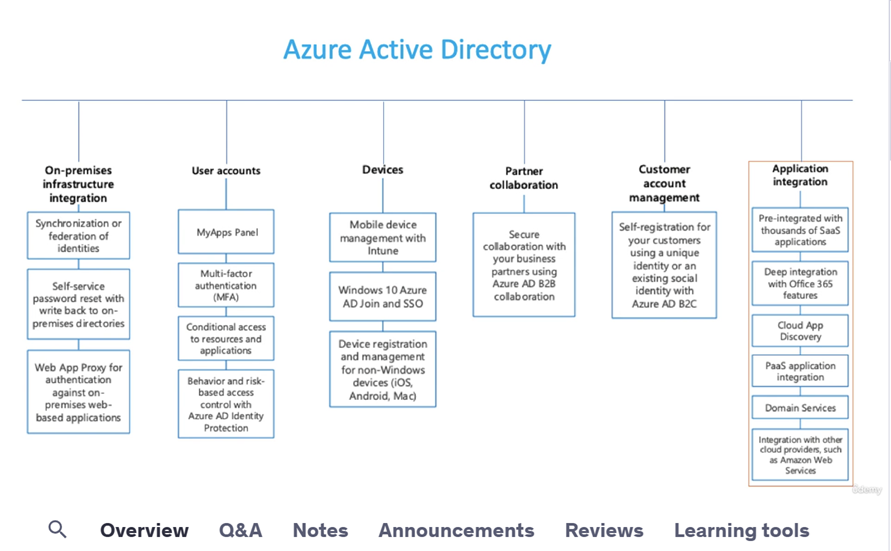
Azure Active Directory is now Microsoft Entra ID.
Answer
Microsoft has changed the name of the uh the directory service of Azure that we formerly known as the Azure AD to the intra ID. Microsoft intra ID is a foundational product of Microsoft Intra. It provides the essential identity, authentication, policy, and protection to secure employees, devices, and enterprise apps and resources.
Microsoft Entra ID is a cloud-based identity and access management solution. It's a directory and identity management service that operates in the cloud and offers authentication and authorization services to various Microsoft services, such as Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and Microsoft Azure.
Entra : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/fundamentals/what-is-entra
Hindi Tutorial : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xEvSFyXBX58&list=PLUGuCqrhcwZzht4r2sbByidApmrvEjL9m&index=2

So any user who is created in the intra ID directory. So they will be getting this domain name. So it means that the user is created in the intra ID directory.
Answer
An Azure subscription grants you access to the Azure services and to the Azure Platform Management Portal. So whenever you create an account in the Azure portal, you have to purchase a subscription in order to access any Azure services. So without subscription you won't be able to access any Azure services or manage them.
The subscription holder manages services like Windows Azure, SQL, Azure storage, virtual machines. So all these services can only be accessed by the account holder who is having an access onto the subscription.
An Azure subscription has a trust relationship with Azure Active Directory or Azure AD, which means that the subscription trusts Azure HD to authenticate users, services and devices. So when you create the account in the Azure portal, first time you get the subscription. Along with that, you get the default Active Directory. So that's the Azure activity tenant you get with the subscription. So that subscription is tied to the Azure Active Directory. So it uses that Azure Active Directory for authenticating user accounts which are configured in the directory. So you can configure those accounts which are configured in the Azure Active Directory to access the resources in the subscription.
Multiple subscriptions can trust the same Azure Active Directory, but each subscription can only trust a single directory. So you can have more than one subscription and they all can be tied to the same Azure Active Directory tenant. So they all can use the same Active Directory. So it means the user accounts which are configured in your Azure Active Directory, you can provide those account access onto all of the subscription that you create and link to this Azure Ready tenant.** However, one subscription can only be tied to one Azure Active Directory. You cannot link a single subscription with more than one tenant.**
Now you have to keep in mind that if your subscription expires, you lose access to all the resources associated with that subscription because all the resources are created within that subscription and you access all those resources or configure or manage those resources and that subscription. So if that subscription get expired, you will lose access on all the resources which are within that subscription.
Multiple subscriptions are created to separate production dev test workloads or for separate billings. So while there is a requirement when you need to have more than one subscription, it may be because you want to separate your workloads. The virtual machine in a subscription by default. Do not communicate with the virtual machine and the different subscription. Unless you are creating VPN gateways between the subscription in order to join them. Also, each subscription are billed separately so you can have a different subscription when you have a different business unit and whose billing you want to track so you can have a different subscription for that business unit.
