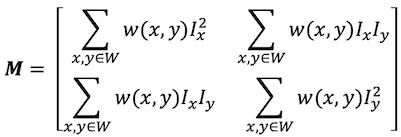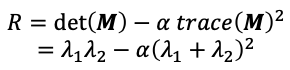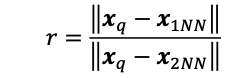Mount Google Drive
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/gdrive')
Make a new folder
import os
path='/content/gdrive/MyDrive/폴더명'
os.mkdir(path)
Calibration (camera matrix, distortion coefficients, rotation and translation vectors)
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, gray.shape[::-1], None, None)
가로 길이 1, 세로 길이 3, 높이 5 인 직육면체를 checkerboard (0,0,0)을 기준
axis = np.float32([[0,0,0], [0,5,0], [1,5,0], [1,0,0], [0,0,-3], [0,5,-3], [1,5,-3], [1,0,-3]])
가로 길이 1, 세로 길이 3, 높이 5 인 직육면체를 checkerboard (2,2,0)을 기준
axis = np.float32([[2,2,2], [2,7,2], [3,7,2], [3,2,2], [2,2,-1], [2,7,-1], [3,7,-1], [3,2,-1]])
Kernel의 크기 변경하며 수행
blur = cv.blur(img, ksize=( , ))
𝛼를 변경하며 수행
shapened_img = np.int32(img) + 𝛼 * detail
- [code]
- image
- getGaussianKernel
- filter2D
kerner1d의 outer product를 계산하여 kernel2d 생성
kernel2d = np.outer(kernel1d, kernel1d.transpose())
-
A simple but Clever Idea
- What we really want: model explains many points "well"
- Least Squares: model makes as few big mistakes as possible over the entire dataset
- New objective: find model for which error is "small" for as many data points as possible
- Method: RANSAC (RAndom SAmple Consensus)
-
RANSAC: Pros and Cons
Pros Cons 1 Ridiculously simple Have to tune parameters 2 Ridiculously effective No theory (so can not derive parameters via theory) 3 Works in general Not magic, especially with lots of outliers
- Compute partial derivatives lx, ly per pixel
- Compute M at each pixel, using Gaussian weighting w
- Compute response function R
- Threshold R
- Take only local maxima (Non-Maxima Suppression, NMS)
(* SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform)
- Blob Detection : Find maxima and minima of blob filter response in scale and space
- With Laplacian
- Edge : zero-crossing
- Blob : Two edges in opposite directions
- When blob is just the rught size, Laplacian gives a large absolute value
- In scale space
- Convolve image with Laplacian at several scales
- Find local maxima and minima of squared Laplacian response in image+sclae space
- With Laplacian
- code
- image
- SIFT
- Descriptors
- Normalize the rotation/scale of the patch
- Compute gradient at each pixel
- Divide into sub-patch (here 2x2, actually 4x4)
- In each sub-patch, compute histogram of 8 gradient directions
- Describe the patch with 4x4x8=128 numbers
- Properties
- Using graidients gives invariance to illumination
- Using histogram of patches gives invariance to small/rotations
- Compactly describe local appearance of patches with 128-dim vector
- It can handle up to ~60 degrees out-of-plane rotation & chages of illumination
- Fast and efficient and lots of code available
- Features: Instance Matching
- Given a features xq, instaed of finding the nearest neighbor to xq, find the nearest neighbor and second nearest neighbor
- This ratio is a good test for matches:
- Descriptors
- [code]
- [image]