A collection of some of my data science projects showcasing my skills in machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data analysis. Includes Jupyter notebook and visualizations demonstrating my expertise and problem-solving abilities.
- Microsoft Malware Detection
- Stripper Well Problem
- Steel Defect Detection
- Student Mental Health - Outlier Detection
- Instagram Follow Recommendation
- Implementations from Scratch
- TF-IDF
- RandomSearchCV
- SGD
- Backpropagation
- Linear Regression with Gradient Descent
- KMeans Clustering
- BERT
- Seq2Seq
- SQL work
- Master's Dissertation
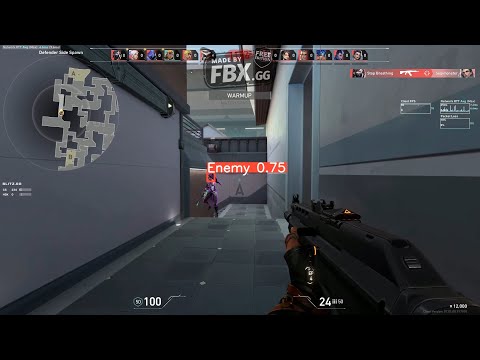
- Valorant - EnemyHead Detection
- Movie Search Engine
- London Sounds
The dataset is taken from The dataset is taken from Microsoft Malware Challenge. This dataset contains .byte and .asm files which are most commonly used in malware detection tasks. . This dataset contains .byte and .asm files which are most commonly used in malware detection tasks. The .byte files contain binary data in hexadecimal format and the .asm files contain the disassembled code of the binary files. There are 10868 .byte and .asm files in the dataset. The task is to classify whether the file classifies as a malware or not.
The motivation behind this project lies in the need to protect users from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats and ensure the safety and integrity of computer systems. By creating a reliable and efficient malware detection system using machine learning, we can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and safeguard our digital lives.
The .byte and .asm files have been transformed into uni-grams and bi-grams, capturing frequency and co-occurrence patterns in the data. Moreover, the binary representations of the .asm files have been converted into pixel values to analyze intensity patterns potentially indicative of malware presence. These feature representations facilitate improved understanding and classification by machine learning algorithms, ultimately enhancing the accuracy of malware detection.
There are 26 and 676 features of .asm uni grams and bi grams respectively. Similarly for .byte files, there are 257 and 66049 features for unigrams and bigrams respectively. The pixel array is 1D - flattened array of 800 pixel values.
| Features Used | Model | Train loss | Test loss | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASM Uni | Random Forest | 1.93 | 1.89 | 73.23 |
| Bytes Bi | Random Forest | 0.019 | 0.073 | 98.35 |
| ASM Uni + Bytes Bi | XGBoost | 0.010 | 0.037 | 99.35 |
| ASM Uni + Bytes Bi | KNN | 0.040 | 0.069 | 98.44 |
| ASM Uni+ Bytes Uni + ASM Bi | XGBoost | 0.008 | 0.017 | 99.72 |
| ASM Bi + ASM Uni + Bytes Bi + ASM Pixel | Random forest | 0.013 | 0.011 | 100 |
One other conclusion that can be drawn from the table is that the model consisting of ASM Bi, ASM Uni, Bytes Bi, and ASM Pixel features achieved a perfect accuracy of 100% on both training and testing data when using the Random Forest model. This suggests that the combination of these features may be particularly effective in distinguishing between malware and benign files. However, it is important to note that the malware detection model might go out of date if it is not regularly trained on latest data.
For in depth details about this project, check out my blog
A Stripper well is a low yield oil well. These wells have low operational costs and have tax breaks which makes it attractive from a business point of view. Almost 80% of the oil wells in the US are Stripper wells.
The well has a lot of mechanical components and the breakdown is quite often compared to other wells. The breakdown occurs at surface level or down-hole level. In a business perspective, time is more valuable than small overhead costs. It is very inefficient to send the repair team without knowing where the failure has occured. Therefore it becomes a neccessity to create an algorithm which predicts where the failure has occured.
