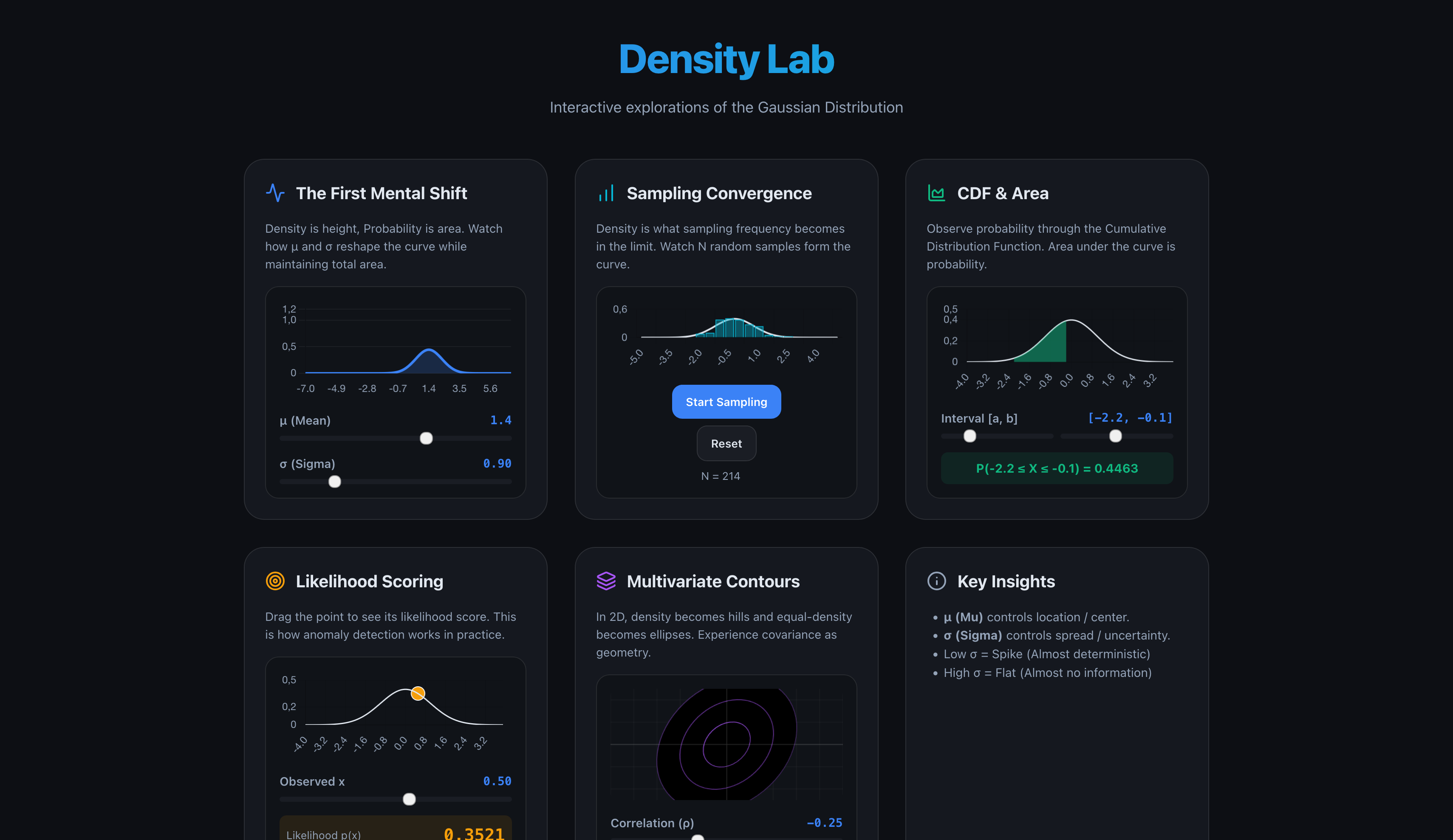
A premium, interactive web application designed to build a deep intuition for continuous probability distributions, the Score function, and the foundations of Diffusion Models.