Tenant : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/external-id/tenant-configurations
Create a new Tanant : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/fundamentals/create-new-tenant
Hindi Tutorial : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mVV_4O_QPI0&list=PLUGuCqrhcwZzht4r2sbByidApmrvEjL9m&index=3
Answer
An Azure subscription grants you access to the Azure services and to the Azure Platform Management Portal. So whenever you create an account in the Azure portal, you have to purchase a subscription in order to access any Azure services. So without subscription you won't be able to access any Azure services or manage them.
The subscription holder manages services like Windows Azure, SQL, Azure storage, virtual machines. So all these services can only be accessed by the account holder who is having an access onto the subscription.
An Azure subscription has a trust relationship with Azure Active Directory or Azure AD, which means that the subscription trusts Azure HD to authenticate users, services and devices. So when you create the account in the Azure portal, first time you get the subscription. Along with that, you get the default Active Directory. So that's the Azure activity tenant you get with the subscription. So that subscription is tied to the Azure Active Directory. So it uses that Azure Active Directory for authenticating user accounts which are configured in the directory. So you can configure those accounts which are configured in the Azure Active Directory to access the resources in the subscription.
Multiple subscriptions can trust the same Azure Active Directory, but each subscription can only trust a single directory. So you can have more than one subscription and they all can be tied to the same Azure Active Directory tenant. So they all can use the same Active Directory. So it means the user accounts which are configured in your Azure Active Directory, you can provide those account access onto all of the subscription that you create and link to this Azure Ready tenant. However, one subscription can only be tied to one Azure Active Directory. You cannot link a single subscription with more than one tenant. Now you have to keep in mind that if your subscription expires, you lose access to all the resources associated with that subscription because all the resources are created within that subscription and you access all those resources or configure or manage those resources and that subscription.
So if that subscription get expired, you will lose access on all the resources which are within that subscription.
Multiple subscriptions are created to separate production dev test workloads or for separate billings. So while there is a requirement when you need to have more than one subscription, it may be because you want to separate your workloads. The virtual machine in a subscription by default. Do not communicate with the virtual machine and the different subscription. Unless you are creating VPN gateways between the subscription in order to join them. Also, each subscription are billed separately so you can have a different subscription when you have a different business unit and whose billing you want to track so you can have a different subscription for that business unit.
Now this is a diagram where you can see that the a single Azure ad tenant account is having three subscription linked. So the dev subscription is hosting all the resources which belongs to a development environment. The test subscription holds all the resources belong to the test environment while the production subscription are having all the resources that belongs to the production environment. And all these subscriptions are separate from each other, but they are linked to a single tenant. So the user which are configured in the tenant can access all three subscription according to the permission assigned for that user. So the billing for those resources will be separate for each subscription. So that will help you in identifying the users of the of the subscription which are being used by your different business units.
Answer
In Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C), there are several types of accounts that can be created. These account types are shared across Microsoft Entra ID, Microsoft Entra B2B, and Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C).
The following types of accounts are available:
Work account - A work account can access resources in a tenant, and with an administrator role, can manage tenants.
Guest account - A guest account can only be a Microsoft account or a Microsoft Entra user that can be used to share administration responsibilities such as managing a tenant.
Consumer account - A consumer account is used by a user of the applications you've registered with Azure AD B2C. Consumer accounts can be created by:
The user going through a sign-up user flow in an Azure AD B2C application
Using Microsoft Graph API by a tenant administrator.
Using the Azure portal by a tenant administrator.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory-b2c/user-overview
Answer
In Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), internal users are those who authenticate with the local tenant, while external users (also known as guest users) authenticate through methods outside the organization's control, such as another organization's Microsoft Entra ID or a Microsoft account.
External users can't ne used configuring Cloud Sync.
**Internal Users:**
Authentication: Authenticate with the local tenant, meaning their credentials are managed within the organization's Azure AD.
Access: Can access resources within the organization's tenant.
Example: Employees or contractors who have accounts within the organization's Azure AD.
Answer
External users can't ne used configuring Cloud Sync. You have to check identities of user account. If user, is belonging to the Microsoft accounts, can't ne used configuring Cloud Sync. So this is kind of a guest user and it cannot be used for configuring cloud sync. Instead, you have to use a user that is either synced from the on premises active Directory or that is created directly in the intra ID. So maybe you have to create a new user in the intra ID directly and assign that role to that user.
