This repository contains JavaScript based commonly used algorithms and data structures.
1 Searching Algorithms
- Linear Search
- Binary Search
- Naive String search
- Kmps Search Algo
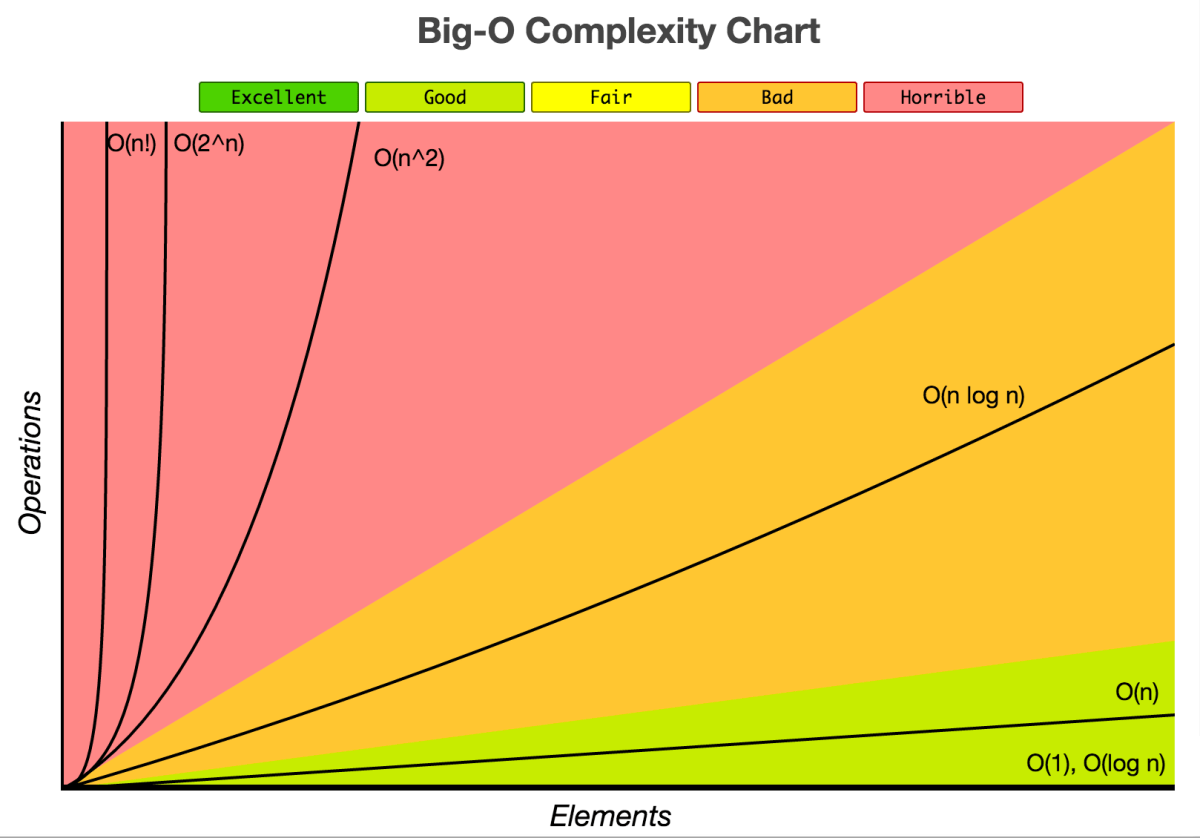
2 Sorting Algorithms
aBubble SortbInsertion SortcSelection Sort
2.1 Advance Sorting Algorithms
aMerge SortbQuick SortcRadix Sort
* Divide and Conquere algorithm
This technique can be divided into the following three parts:
Divide: This involves dividing the problem into some sub problem.
Conquer: Sub problem by calling recursively until sub problem solved.
Combine: The Sub problem Solved so that we will get find problem solution.
