such as "don't like" regardless of where it happens in the tweet.
- I
don't likewatching those types of films - That's the one thing I really
don't like. - I saw the movie, and I
don't likehow it ended.
우리의 특별한 경우, tweet내에서 어느 위치인지는 상관 없이 "don't like"와 같은 부정적인 문장을 포착할 수 있었다.
- Source: wildml.com
2-2) LSTMs
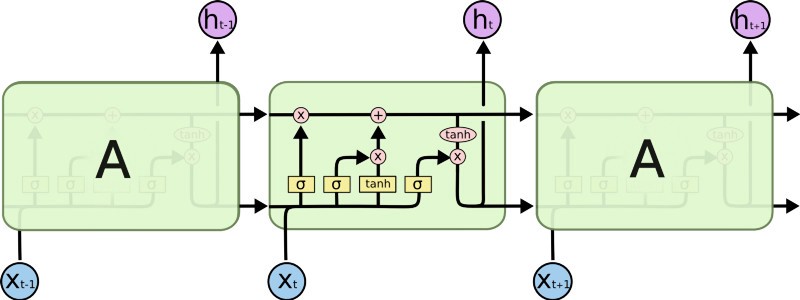
Long-Term Short Term Memory (LSTMs) are a type of network that has a memory that "remembers" previous data from the input and makes decisions based on that knowledge. These networks are more directly suited for written data inputs, since each word in a sentence has meaning based on the surrounding words (previous and upcoming words).
Long-Term Short Term Memory(LSTMs)는 input에서 이전 데이터를 "기억"하고, 그 지식을 바탕으로 결정을 내리는 메모리를 가진 네트워크의 일종이다. 이러한 network는 문장의 각 단어가 주변 단어(앞 단어, 뒷 단어)를 기반으로 의미를 가지기 때문에 written data input(글로 쓰여진 데이터)으로 더 직접적으로 적합하다.
In our particular case, it is possible that an LSTM could allow us to capture changing sentiment in a tweet. For example, a sentence such as: At first I loved it, but then I ended up hating it. has words with conflicting sentiments that would end-up confusing a simple Feed-Forward network. The LSTM, on the other hand, could learn that sentiments expressed towards the end of a sentence mean more than those expressed at the start.
우리의 특별한 경우, LSTM은 tweet에서 변하는 감정을 포착할 수 있도록 해준다. 예를 들어, 처음에는 좋아했지만 나중에는 싫어하게 되었다.와 같은 문장의 경우에는 단순한 Feed-Forward network를 혼란스럽게 할 수 있는 상반된 감정을 가진 단어들이 있다. 반면 LSTM은 문장의 끝에 표현된 감정이 처음에 표현된 감정보다 더 큰 의미가 있다는 것을 알 수 있다.
- Source: colah.github.io
3. Twitter Data
The Twitter data used for this particular experiment was a mix of two datasets:
이 특정 실험에 사용된 Twitter 데이터는 다음 두 개의 데이터셋을 혼합한 것이다.
- The University of Michigan Kaggle competition dataset.
- The Neik Sanders Twitter Sentiment Analysis corpus.
In total these datasets contain 1,578,627 labeled tweets.
이 전체 데이터셋에는 1,578,627개의 라벨링된 tweet들이 포함되어 있다.
4. CNN-LSTM Model
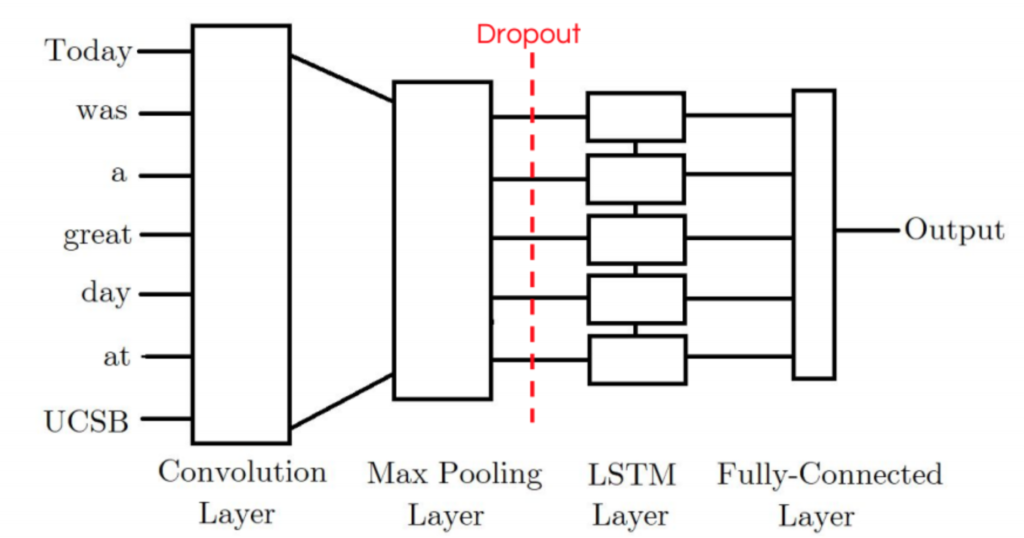
The first model I tried was the CNN-LSTM Model. Our CNN-LSTM model combination consists of an initial convolution layer which will receive word embeddings as input. Its output will then be pooled to a smaller dimension which is then fed into an LSTM layer. The intuition behind this model is that the convolution layer will extract local features and the LSTM layer will then be able to use the ordering of said features to learn about the input’s text ordering. In practice, this model is not as powerful as our other LSTM-CNN model proposed.