The goal of the project is to predict whether the mechanical component has failed in the surface level or down-hole level. This information can be used to send the repair team to address the failure in either of the levels and save valuable time.
The dataset is provided by ConocoPhilips. The dataset has 345 features which are taken from the sensors that collect a variety of information at surface and bottom levels. There are 50084 instances.
- The dataset is heavily imbalanced
- 172 features with greater than 25% missing values
- 6 features with outliers
- Many highly correlated features
- Checking whether missing values are saying something
Maybe the missing values actually say something valuable regarding the equipment failure. I will check if this is the case by using Hamming distance between features with missing values and the target class. The logic is, if there is any relation with failure and nan values, the hamming distance with be very high. I am removing all features that do not have a significant value of hamming distance in this preprocess stage.
- Removing highly correlated features
Removing all features that have corelation greater than 0.85. This will lead to reduction in data dimension and also boosting algorithms will work better.
- Scaling feature
Normalizing all the features so that it can be readily used for any model without extra scaling techniques.
| Model | F1 Score | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Misclassified points out of 16001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 99.995 | 77 |
| XGBoost | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 99.996 | 66 |
| AdaBoost | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.68 | 99.995 | 75 |
| Decision Tree | 0.80 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 99.989 | 166 |
| ANN | 0.78 | 0.58 | 0.85 | 99.990 | 153 |
| Best Ensemble | 0.82 | 0.54 | 0.84 | 99.989 | 174 |
New features impact the accuracy of the model by around 30%. XGBoost has the best F1 score.
For in depth details about this project, check out my blog
In manufacturing industries, one of the main problems is detection of faulty production parts. Detected faulty parts are recycled.But in cases where it is not detected, it can lead to dangerous situations for the customer and reputation of the company. The goal of the project is to write algorithm that can localize and classify surface defects on a steel sheet. If successful, it will help keep manufacturing standards for steel high.
The dataset is provided by one of the leading steel manufacturers in the world, Servastal. Severstal is leading the charge in efficient steel mining and production. The company recently created the country’s largest industrial data lake, with petabytes of data that were previously discarded.
The dataset contains 3 features - ImageId, ClassId and Encoded Pixels.
ClassId consists of four unique classes, which are the 4 types of defects and maybe present individually or simultaneously in an image. There are 7095 observations in the train dataset. There are no missing values. The segment for each defect class are encoded into a single row, even if there are several non-contiguous defect locations on an image. The segments are in the form of encoded pixels.
- There is imbalance in dataset
- Few parts have two types of defects at the same time
The classes are heavily imbalanced. Also, the size of the dataset is small. Therefore, I augmented the images such that it compensates for class imbalance and also increases the amount of training data.
I have chosen dice coefficient as the performance metric. It is because the result masks needs to have both good precision and a good recall. I have used Binary Crossentropy as loss function. It is used here because the insight of an element belonging to a certain class should not influence the decision for another class because some images might contain more than 1 class.
| Model | Loss | Epochs |
|---|---|---|
| Residual Unet | 0.0513 | 15 |
| Unet | 0.0125 | 23 |
A new model can be built called Hierarchical Multi-Scale Attention for Semantic Segmentation. This model might be able to give even better results than Unet.
This dataset offers a fascinating insight into gender differences in fear-related personality traits and their correlation with physical strength across five university samples. The dataset includes self-report measures of HEXACO Emotionality to explore the effects of physical strength on fear-related personality traits - which is key information to consider when designing interventions for mental health issues.
Based on the questionnaire and the surverys done by students, I will try to identify any outliers in the data. These outliers would meant that the student would be in a bad mental state and would require mental health support.
- Males have greater grip strength than females
- Males have greater chest size than females
- Females have overall greater anxiety scores than males
- Both genders have around the same level of emotional dependence scores
- Both genders have around the same level of fearfulness scores
- Females have greater empathy than males
There are too many questionnaires and personality related attributes to make a plot out of. So I am grouping the relevant features together. There are no missing values.
