This repository provides a toolkit to train deep-learning models from synthetic, labeled atomic force microscopy (AFM) images in COCO format. We developed this workflow for nanoengineered and biological samples as described in "SimuScan: Label-Free Deep Learning for Autonomous AFM", but it can be easily generalized to other types of samples depending on the synthetic data prepared for model training. In addition, it includes tools to convert annotations to multiple formats (U-Net, YOLO, Detectron2) and to train models for object detection and segmentation. It also provides a graphical user interface that interacts with Nanosurf’s DriveAFM to optimize autonomous, high-resolution feature discovery on nanoengineered and biological samples at the micro–nanoscale.
The root directory includes the following top-level folders:
-
Dataset: Stores synthetic datasets in different annotation formats:See AFM Image Dataset.date_XXX_COCO: Dataset formatted for use with Detectron2 or other COCO-compatible models.dateXXX_YOLO: Dataset formatted for YOLO-based models.dateXXX_UNET: Dataset formatted for UNET-based models.
-
detectron2: Requires a local installation or modifications of the Detectron2 framework, which is used for training and inference. For installation instructions, see the official Detectron2 installation guide. -
training: Training utilities and model pipelines:coco_data_converter.py: Converts COCO annotations to YOLO/UNET-compatible formats.trainer_Detectron2.py: Script for training and evaluating models using Detectron2.trainer_YOLOseg.py: Script for training and running YOLOv8 for detection/segmentation tasks.trainer_UNET.py: Script for training and running UNET for pixel-wise classification tasks.
-
Out_training: Output results from model training runs (all trained models used in the manuscript can be downloaded from Zenodo):results_detectron2: Trained weights, logs, and output predictions from Detectron2.results_yolo_training: Output and logs from YOLO training runs.results_unet_training: Output and logs from UNET training runs.
-
AppAutomatization: Contains the graphical user interface that connects to the AFM to automatically and autonomously perform high-resolution target discovery.
-
Installation: Clone the repository and install the required packages (recommended to use a virtual environment):
git clone https://github.com/Rmillansol/SimuScan-AFMtools.git cd SimuScan-AFMtools pip install -r requirements.txtThe use of the detector2 requires a local installation of the Detectron2 framework, which is used for training and inference. For installation instructions, see the official Detectron2 installation guide.
-
Generate Synthetic Data:
The synthetic datasets used to train the models in this work were generated using SimuScan, a standalone synthetic AFM data generator.SimuScan is distributed as a precompiled executable (
SimuScan.exe), allowing users to generate realistic, fully labeled AFM datasets without requiring a Python environment.-
Physics-informed AFM simulation
Incorporates AFM-specific artifacts such as tip convolution, scanner tilt and bow, drift, electronic noise, and substrate roughness. -
Configuration-driven dataset generation
Dataset properties (image size, number of images, object types, noise levels, etc.) are fully controlled via a human-readable configuration file, ensuring reproducibility. -
Automatic ground-truth generation
Produces pixel-accurate segmentation masks and object annotations compatible with common deep-learning frameworks. -
Ready-to-use datasets for model training
Outputs datasets formatted for object detection and segmentation workflows (e.g., YOLO, U-Net, Detectron2).
Precompiled binaries and example configurations are openly available on Zenodo:
👉 https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17957102The synthetic datasets used to train the models were generated with the SimuScan synthetic data generator.
These datasets are openly available for download at Zenodo. -
-
Convert Annotations: Use
coco_data_converter.pyto translate the dataset into YOLO format if needed. -
Train Models:
- Use
trainer_Detectron2.pyfor training with Detectron2. - Use
trainer_YOLOseg.pyfor training with YOLOv8 segmentation. - Use
trainer_UNET.pyfor training with UNET.
- Use
-
Autonomous Feature Discovery: Copy the
AppAutomatizationfolder to the computer connected to the DriveAFM instrument and launch the GUI:python AppAutomatitation/AppAutoDetectionObjects.py
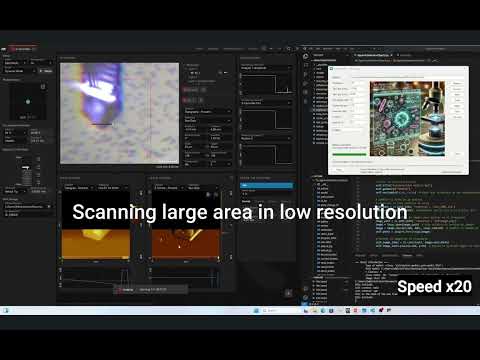
An intuitive window will open where you can:
- Connect to the microscope.
- Select the gallery and set initial scanning parameters.
- Select the YOLO model and target class under study.
- Set the stop criterion.
Once the parameters are set, click the Start button. The microscope will automatically explore regions of the sample at low resolution to search for targets and then capture them at high resolution until the stop criterion is met. You can watch an example video here:
If you use this repository or any part of it in your work, please cite:
Millan-Solsona, R. et al. (2025). SimuScan: Label-Free Deep Learning for Autonomous AFM.
DOI: [10.21203/rs.3.rs-7724735/v1] (https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-7724735/v1)
Developed by Ruben Millan-Solsona
Contact: solsonarm@ornl.gov
Google Scholar | ORCID
The contents of this repository are licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License.
This applies only to the code and resources provided here, not to the full SimuScan framework.
You are free to share and adapt the material for any purpose, even commercially, with appropriate credit.
See the LICENSE file for details.