내가 처음 시도한 모델은 CNN-LSTM 모델이다. CNN-LSTM 모델 조합은 word embedding을 input으로 받을 수 있는 initial convolution layer로 이루어져 있다. CNN-LSTM 모델 조합의 output은 LSTM의 layer에 공급되는 것보다 더 작은 dimension으로 pooling될 것이다. 이 모델은 convolution layer가 local feature를 추출하고 그 다음 LSTM layer가 input 텍스트의 순서를 배우기 위해서 해당 feature의 순서를 사용할 수 있을 것이라고 생각했다. 실제로 이 모델은 제안된 다른 LSTM-CNN 모델보다 강력하지 않았다.
5. LSTM-CNN Model
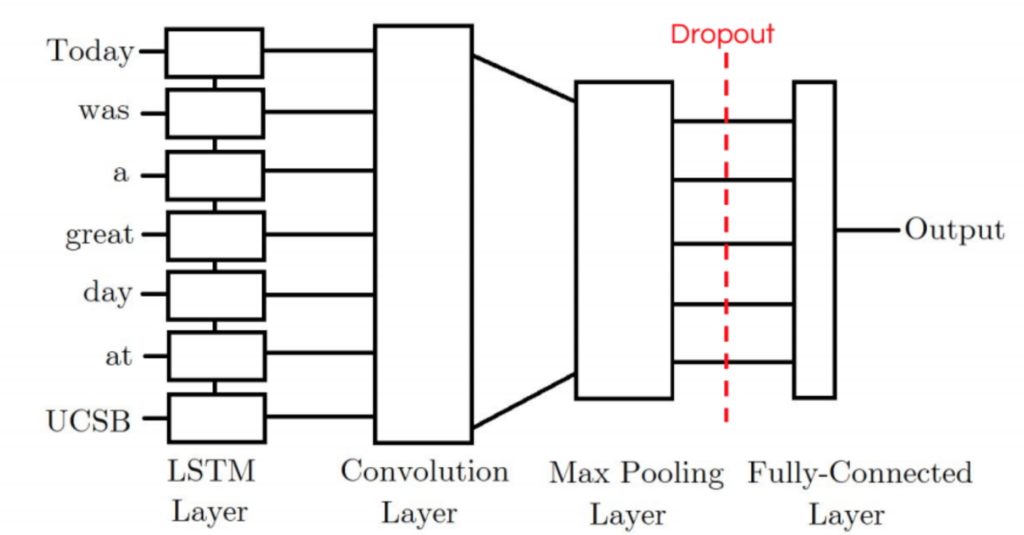
Our CNN-LSTM model consists of an initial LSTM layer which will receive word embeddings for each token in the tweet as inputs. The intuition is that its output tokens will store information not only of the initial token, but also any previous tokens; In other words, the LSTM layer is generating a new encoding for the original input. The output of the LSTM layer is then fed into a convolution layer which we expect will extract local features. Finally the convolution layer’s output will be pooled to a smaller dimension and ultimately outputted as either a positive or negative label.