TSNE - At low n_iterations, there are some visually noticeable outlier points PCA - Using the Local outlier Factor, there is evidence of existance of outliers in the data.
Further investigation into the dataset is required to establish conclusive evidence that poor mental health can be accurately detected. While there is potential for significant improvements in this area, it is important to acknowledge that expertise in psychology is necessary for a thorough analysis, which I currently lack.
The dataset used for this project contains information about Instagram users and their connections. The data includes user profiles, their followers, and the users they follow. This information is valuable for understanding user preferences and behavior in order to provide tailored friend recommendations.
The goal of this project is to develop a friend recommendation system for Instagram users by leveraging machine learning techniques. By analyzing user networks and connections, the recommendation system aims to suggest potential friends for users to follow, thereby enhancing their experience on the platform.
The dataset undergoes several preprocessing steps to make it suitable for machine learning algorithms. The following features are extracted and transformed:
-
Preferential Attachment: Computing the preferential attachment for pairs of nodes, considering the number of followers and followees for each user. This feature is a measure of how likely two users are to connect based on their existing connections.
-
SVD Features: The code uses precomputed SVD features (svd_u and svd_v vectors) that are derived from the adjacency matrix of the graph. These features capture the latent relationships between users in the network, which can help the model understand the underlying structure of the network.
-
Dot products of SVD features: The element-wise dot products of the svd_u and svd_v vectors are calculated to generate new features. These new features can help capture the similarity between users in the network.
After these preprocessing steps, the dataset is ready for training the XGBoost model to make recommendations.
The XGBoost Classifier is employed as the primary machine learning model for this project. The model is trained and tested using various hyperparameters to optimize its performance. The model's performance is evaluated using the F1 score. A grid search of hyperparameters is performed to find the best combination of max_depth, learning_rate, and n_estimators for the XGBoost model.
After identifying the optimal hyperparameters, the model is trained, and predictions are made for both the train and test sets. Confusion, precision, and recall matrices are plotted to visualize and better understand the model's performance.
The XGBoost Classifier achieved a Maximum Accuracy of 93.50% on the test set. The optimal hyperparameters for the model were found to be:
- max_depth: 10
- learning_rate: 0.01
- n_estimators: 50
Using these hyperparameters, the model effectively predicted Instagram friend recommendations. The confusion, precision, and recall matrices provided a comprehensive view of the model's performance, allowing us to better understand its strengths and limitations.
The Instagram Friend Recommendation System successfully suggests potential friends for users to follow, enhancing their experience on the platform. Further improvements can be made by exploring additional features, fine-tuning the model, and incorporating user feedback to refine the recommendations.
These are the algorithms that have been implemented from scratch without relying on external libraries such as scikit-learn. This not only showcases a deep understanding of the underlying concepts but also demonstrates strong coding skills and the ability to create custom solutions.
The future of AI shows promising possibilities in the field of communication such as therapy, retail, customer service, reception desks etc. However, despite the significant progress, there is a lack of research that explores the extent to which AI can be used to distinguish passive aggression or sarcasm. Thus, the aim of this project is to investigate the potential of AI in detecting this subtle human expressiveness by utilizing audio, video and textual data, along with the contextual information leading to the sarcasm
Valorant games were played and recorded using FBX Game Recorder. The saved recordings were exported in .mp4 format. Using the VLC media player, screenshots of the required images were taken. The screenshots were then labelled using the labelImg.py which is commonly used to annotate images. The annotations were saved in the format as required for Yolo. Object detection model Yolov8n and Yolov8s were trained on the custom dataset. The datasets and parameters of this model are not made public to prevent malicious use. Pruning and Quantization was applied on the final weights of the model inorder to boost the fps, resulting from boost of 12-19fps to 74-80fps. The result of the Yolov8n is as below.
The dataset used for this project consists of movie metadata such as titles, genres, ratings, and reviews. It also includes user information like viewing history and preferences. This comprehensive dataset is essential for providing accurate and personalized movie recommendations to users.
The objective of this project is to develop a search engine that can recommend movies to users based on their description of the movie they want to watch. Utilizing machine learning algorithms and natural language processing techniques, the system aims to provide highly relevant movie suggestions to enhance user satisfaction and engagement.