Answer
Microsoft Entra Domain Services (formerly Azure Active Directory Domain Services), part of Microsoft Entra, enables you to use managed domain services—such as Windows Domain Join, group policy, LDAP, and Kerberos authentication—without having to deploy, manage, or patch domain controllers. Azure Active Directory Domain Services (Azure AD DS) is another cloud-based IAM service but it provides fully managed domain services as well. The service includes domain join, group policy, LDAP, and Kerberos authentication as its main distinctions. That said, you can use Azure AD DS with any Azure virtual machine.
Azure AD DS can be a good choice for organizations that want to:
- Move their on-premises Active Directory (AD) to the cloud.
- Provide cloud-based resources to users who need to authenticate with a Windows domain.
- Run legacy applications that require a Windows domain
Answer
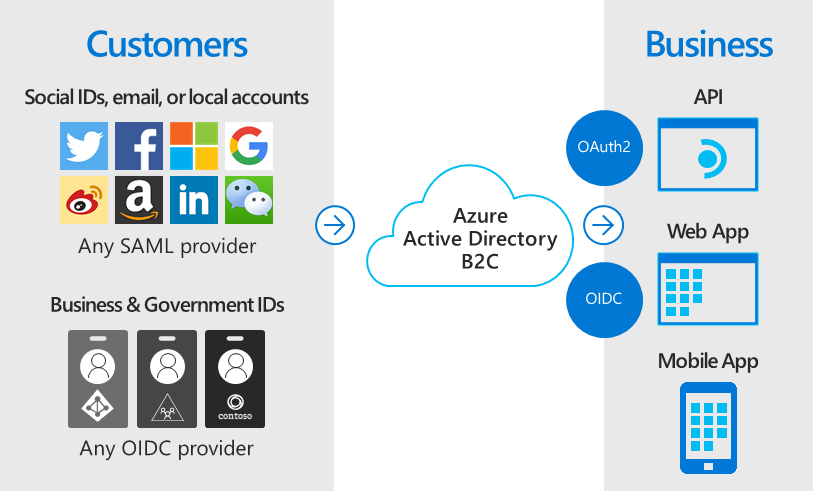
Azure Active Directory B2C provides business-to-customer identity as a service. Your customers can use their preferred social, enterprise, or local account identities to get single sign-on access to your applications and APIs.
Azure AD B2C Overview
Answer
On-premise involves hosting and managing software and data on your own servers, while cloud computing relies on third-party providers to host and manage resources over the internet.
On-Premises: Control: On-premise solutions offer the highest degree of control over your infrastructure, security, and data. You have complete ownership and can customize the environment to your specific needs. Security: On-premise can be perceived as more secure because the data and systems are physically located within your premises, potentially limiting access to authorized personnel. Cost: On-premise solutions typically require a significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and ongoing maintenance costs. Scalability: Scaling on-premise infrastructure can be challenging and expensive, requiring the purchase and installation of new hardware. Management: On-premise solutions require a dedicated IT team for management, maintenance, and support. Example: A large enterprise might choose on-premise for highly sensitive data, requiring strict control over its environment.
Cloud Computing: Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing excels in scalability and flexibility, allowing you to quickly adjust resources based on demand. Cost Efficiency: Cloud solutions often offer a pay-as-you-go model, which can be more cost-effective than on-premise, especially for fluctuating workloads. Accessibility: Cloud-based resources can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, providing greater flexibility and remote access. Maintenance: Cloud providers handle maintenance, updates, and security, reducing the burden on your IT team. Security: Cloud security is managed by the provider, and while they have robust security measures, they can also be a single point of failure. Example: A startup might choose cloud computing for its agility and cost-effectiveness, particularly when dealing with variable workloads.
Hybrid Approach: Many organizations are adopting a hybrid approach, combining on-premise and cloud resources to leverage the benefits of both.
Note
Microsoft Entra ID / Azure Active Directory in HINDI : Hindi Tutorial Link
AZ-104 | Azure Administrator Associate Full Course in HINDI : Hindi Tutorial Link
Tip
Helpful advice for doing things better or more easily.
Important
Key information users need to know to achieve their goal.
Warning
Urgent info that needs immediate user attention to avoid problems.
Caution
Advises about risks or negative outcomes of certain actions.