CNN-LSTM 모델은 initial LSTM layer로 구성되며, LSTM layer는 tweet의 각 토큰에 대한 word embedding을 input으로 받는다. 이 모델은 output 토큰이 초기 토큰뿐만 아니라 이전 토큰의 정보를 저장할 것이라고 생각했다. 즉, LSTM layer는 원래 input에 대한 새로운 encoding을 생성한다. LSTM layer의 output은 local feature를 추출할 것이라고 기대하는 convolution layer에 제공한다. 마지막으로 convolution layer의 output은 작은 dimension으로 pooling되고 궁극적으로는 양수 또는 음수 라벨로 출력된다.
6. Results
We setup the experiment to use training sets of 10,000 tweets and testing sets of 2,500 labeled tweets. These training and testing sets contained equal amounts of negative and positive tweets. We re-did each test 5 times and reported on the average results of these tests.
실험에서 training셋으로 10,000개의 tweet과 testing셋으로 2,500개의 라벨링된 tweet을 사용했다. 이러한 training과 testing셋은 동일한 양의 부정적인 tweet과 긍정적인 tweet이 포함되도록 했다. 우리는 이러한 테스트를 5번 시도했고, 이 테스트의 평군 결과를 기록했다.
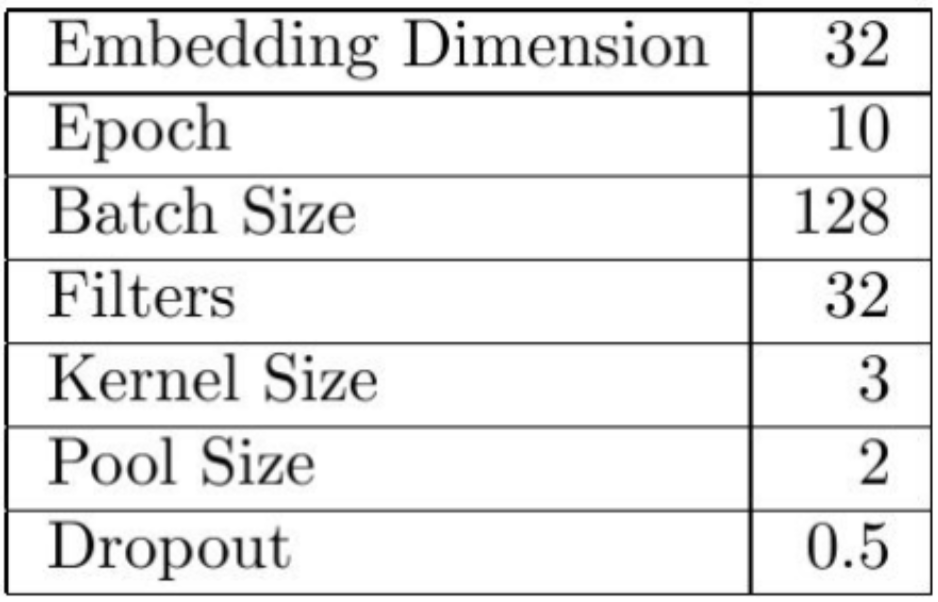
We used the following parameters which we fine-tuned through manual testing:
우리는 수동 테스트를 통해 다음과 같이 fine-tuned된 parameter를 사용했다.
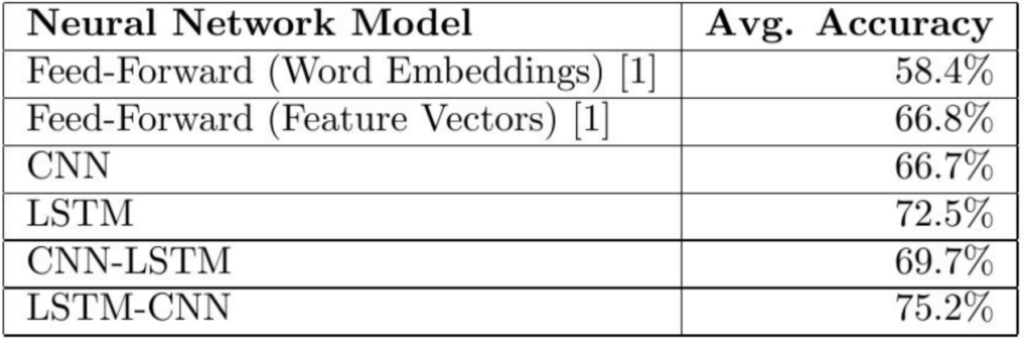
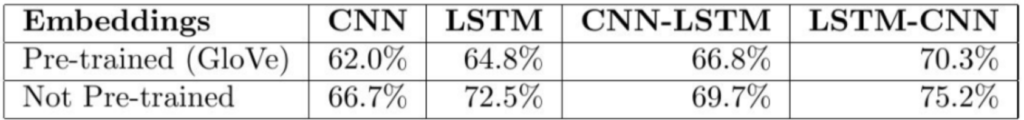
The actual results were as follows:
실제 결과는 다음과 같았다.
