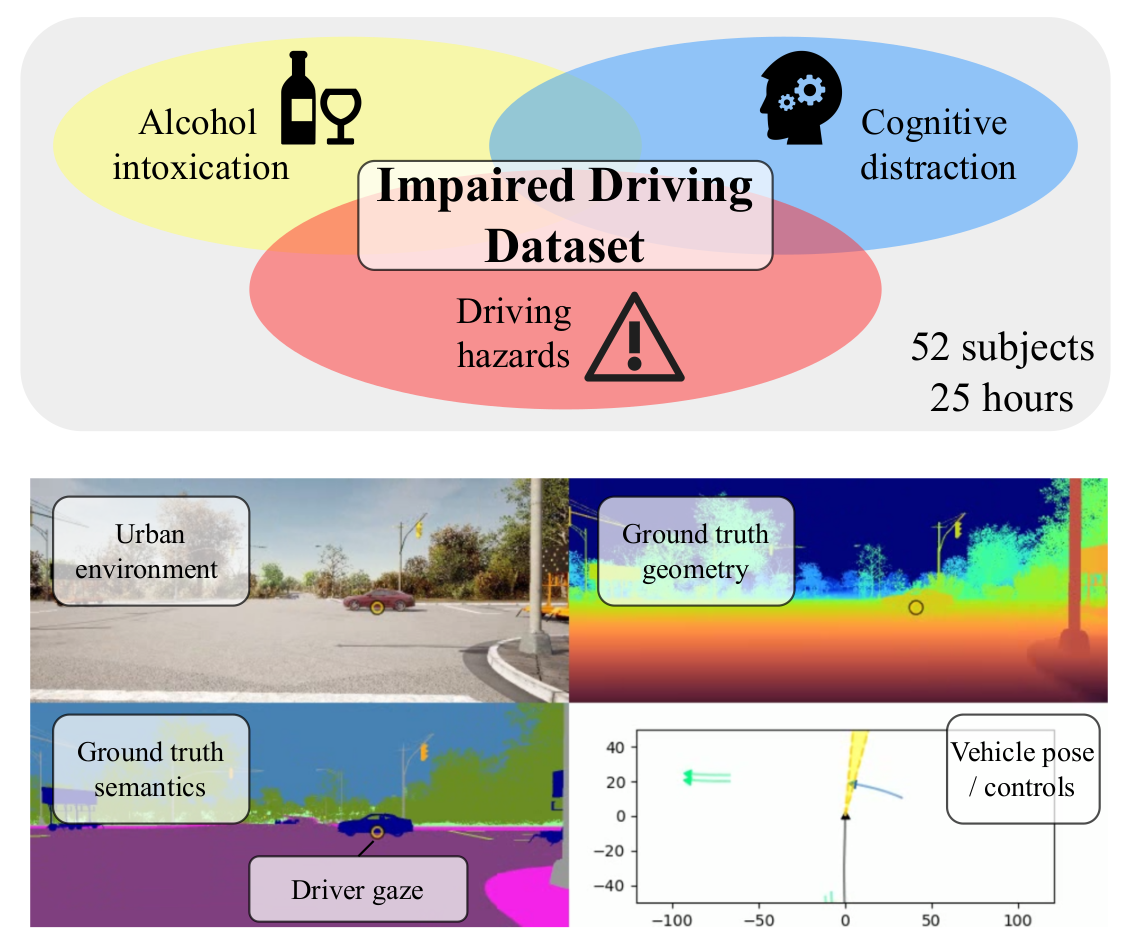
The code in this repo explores the modeling of driver behavior, including control of the vehicle and gaze patterns, while possibly impaired. This analysis is supported by the Impaired Driving Dataset (IDD) - the project page for which can be found at https://toyotaresearchinstitute.github.io/IDD/
git submodule update --init
micromamba create -f environment.dbm.yml
micromamba activate dbm
In order to download a sample of IDD, which is the main dataset used by this pipeline, run the following:
./data/download_processed_dataset.py --output_dir ~/data/IDD/Processed --version sample
You can verify this data and then download a larger part of the dataset, or the whole dataset, by changing the version parameter. For more information on versions, look in "data/configs/public-dataset.yaml". To replicate the results from the IDD paper, you will at least need version "no-video", which is 16.6 GB large.
- analysis: Various scripts used in feature and model output analysis. Contains the feature significance tests from the IDD paper.
- data: Scripts to download the dataset and documentation for use (see contained README).
- exp: Contains lists of experiment configs to call with "run_experiments.py".
- features: Scripts to extract various derived features. Contains a README that explains how to set up any new feature extraction.
- hail-datasets: Contains the dataloader implementation.
- models: The machine learning models used by the training script.
- submodules: The other git repo dependencies used by the feature extraction or training.
- utils: Common utilities used across the entire repo.
- viz: Visualization tools used to create publication images, videos, and tables.
To train and validate a model, use the "train.py" script. See "utils/parse_args.py" for a list of command line parameters. For a list of example experiments used in the IDD paper, see "exp/example.txt". Outputs will be generated in the "checkpoints" directory by default. Parameters can also be selected to track the outputs on Weights and Biases (WandB).
Alternatively, you can use the "run_experiments.py" script to run a set of experiments sequentially, possibly in parallel threads and GPUs. For example, the following will run the experiments in "exp/example.txt" with a total of 4 threads split across 2 GPUs:
./run_experiments.py -e exp/example.txt --experiments_per_gpu 2 --num_gpu 2
Note that the "--num_repeats" argument defined in "exp/example.txt" will determine the total repeats of each line of the experiment, iterating through the test_split_index and random_seed used for each.
./analysis/feature_test.py
./run_experiments.py -e exp/example.txt --experiments_per_gpu 1 --num_gpu 1
./analysis/itsc25.py checkpoints