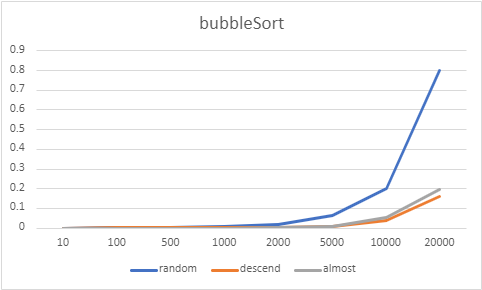
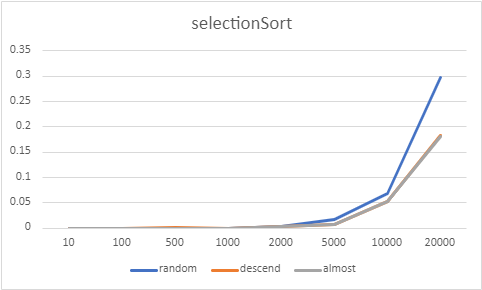
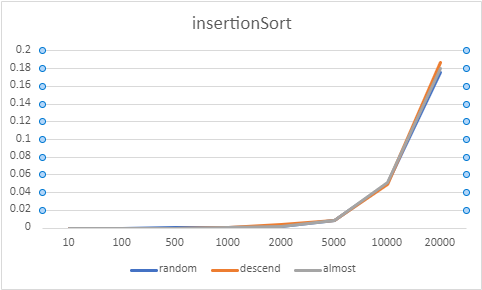
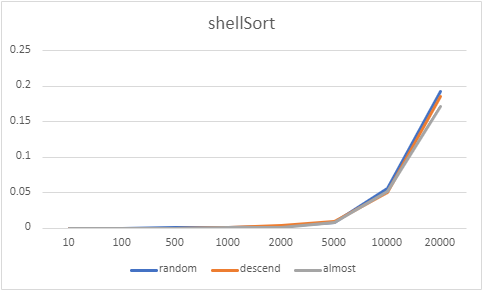
다음은 버블정렬, 선택정렬, 삽입정렬, 쉘정렬을 구현하고, 각 배열별로 정렬된 상태(랜덤, 내림차순 정렬, 대부분 정렬)에 따른 수행시간의 차이를 알아본다.
import java.util.*;
interface SortMethods{ //정렬 방법
void bubbleSort(int[] x,int n);
void selectionSort(int[] x,int n);
void insertionSort(int[] x,int n);
void shellSort(int[] x,int n);
}
interface SortDegree{ //배열의 정렬 정도
void random(int[] x,int n); //랜덤
void descendingSort(int[] x,int n); //내림차순 정렬
void almostSort(int[] x,int n); //거의 정렬이 되어있는 상태
}
class Sort implements SortMethods,SortDegree {
static void swap(int[] x, int a, int b) {
int t = x[a];
x[a] = x[b];
x[b] = t;
}
@Override
public void bubbleSort(int[] x, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n - i; j++)
if (x[j] > x[j + 1])
swap(x, j, j + 1);
}
@Override
public void selectionSort(int[] x, int n) {
int min;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
min = x[i];
int k=i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (x[j] < min)
k=j;
swap(x,i,k);
}
}
@Override
public void insertionSort(int[] x, int n) {
int k;
int j;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
k=x[i];
j=i-1;
while(j>=0&&x[j]>k){
x[j+1]=x[j];
j=j-1;
}
x[j+1]=k;
}
}
@Override
public void shellSort(int[] x, int n) {
int k,j;
for(int h=n/2;h>0;h/=2) {
for (int i=h;i<n;i++){
k=x[i];
j=i;
while(j>=h&&x[j-h]>k){
x[j]=x[j-h];
j=j-h;
}
x[j]=k;
}
}
}
public void time(int[] x,int n,String s1,String s2){
double beforeTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bubbleSort(x,n);
double afterTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
double secDiffTime = (afterTime - beforeTime) / 1000;
System.out.println(s1+"정렬에서의 "+s2+"시간:"+secDiffTime);
}
@Override
public void random(int[] x,int n) {
Random r=new Random();
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++)
x[i]=r.nextInt(100)+1;
time(x,n,"랜덤","bubbleSort");
time(x,n,"랜덤","selectionSort");
time(x,n,"랜덤","insertionSort");
time(x,n,"랜덤","shellSort");
}
@Override
public void descendingSort(int[] x,int n) {
Arrays.sort(x);
int[] k=x.clone();
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++)
x[i]=k[n-i-1];
time(x,n,"내림차순","bubbleSort");
time(x,n,"내림차순","selectionSort");
time(x,n,"내림차순","insertionSort");
time(x,n,"내림차순","shellSort");
}
@Override
public void almostSort(int[] x,int n) {
Arrays.sort(x);
for(int i=0;i<x.length/50;i++)
swap(x,i+20,x.length-i-1);
time(x,n,"대부분","bubbleSort");
time(x,n,"대부분","selectionSort");
time(x,n,"대부분","insertionSort");
time(x,n,"대부분","shellSort");
}
}
public class SortAlgorithm{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
Sort s=new Sort();
int n=sc.nextInt();
int[] x=new int[n];
s.random(x,n);
s.descendingSort(x,n);
s.almostSort(x,n);
}
}interface SortMethods{ //정렬 방법
void bubbleSort(int[] x,int n);
void selectionSort(int[] x,int n);
void insertionSort(int[] x,int n);
void shellSort(int[] x,int n);
}
interface SortDegree{ //배열의 정렬 정도
void random(int[] x,int n); //랜덤
void descendingSort(int[] x,int n); //내림차순 정렬
void almostSort(int[] x,int n); //거의 정렬이 되어있는 상태
}위와 같이 interface 두개를 선언해서 정렬 방법 4개와 정렬된 정도 3개를 각각 나타낸다.