Our CNN-LSTM model achieved an accuracy of 3% higher than the CNN model, but 3.2% worse than the LSTM model. Meanwhile, our LSTM-CNN model performed 8.5% better than a CNN model and 2.7% better than an LSTM model.
CNN-LSTM 모델은 CNN 모델보다 3% 높은 정확도를 얻었지만 LSTM 모델보다 3.2% 낮은 정확도를 얻었다. 한편, LSTM-CNN 모델은 CNN 모델보다 8.5%, LSTM 모델보다 2.7% 더 나은 성능을 보였다.
These results seem to indicate that our initial intuition was correct, and that by combining CNNs and LSTMs we are able to harness both the CNN’s ability in recognizing local patterns, and the LSTM’s ability to harness the text’s ordering. However, the ordering of the layers in our models will play a crucial role on how well they perform.
이러한 결과는 우리의 처음 직감이 옳았음을 나타내며, CNN과 LSTM을 결합함으로써 CNN의 local 패턴 인식 능력과 LSTM의 텍스트 순서를 이용하는 능력을 사용할 수 있다는 것을 보여준다. 그리고 모델에서 layer의 순서는 각 layer 성능에 결정적인 역할을 할 것이다.
We believe that the 5.5% difference between our models is not coincidental. It seems that the initial convolutional layer of our CNN-LSTM is loosing some of the text’s order / sequence information. Thus, if the order of the convolutional layer does not really give us any information, the LSTM layer will act as nothing more than just a fully connected layer. This model seems to fail to harness the full capabilities of the LSTM layer and thus does not achieve its maximum potential. In fact, it even does worse than a regular LSTM model.
우리는 모델 사이의 5.5%의 차이가 우연이라고 생각하지 않는다. CNN-LSTM 모델의 initial convolutional layer가 텍스트의 순서 / sequence 정보를 일부 잃어버리고 있는 것처럼 보인다. 따라서, 만약 convolution layer의 순서가 실제로 우리에게 어떤 정보도 주지 않는다면, LSTM layer는 단지 fully connected layer 이상의 역할을 하지 않을 것이다. CNN-LSTM 모델은 LSTM layer의 모든 능력을 사용하지 못하지 때문에 최대로 능력을 달성하지 못한다. 사실, CNN-LSTM 모델은 일반 LSTM 모델보다 더 좋지 않다.
On the other hand, the LSTM-CNN model seems to be the best because its initial LSTM layer seems to act as an encoder such that for every token in the input there is an output token that contains information not only of the original token, but all other previous tokens. Afterwards, the CNN layer will find local patterns using this richer representation of the original input, allowing for better accuracy.
반면에, LSTM-CNN 모델은 모든 input token에 대해 원래 토큰 뿐만 아니라 모든 이전 토큰에 대한 정보를 포함한 output 토큰이 있어 LSTM layer가 encoder로 동작하기 때문에 LSTM-CNN 모델이 가장 적합한 것으로 보인다. 그 뒤에, CNN layer는 원래 input에 대한 풍부한 표현을 사용하여 local 패턴을 찾아 정확도를 높일 수 있다.
7. Further Observations
Some of the observations I made during the testing (and which are explained in much more detail on the paper):
테스트 중에 수행한 일부 관찰 사항(그리고 이것들은 논문에 훨씬 더 자세히 설명되어 있다.)
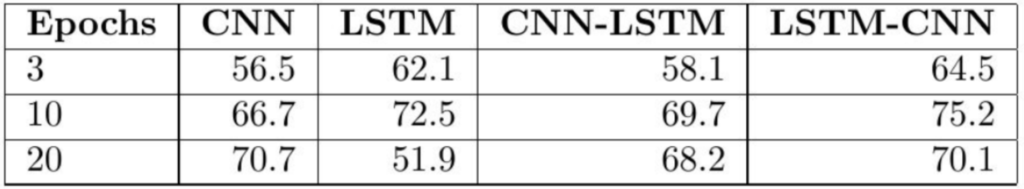
7-1) Learning Rates
CNN & CNN-LSTM models need more epochs to learn and overfit less quickly, as opposed to LSTM & LSTM-CNN models.