The lab is organized into three specialized tabs:
- Foundations: Core Gaussian properties, sampling convergence, and CDF calculus.
-
Score Theory: The mathematics of
$\nabla \log p(x)$ , ISM vs ESM, and Pseudo-Likelihood. - Diffusion Labs: Forward SDE processes and Denoising Score Matching (DSM).
- Intuition: Density ≠ Probability.
-
Interactive: Sliders for
$\mu$ (mean) and$\sigma$ (standard deviation) show how the "height" (density) changes while the "area" (probability) remains 1.
- Intuition: Density is what sampling frequency becomes in the limit.
- Interactive: Generate random samples in real-time and watch the histogram converge to the theoretical PDF ($p(x)$).
-
Intuition:
$P(a \leq X \leq b) = \int_{a}^{b} p(x) dx$ . - Interactive: Drag interval boundaries and see the shaded area calculate the cumulative probability.
- Intuition: Density as a "Normality Score".
- Interactive: Drag a point along the axis to see its likelihood. Highlights how anomaly detection is mathematically grounded in density values.
- Intuition: Covariance is Geometry.
-
Interactive: Adjust correlation (
$\rho$ ) and observe how the density "hills" tilt and stretch into ellipses.
-
Intuition:
$s(x) = \nabla \log p(x)$ points to the peak. - Interactive: Watch the "score field" (vector arrows) pull points toward the data mode. Essential for understanding Diffusion Models and Energy-Based Models.
-
Intuition: Maximize individual conditional likelihoods
$p(x_i | x_{-i})$ instead of the full joint. - Interactive: Observe conditional Gaussian slices and watch the product reach its max at the true parameter value. Efficient for models with intractable normalizers.
- Intuition: Structured patterns dissolve into Gaussian noise.
-
Interactive: Corrupt a "data manifold" with increasing
$\sigma$ levels to visualize the forward process used in SDE and Diffusion models.
-
Intuition:
$J_{ESM}(\theta) = J_{ISM}(\theta) + C$ . - Interactive: Minimize the Implicit Score Matching objective without ever knowing the ground-truth density. Watch how matching the "divergence" of the score field is equivalent to matching the vectors.
- Intuition: Score Matching is equivalent to Denoising Autoencoders (SMDAE).
-
Interactive: Perturb a clean sample
$x$ with noise to get$\tilde{x}$ . The DSM objective trains the model to point from$\tilde{x}$ back to$x$ , which is equivalent to estimating the score of the data distribution.
- Intuition: The "Hello World" of generative models. Watch the full diffusion process in action.
-
Interactive: Generate 2D point clouds (circle, spiral, multi-modal, moon) and watch them evolve from pure Gaussian noise to structured shapes. Real-time formula evaluation shows
$\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_t}$ values during animation.
- Framework: React (Vite)
- Styling: Vanilla CSS (Modern design system, Dark Mode, Glassmorphism)
- Plotting: Chart.js + react-chartjs-2
- Math Rendering: KaTeX for real-time LaTeX evaluation.
- Math Logic: Box-Muller transform for sampling, Error Function approximations for CDF.
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/VicoErv/density-lab.git
# Install dependencies
npm install
# Start development server
npm run dev
# Build for production
npm run buildThis project implements and visualizes concepts from the following foundational papers:
-
Hyvärinen, A. (2005). Estimation of Non-Normalized Statistical Models by Score Matching. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 6(24), 695-709.
- Introduced Score Matching and the ISM/ESM equivalence for learning unnormalized models.
-
Vincent, P. (2011). A Connection Between Score Matching and Denoising Autoencoders. Neural Computation, 23(7), 1661-1674.
- Proved that Denoising Autoencoders (DAE) are equivalent to Score Matching under Gaussian noise.
-
Ho, J., Jain, A., & Abbeel, P. (2020). Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. NeurIPS 2020.
- Foundational paper on DDPM, establishing connections between diffusion models and denoising score matching with Langevin dynamics.
-
Besag, J. (1974). Spatial Interaction and the Statistical Analysis of Lattice Systems. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 36(2), 192-225.
- Introduced Pseudo-Likelihood for models with intractable partition functions.
MIT