@Override
public void bubbleSort(int[] x, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n - i; j++)
if (x[j] > x[j + 1])
swap(x, j, j + 1);
}
@Override
public void selectionSort(int[] x, int n) {
int min;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
min = x[i];
int k=i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (x[j] < min)
k=j;
swap(x,i,k);
}
}
@Override
public void insertionSort(int[] x, int n) {
int k;
int j;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
k=x[i];
j=i-1;
while(j>=0&&x[j]>k){
x[j+1]=x[j];
j=j-1;
}
x[j+1]=k;
}
}
@Override
public void shellSort(int[] x, int n) {
int k,j;
for(int h=n/2;h>0;h/=2) {
for (int i=h;i<n;i++){
k=x[i];
j=i;
while(j>=h&&x[j-h]>k){
x[j]=x[j-h];
j=j-h;
}
x[j]=k;
}
}
}위에 인터페이스에 선언한 메소드를 구현한다.
@Override
public void random(int[] x,int n) {
Random r=new Random();
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++)
x[i]=r.nextInt(100)+1;
time(x,n,"랜덤","bubbleSort");
time(x,n,"랜덤","selectionSort");
time(x,n,"랜덤","insertionSort");
time(x,n,"랜덤","shellSort");
}
@Override
public void descendingSort(int[] x,int n) {
Arrays.sort(x);
int[] k=x.clone();
for(int i=0;i<x.length;i++)
x[i]=k[n-i-1];
time(x,n,"내림차순","bubbleSort");
time(x,n,"내림차순","selectionSort");
time(x,n,"내림차순","insertionSort");
time(x,n,"내림차순","shellSort");
}
@Override
public void almostSort(int[] x,int n) {
Arrays.sort(x);
for(int i=0;i<x.length/50;i++)
swap(x,i+20,x.length-i-1);
time(x,n,"대부분","bubbleSort");
time(x,n,"대부분","selectionSort");
time(x,n,"대부분","insertionSort");
time(x,n,"대부분","shellSort");
}
}역시 위에 인터페이스에 선언한 메소드를 구현한다.
random은 1~100사이의 임의의 수로 배열을 나타내는 메소드이고,
descendingSort는 내림차순으로 배열을 나타내는 메소드,
almostSort는 오름차순으로 정렬된 베열에서 조금만 바꿔주는 메소드이다.
public void time(int[] x,int n,String s1,String s2){
double beforeTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bubbleSort(x,n);
double afterTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
double secDiffTime = (afterTime - beforeTime) / 1000;
System.out.println(s1+"정렬에서의 "+s2+"시간:"+secDiffTime);
}time메소드는 얼마나 정렬된 배열에서 어떤 정렬을 사용하는지에 따라 시간이 얼마나 걸리는지를
나타내주는 메소드이다.
위와 같이 10~20000개의 배열로 성능 구현을 해보았는데, 네 정렬 모두 내림차순 배열과, 대부분 정렬된 상태에서의 배열에서는 비슷한 성능이 구현되었고, 버블정렬과 선택정렬의 경우 랜덤 배열에서는 다른 배열에서보다 성능이 안 좋게 나타났다. 그 중에서도 버블정렬이 가장 성능이 안 좋게 나왔다.