CNN, CNN-LSTM 모델은 LSTM, LSTM-CNN 모델과는 달리 학습을 빠르게 하고 overfit을 줄이기 위해 더 많은 epoch이 필요하다.
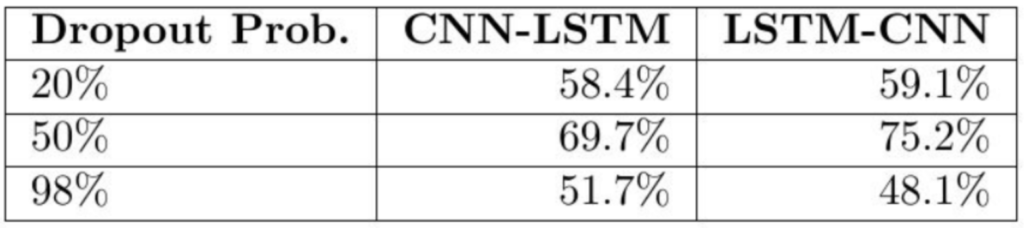
7-2) Drop Rates
This wasn't so much of a surprise, but I did notice that it is very important to add a Dropout layer after any Convolutional layer in both the CNN-LSTM and LSTM-CNN models.
이것은 많이 놀라운 것은 아니었지만, CNN-LSTM 모델과 LSTM-CNN 모델 둘 다 convolutional layer뒤에 dropout layer를 추가하는 것이 매우 중요하다는 것을 알아차렸다.
(Note: in this case Dropout Prob. is how likely we are to drop a random input.)
(참고: 이 경우, Dropout Prob.는 random input을 얼마나 뺄 것인지에 대한 비율이다.)
7-3) Pre-Trained Word Embeddings
I attempted to use pre-trained word embeddings, as opposed to having the system learn the word embeddings form our data. Surprisingly using these pre-trained GloVe word embeddings gave us worst accuracy. I believe this might be due to the fact that twitter data contains multiple misspellings, emojis, mentions, and other twitter-specific text irregularities that weren't taken into consideration when building the GloVe embeddings.
나는 우리의 데이터에서 word embedding을 학습하는 시스템을 갖는 것과 반대로, pre-trained word embeddings을 사용하려고 시도했다. 놀랍게도, pre-trained GloVe word embedding은 최악의 정확도를 얻었다. 나는 다수의 철자 오류, 이모티콘, 멘션 및 기타 twitter 관련 텍스트 불규칙성을 가지고 있는 twitter 데이터가 GloVe embedding을 구축할 때 고려되지 않았기 때문일지도 모른다고 생각한다.
8. Conclusions & Future Work
In terms of future work, I would like to test other types of LSTMs (for example Bi-LSTMs) and see what effects this has on the accuracy of our systems. It would also be interesting to find a better way to deal with misspellings or other irregularities found on twitter language. I believe this could be achieved by building Twitter specific word-embeddings. Lastly, it would be interesting to make use of Twitter specific features, such as # of retweets, likes, etc. to feed along the text data.
향후 작업적인 측면에서, 다른 종류의 LSTMs(예를들면 Bi-LSTMs)을 테스트하여 이것이 우리 시스템의 정확도에 어떤 영향을 미치는지 확인하고 싶다. 또한 twitter 언어에서 발견되는 철자 오류나 기타 불규칙성에 대한 더 좋은 방법을 찾는 것도 흥미로울 것이다. 나는 Twitter만의 word embedding을 구축할 수 있을 것이라고 생각한다. 마지막으로, 텍스트 데이터를 feed(추가)하기 위해 retweet을 위한 #, 좋아요 등과 같은 twitter 특정 feature를 이용하는 것도 재미있을 것이다.
On a personal note, this project was mainly intended as an excuse to further understand CNN and LSTM models, along with experimenting with Tensorflow. Moreover, I was happy to see that these two models did much better than our previous (naive) attempts.
개인적으로 이 프로젝튼 Tensorflow를 실험하면서 CNN과 LSTM 모델을 더 이해하기 위한 핑계였다. 게다가 나는 CNN과 LSTM 모델이 이전의 시도(naive)보다 훨씬 좋은 것을 보고 기뻤다.
As always, the source code and paper are publicly available: paper & code. If you have any questions or comments feel free to reach out. Happy coding! 🙂
항상 그렇듯이, 소스 코드와 논문은 공개적으로 사용 가능하다: 논문 & 코드. 질문이나 의견이 있으면 언제든지 연락해라. 즐거운 코딩해라!