-
Example
- Quick Sort
- Merge Sort
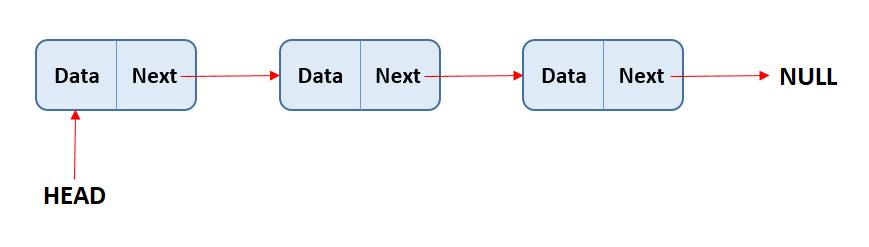
1 Linked list
It is an Data structure in which each node contains link of its next node
- Singly linked list
- Doubly linked list
- Circular linked list
2 Stacks and Queues
Stack is a linear data structure which
follows
a particular
order in which the
operations are performed.
whereas
A Queue is a linear structure which follows
a particular order in which the operations
are performed. The order is
First In First Out (FIFO).
The difference between stacks and queues
is in removing. In a stack we remove the item
the most recently added; in a queue, we remove
the item the least recently added.
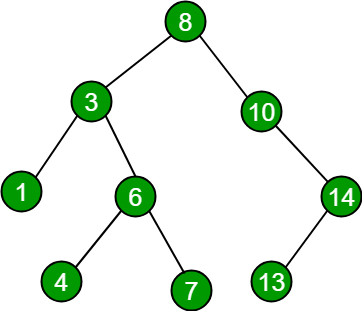
3 Trees
- Binary Search Tree (Bst)
- Avl Tree or Height Balancing Tree
* Binary Search Tree is a node-based
binary tree data structure which has the
following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- The left and right subtree each must also be a binary search tree.
* AVL tree is a self-balancing
Binary Search Tree (BST) where the
difference between heights of left and
right subtrees cannot be more than one
for all nodes.
4 Binary Heap
Binary Heap is a Binary Tree with following properties.
a It’s a complete tree (All levels are completely
filled except possibly the last level
and the last level has all keys as left as
possible). This property of Binary Heap
makes them suitable to be stored in an array.
b A Binary Heap is either Min Heap or Max Heap.
In a Min Binary Heap, the parent Element is smaller than
that of its left and rightChild Whereas in Max Binary
Heap its Vice Versa
5 Priority Queue
Priority queue has same method but with a major difference. In Priority queue items are ordered by key value so that item with the lowest value of key is at front and item with the highest value of key is at rear or vice versa. So we're assigned priority to item based on its key value. Lower the value, higher the priority. A Priority Queue is Build with with Binary heap
6 Hash Tables
Hash Table is a data structure which stores data in an associative manner. In a hash table, data is stored in an array format, where each data value has its own unique index value. Access of data becomes very fast if we know the index of the desired data.
Thus, it becomes a data structure in which insertion and search operations are very fast irrespective of the size of the data. Hash Table uses an array as a storage medium and uses hash technique to generate an index where an element is to be inserted or is to be located from.
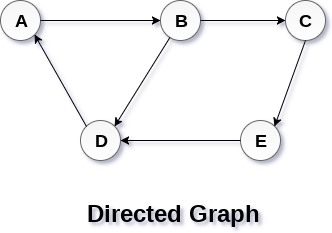
7 Graph
A graph can be defined as group of vertices and edges that are used to connect these vertices. A graph can be seen as a cyclic tree, where the vertices (Nodes) maintain any complex relationship among them instead of having parent child relationship.
-
Types of Graph
- Directed
- UnWeighted
Shortest Path finding Algorithm
Dijkstra’s Algorithm allows you to calculate the shortest path between one node of your choosing and every other node in a graph.
Here’s how the algorithm is implemented:
-
Mark all nodes as unvisited.
-
Mark the selected initial node with a current distance of 0 and the rest with infinity.
-
Set the initial node as current node.
-
For the current node, consider all of its unvisited neighbors and calculate their distances by adding the current distance of current node to the weight of the edge connecting neighbor node and current node.
-
Compare the newly calculated distance to the current distance assigned to the neighboring node and set is as the new current distance of neighboring node.
-
When done considering all of the unvisited neighbors of the current node, mark the current node as visited.
-
If the destination node has been marked visited then stop. The algorithm has finished.
-
Otherwise, select the unvisited node that is marked with the smallest distance, set it as the new current node, and go back to step 4.