Before feeding the data into machine learning algorithms, several preprocessing steps are taken to prepare the dataset: Text Normalization: Titles and reviews are converted to lowercase, punctuation is removed, and stemming is applied to reduce the words to their root form. Feature Extraction: Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) is used to represent movie descriptions and reviews in vectorized form. User Profiling: User preferences and viewing history are analyzed to create a feature vector representing each user's tastes in movies. After completing these preprocessing steps, the dataset is ready for training using a content-based filtering model.
For this project, the Okapi BM25 algorithm serves as the primary model for the recommendation system. Okapi BM25 is particularly useful for ranking and information retrieval tasks. The algorithm takes into account the frequency of terms in each document and the inverse document frequency across the corpus, along with additional length normalization, to provide a relevance score for each movie in relation to the user query or profile.
Conclusion This Movie Search Engine project successfully demonstrated how to implement and understand the Okapi BM25 algorithm for search engines. Through this project, significant insights were gained into the working of search algorithms and how to apply them to real-world datasets. Future work could involve implementing additional features like user reviews and ratings to further enhance search results.
This notebook is classification of a sounds dataset called MLEnd sound dataset. This dataset consists of 2500 samples with of on average, 8 seconds long audio data captured around different areas of London. The problem formulation for this advanced mini-project is to predict whether the given sound is taken from which area of London
This pipeline takes path-to-audio files and path-to-csv file as input. The output will be preprocessed dataframe created from these files.
Intermediate stages:
Stage 1: Loading audio-files-path as list, and dataframe using csv.
Stage 2: Two specific audio files are corrupted so removing these files from input data
Stage 3: Data augmentation: Since the available data is only 2500 files, I will use augmentation techniques to create more data, 2500x8=20000 data. After augmentation, each audio will be loaded as mel frequency cepstrum coefficients (mfcc). Now these mfcc's will be averaged and made into an array. Transform the mfcc array into appriopriate shape. Merge class labels with the array and output the extracted data. The data output shape should be 2498x8=19984 rows and 2 columns. Make note that the first column has a 20 dimensional array of mfcc of the audio data.
Stage 4: Transform the mfcc array into appriopriate shape. Merge class labels with the array and output the extracted data. The data output shape should be 2498x4=9992 rows and 2 columns. Make note that the first column has a 20 dimensional array of mfcc of the audio data.
The ML model I will be using is a basic Deep Neural Network. I want to use this model beacause I am more interested in deep learning rather than classical machine learning. This is the reason I have augmented the data to create more data too. Also, mfcc audio data works extremely well on neural networks. The model is a sequential network. There are a total of 10 hidden layers. I will briefly explain below:
The first layer is input layer. Last layer is the output layer. All the layers in between are hidden layers. The first hidden layer flattens in input, next layer normalizes the batches. Now the layers are dense and dropouts layer 12 consecutive times. Each dense layer has relu as activation, except the output layer, where I have used softmax.
Adam is the optimizer with learning rate 0.002. Loss used is categorical_crossentropy. Metrics is AUC.
Early stopping is used if there is no improvement in validation accuracy across 30 conintuous steps. Learning rate is reduced if there is no improvement in validation accuracy for 3 steps. Minimum learning rate is set at 0.00001
The model is set to run for 500 epochs, however, it is allowed to stop early.
In this pipeline, I will plot the performance of the model. The inputs will be model-history from the previous pipeline
In this pipeline, I will give audio file as input, and it will predict whether the sound is from indoor or outdoor.
The performance metrics used in the model is auc. Since it is multi classification task, auc is a good enough metric. Categorical crossentropy loss is calculated at end of each epoch. This is appropriate because the multi classification of categorical variable. Confusion matrix is plotted in the visualization part for test result. Also, train&validation auc plots is also plotted. train&validation loss is also plotted to show there is no overfit of DNN model.
Achieved an exceptional 99.99% AUC on unseen data. The model accurately pinpoints the origin of sound within London.